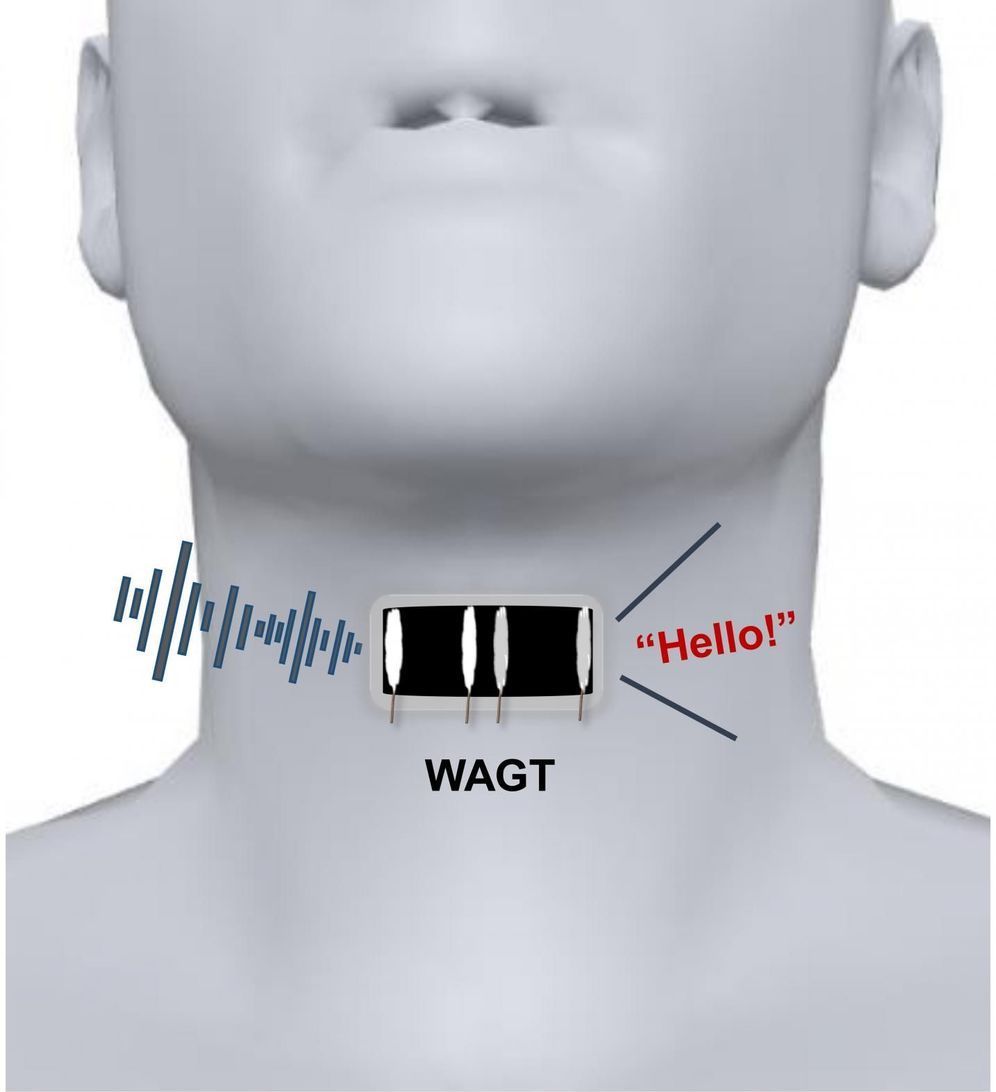
Most people take speech for granted, but it’s actually a complex process that involves both motions of the mouth and vibrations of folded tissues, called vocal cords, within the throat. If the vocal cords sustain injuries or other lesions, a person can lose the ability to speak. Now, researchers reporting in ACS Nano have developed a wearable artificial throat that, when attached to the neck like a temporary tattoo, can transform throat movements into sounds.
Scientists have developed detectors that measure movements on human skin, such as pulse or heartbeat. However, the devices typically can’t convert these motions into sounds. Recently, He Tian, Yi Yang, Tian-Ling Ren and colleagues developed a prototype artificial throat with both capabilities, but because the device needed to be taped to the skin, it wasn’t comfortable enough to wear for long periods of time. So the researchers wanted to develop a thinner, skin-like artificial throat that would adhere to the neck like a temporary tattoo.
To make their artificial throat, the researchers laser-scribed graphene on a thin sheet of polyvinyl alcohol film. The flexible device measured 0.6 by 1.2 inches, or about double the size of a person’s thumbnail. The researchers used water to attach the film to the skin over a volunteer’s throat and connected it with electrodes to a small armband that contained a circuit board, microcomputer, power amplifier and decoder. When the volunteer noiselessly imitated the throat motions of speech, the instrument converted these movements into emitted sounds, such as the words “OK” and “No.” The researchers say that, in the future, mute people could be trained to generate signals with their throats that the device would translate into speech.