Researchers at Chalmers University of Technology, Sweden, have disproved the prevailing theory of how DNA binds itself. It is not, as is generally believed, hydrogen bonds which bind together the two sides of the DNA structure. Instead, water is the key. The discovery opens doors for new understanding in research in medicine and life sciences. The findings are published in PNAS.
DNA is constructed of two strands consisting of sugar molecules and phosphate groups. Between these two strands are nitrogen bases, the compounds that make up genes, with hydrogen bonds between them. Until now, it was commonly thought that those hydrogen bonds held the two strands together.
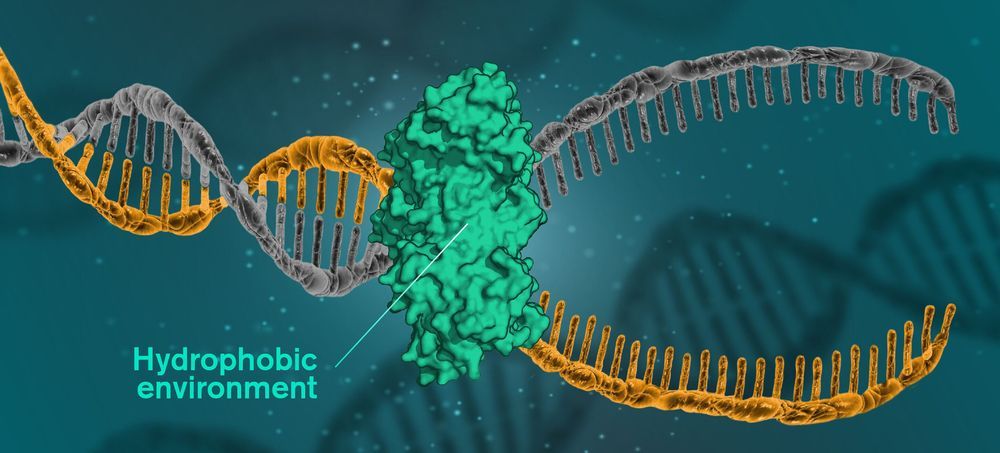
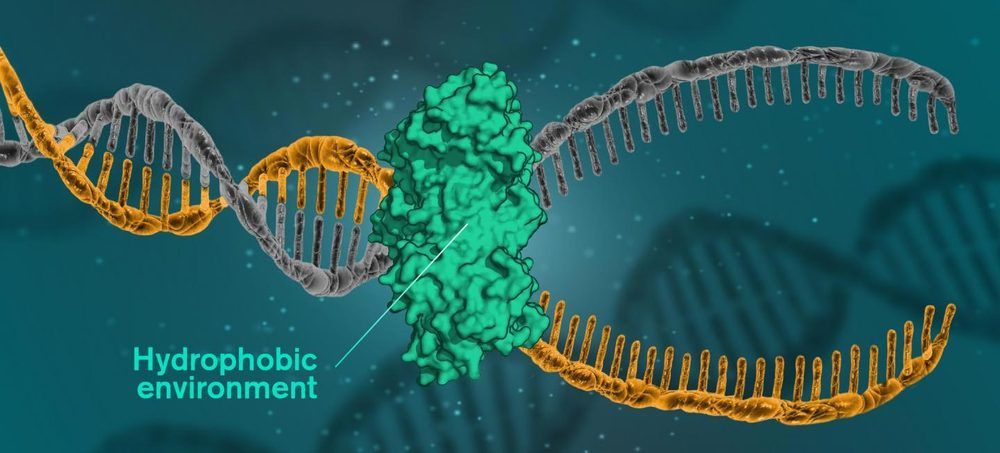
But now, researchers from Chalmers University of Technology show that the secret to DNA’s helical structure may be that the molecules have a hydrophobic interior, in an environment consisting mainly of water. The environment is therefore hydrophilic, while the DNA molecules’ nitrogen bases are hydrophobic, pushing away the surrounding water. When hydrophobic units are in a hydrophilic environment, they group together to minimize their exposure to the water.