What does electrical activity and dust storms on Mars have in common? This is what a recent study published in Nature hopes to address as a team of scienti | Space


As nearly one in six couples experience fertility issues, in-vitro fertilization (IVF) is an increasingly common form of reproductive technology. However, there are still many unanswered scientific questions about the basic biology of embryos, including the factors determining their viability, that, if resolved, could ultimately improve IVF’s success rate.
A new study from Caltech examines mouse embryos when they are composed of just two cells, right after undergoing their very first cellular division. This research is the first to show that these two cells differ significantly—with each having distinct levels of certain proteins.
Importantly, the research reveals that the cell that retains the site of sperm entry after division will ultimately make up the majority of the developing body, while the other largely contributes to the placenta. While the studies were done in mouse models, they provide critical direction for understanding how human embryos develop. Indeed, the researchers also assessed human embryos immediately after their first cellular division and found that these two cells are likewise profoundly different.

Most of us first hear about the irrational number π (pi)—rounded off as 3.14, with an infinite number of decimal digits—in school, where we learn about its use in the context of a circle. More recently, scientists have developed supercomputers that can estimate up to trillions of its digits.
Now, physicists at the Center for High Energy Physics (CHEP), Indian Institute of Science (IISc) have found that pure mathematical formulas used to calculate the value of pi 100 years ago has connections to fundamental physics of today—showing up in theoretical models of percolation, turbulence, and certain aspects of black holes.
The research is published in the journal Physical Review Letters.
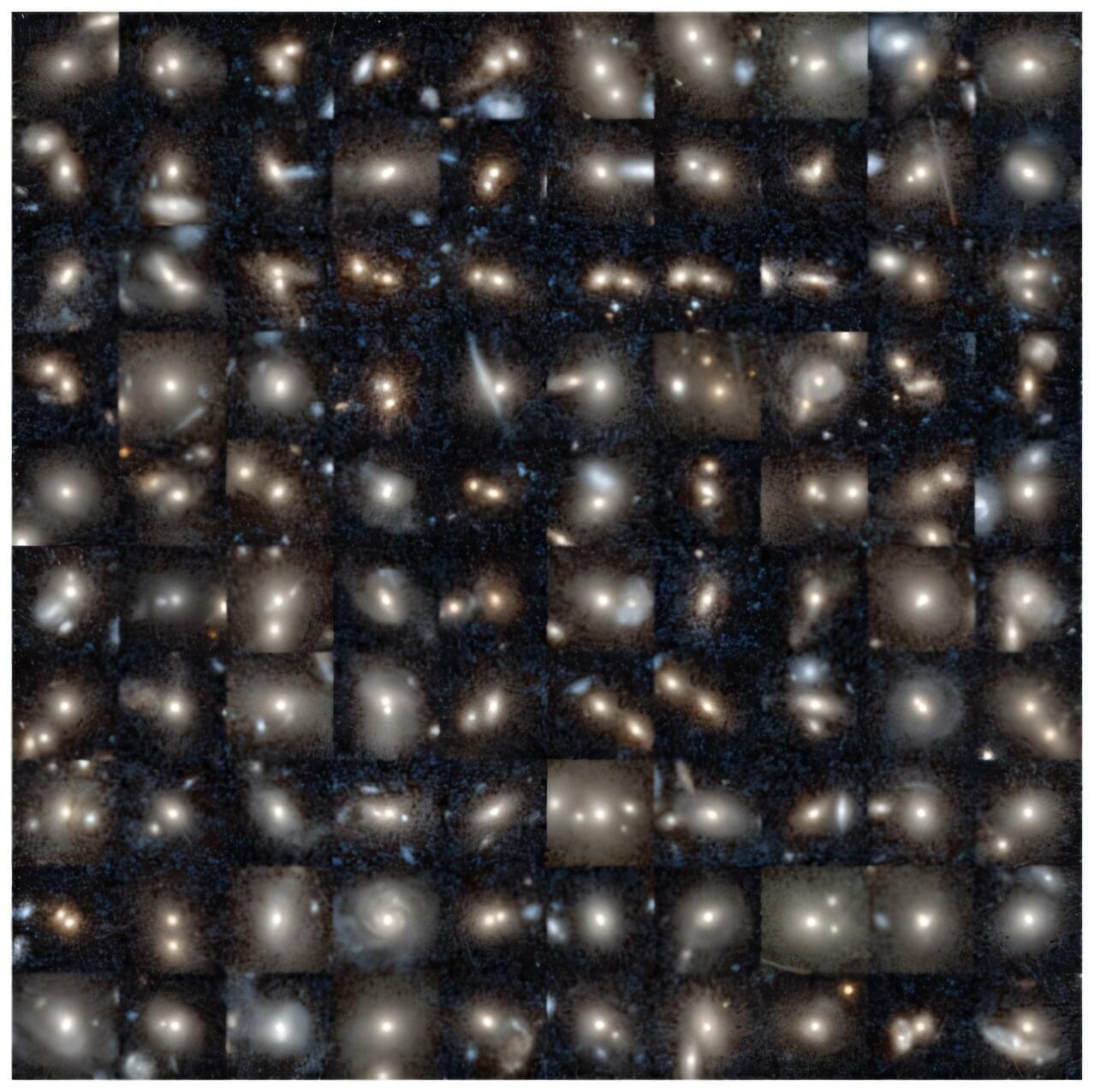

Astronomers have long debated the role of galaxy mergers in powering active supermassive black holes. Now an unprecedented dataset of a million galaxies from the Euclid telescope provides evidence that mergers play a dominant role and are even the primary trigger for the most luminous black holes.
Almost all massive galaxies harbor a supermassive black hole (SMBH) at their centers. Most of them simply lurk in the dark while quietly reeling in gas, dust and stars from their surroundings. These materials gather in the black hole’s accretion disk before their irreversible dive into the abyss, thereby emitting the only slight hint of radiation that gives away the black hole’s location.
A small fraction of galaxies possess an SMBH that shines brightly or even pushes out material from its poles. These are called active galactic nuclei (AGN). Some astronomers have hypothesized that violent collisions between galaxies may play an important role in the ignition of AGN. The resulting turbulence could cause the extra material to pile up in an SMBH’s accretion disk, where friction and compression make it hot enough to shine brightly. In the most extreme cases, the AGN are so bright that they completely outshine their host galaxies.
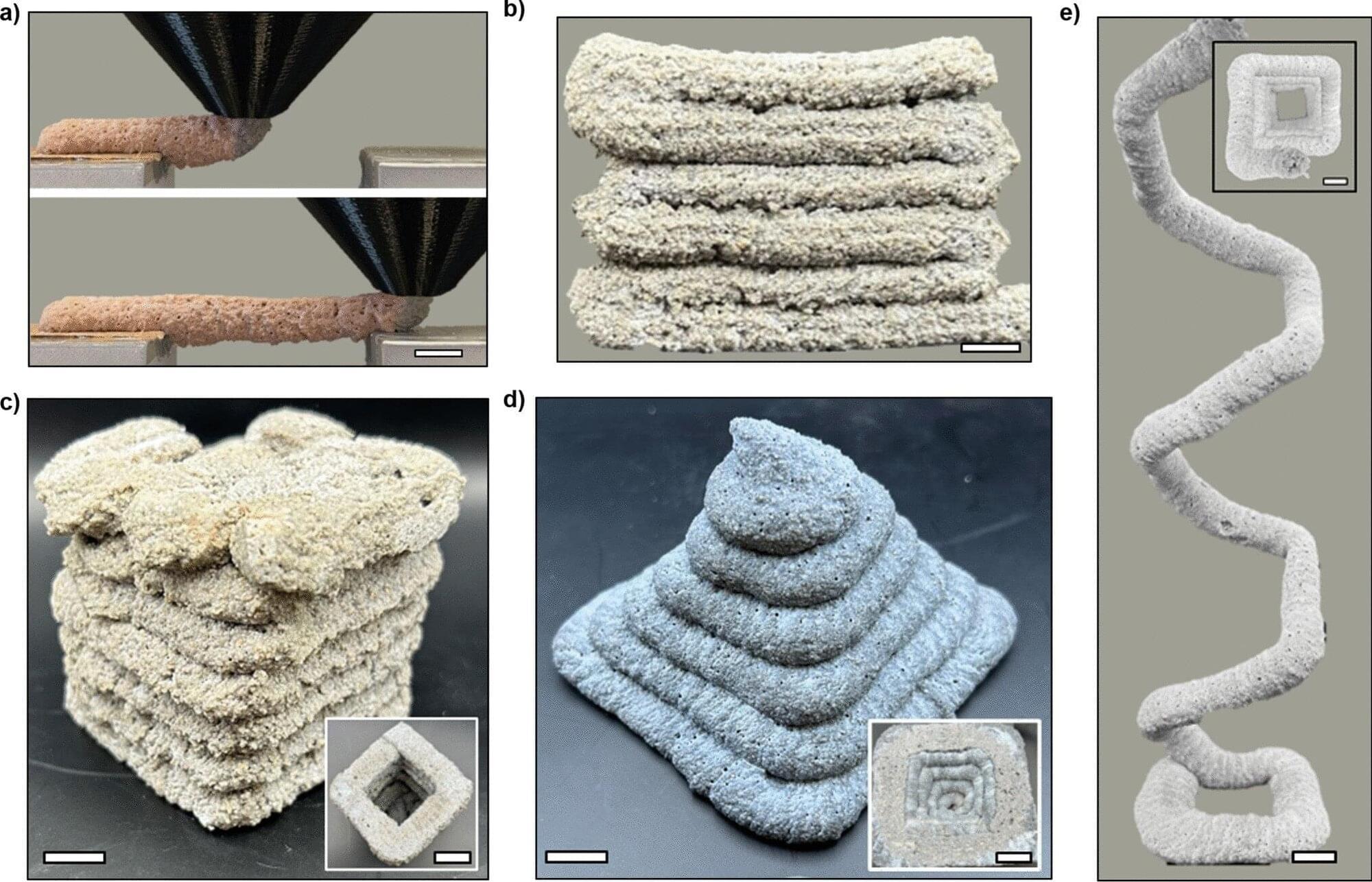
Researchers at Oregon State University have developed a quick-setting, environmentally friendly alternative to concrete they hope can one day be used to rapidly 3D print homes and infrastructure.
Also known as additive manufacturing, 3D printing is already being used to help solve construction challenges such as the global housing crisis that’s emerged as Earth’s population approaches 8.5 billion.
But cement, the binding agent in concrete, accounts for about 8% of the planet’s carbon dioxide emissions, and concrete’s curing time—which can be multiple days—and required structural supports can inhibit progress on construction projects.

Tesla has released a new clip of its Optimus humanoid robot running inside a lab. The video comes from the official Optimus account on X and Elon Musk shared it with his followers soon after. The robot jogs past other units in the background and keeps a steady pace on the lab floor.
Also, The team said that they had set a new personal record in the lab. Musk also stressed the internal record had been broken, which puts fresh attention on how far the project has moved in a short time.
Just set a new PR in the lab pic.twitter.com/8kJ2om7uV7 — Tesla Optimus (@Tesla_Optimus) December 2, 2025