Circa 2019
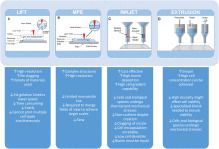
The evolution of micro and nanofabrication approaches significantly spurred the advancements of cardiac tissue engineering over the last decades. Engineering in the micro and nanoscale allows for the rebuilding of heart tissues using cardiomyocytes. The breakthrough of human induced pluripotent stem cells expanded this field rendering the development of human tissues from adult cells possible, thus avoiding the ethical issues of the usage of embryonic stem cells but also creating patient-specific human engineered tissues. In the case of the heart, the combination of cardiomyocytes derived from human induced pluripotent stem cells and micro/nano engineering devices gave rise to new therapeutic approaches of cardiac diseases. In this review, we survey the micro and nanofabrication methods used for cardiac tissue engineering, ranging from clean room-based patterning (such as photolithography and plasma etching) to electrospinning and additive manufacturing. Subsequently, we report on the main approaches of microfluidics for cardiac culture systems, the so-called “Heart on a Chip”, and we assess their efficacy for future development of cardiac disease modeling and drug screening platforms.