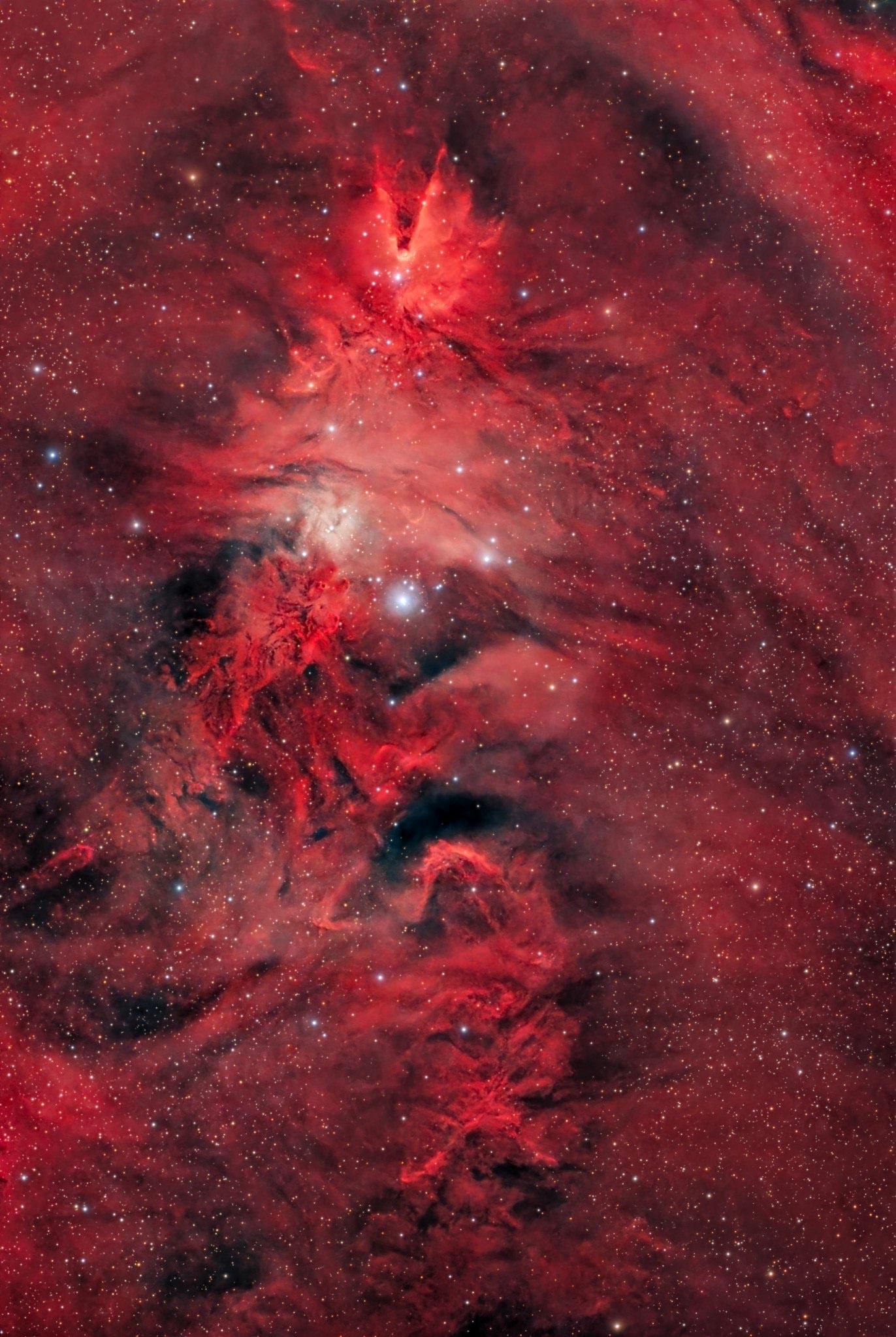
Just in time for Christmas, a vast star-forming region shaped like a Christmas tree is lighting up space 2,700 light-years from Earth.
NGC 2,264 is a vast region of space where new stars are actively forming, located about 2,700 light-years from Earth in the faint constellation Monoceros, also known as the Unicorn. Astronomers use catalog names like NGC 2,264 to identify and track objects beyond our solar system, and this particular one stands out for its intricate mix of glowing clouds and young stars. Positioned near the celestial equator and close to the flat disk of the Milky Way, this region is visible at certain times of year from much of the world.
How young stars light up space