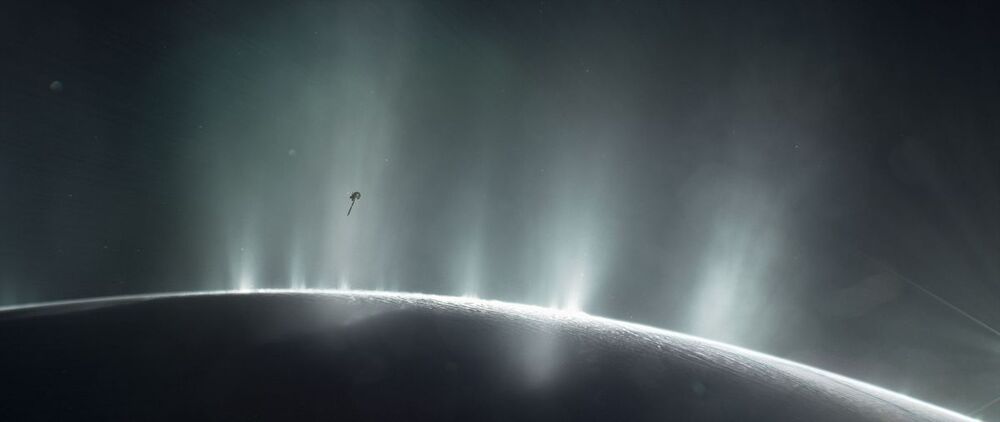
Photons explore quantum maze faster than possible for any classical computer.

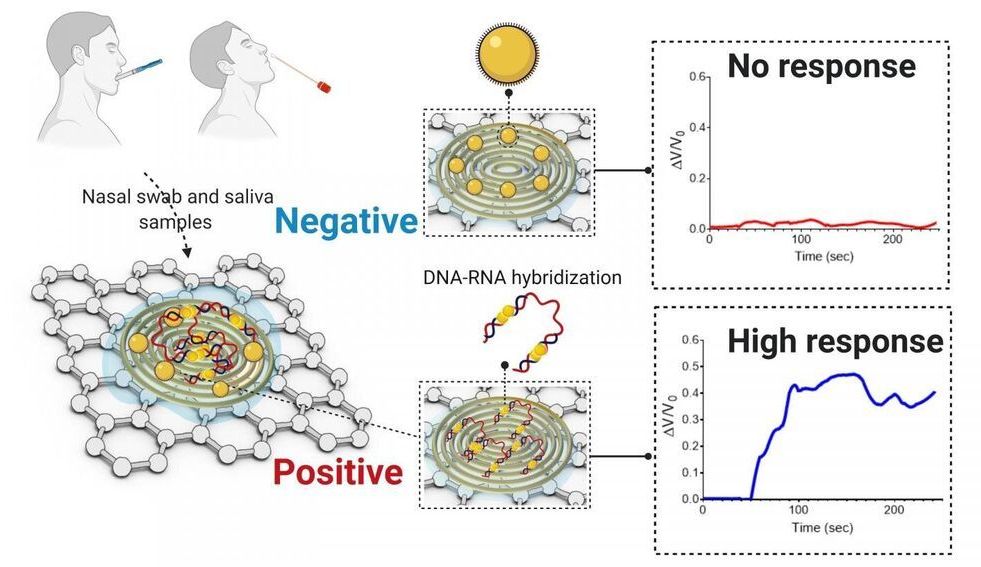
As the COVID-19 pandemic continues to spread across the world, testing remains a key strategy for tracking and containing the virus. Bioengineering graduate student, Maha Alafeef, has co-developed a rapid, ultrasensitive test using a paper-based electrochemical sensor that can detect the presence of the virus in less than five minutes. The team led by professor Dipanjan Pan reported their findings in ACS Nano.
“Currently, we are experiencing a once-in-a-century life-changing event,” said Alafeef. “We are responding to this global need from a holistic approach by developing multidisciplinary tools for early detection and diagnosis and treatment for SARS-CoV-2.”
There are two broad categories of COVID-19 tests on the market. The first category uses reverse transcriptase real-time polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) and nucleic acid hybridization strategies to identify viral RNA. Current FDA-approved diagnostic tests use this technique. Some drawbacks include the amount of time it takes to complete the test, the need for specialized personnel and the availability of equipment and reagents.


NEW YORK (AP) — Brain scans offer a tantalizing glimpse into the mind’s mysteries, promising an almost X-ray-like vision into how we feel pain, interpret faces and wiggle fingers.
Studies of brain images have suggested that Republicans and Democrats have visibly different thinking, that overweight adults have stronger responses to pictures of food and that it’s possible to predict a sober person’s likelihood of relapse.
But such buzzy findings are coming under growing scrutiny as scientists grapple with the fact that some brain scan research doesn’t seem to hold up.
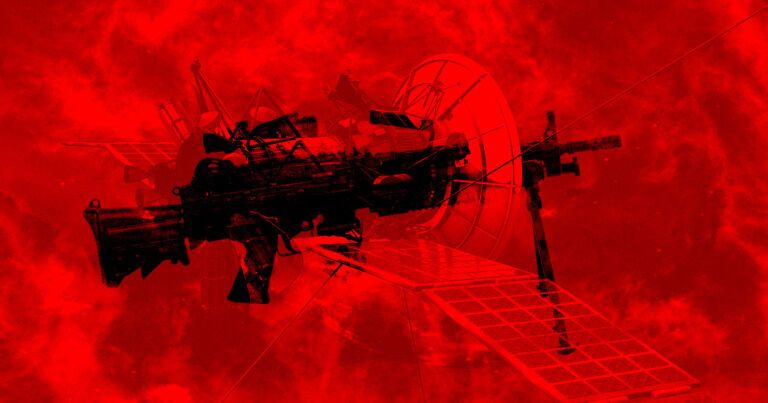



Mohsen Fakhrizadeh, Iran’s top nuclear scientist, was killed on November 27 by a “smart satellite-controlled machine gun” that used AI, the country’s Revolutionary Guards commander Brig-Gen Ali Fadavi told local media, as the BBC reports.
The scientist was allegedly killed by a weapon mounted to a pickup truck, which shot Fakhrizadeh inside a vehicle from a distance — but spared his wife sitting right next to him.
The weapon “focused only on martyr Fakhrizadeh’s face in a way that his wife, despite being only 25cm [10 inches] away, was not shot,” Gen Fadavi, Revolutionary Guards deputy commander, told a ceremony on Sunday, as quoted by the BBC.
For now, it looks like our best bet for going interstellar is to rely on robotic spacecraft that are optimized for speed.
For countless generations, the idea of traveling to an extrasolar planet has been the stuff of dreams. In the current era of renewed space exploration, interest in interstellar travel has understandably been rekindled. However, beyond the realm of science fiction, interstellar space travel remains a largely theoretical matter.
Between the sheer expense involved, the need for technological developments to happen first, and the nature of spacetime itself, sending people to another star system is something that is not likely to happen for a long time – if ever. But in spite of the challenges, the hope remains.
So will humanity ever go interstellar? Let’s break it down categorically and see how hard it might be. First up, there are the laws of physics, which aren’t too accomodating on this front.