According to Arpit Joshipura, The Linux Foundation’s general manager of networking, edge computing will overtake cloud computing by 2025.
The National Security Agency develops advanced hacking tools in-house for both offense and defense—which you could probably guess even if some notable examples hadn’t leaked in recent years. But on Tuesday at the RSA security conference in San Francisco, the agency demonstrated Ghidra, a refined internal tool that it has chosen to open source. And while NSA cybersecurity adviser Rob Joyce called the tool a “contribution to the nation’s cybersecurity community” in announcing it at RSA, it will no doubt be used far beyond the United States.
No one’s better at hacking than the NSA. And now one of its powerful tools is available to everyone for free.
While most of the attention has been on Google Stadia and Microsoft xCloud, Tencent has also been working on cloud gaming. China’s biggest gaming company has been talking about letting people go from viewing live streams to playing along with the same streamer with just a click — without ever having to download the game.
One of the big reasons China is perfect for cloud gaming? 5G.
Google Stadia and Microsoft xCloud are pushing cloud gaming, but Tencent could be the real one to watch.
Billionaire entrepreneur Elon Musk has unveiled the latest iteration of his space company’s newly assembled Starship, outlining a speedy development timeline for the centerpiece vehicle of SpaceX’s quest to launch humans to the moon and Mars.
Musk showed a crowd of space enthusiasts and reporters at SpaceX’s rocket development site late on Saturday in the remote village of Boca Chica, Texas, animations of Starship landing on the moon and Mars and predicted that the rocket’s first orbital flight could come in the next six months, followed by missions to space with humans aboard the next year.
“This is basically the holy grail of space,” Musk said, standing between a towering, newly assembled Starship rocket and Falcon 1 — the company’s first vehicle whose debut orbital mission was celebrated by SpaceX 11 years ago.
We hear it daily — “Launch your drone program!” Uninspired marketing campaigns littered across social media, websites and emails. A detrimental circle of brands mirroring brands, unwittingly stalling the rise of drones. The problem is, as an industry, they’re missing the damn point. Take for example a use case we see all too often — construction. When handheld drills started showing up on jobsites, we didn’t hear Black + Decker say, “launch your drill program!” Why not? Drills are just enablers. They allow workers to do what they were already doing — except better, faster and more efficiently. The breakthrough had little to do with the actual tool itself, and more the new ability to enable faster holes. Drones are no different.
The goal isn’t to “put a drone on every construction site.” Drones are promising new vehicles that have the potential to transform industry, but they also inherently introduce new costs and complexities. The thought of adding new tools, new responsibilities, new certifications and permits, and new burdens to an already complex operation is the exact opposite of what most project managers consider helpful. This might begin to explain why drone service providers today are collectively struggling to grow at any meaningful velocity. We’re creating “launch your drone programs” solutions that make it easier for businesses to own and operate drones, when we should be making the drone invisible, and become laser-focused on the data drones generate and an infrastructure that supports rapid spatial insights.
We need to stop putting drones on construction sites, and start giving the industry the very thing that drones enable — insight. Drones will be on every job site in the next few years, but not as another tool on the tool belt. The project manager isn’t adopting a drone program. They’re adopting a visual insights program that captures a new, historical perspective across their sites. They’re providing situational awareness holistically throughout their organization. They’re making decisions based on the actual state of projects, and the insights affordable by new perspectives and sensors.
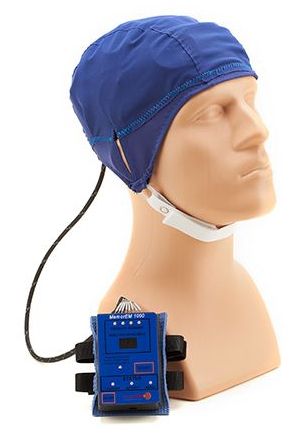
A small clinical trial, announced by U.S. company NeuroEM Therapeutics, shows reversal of cognitive impairment in Alzheimer’s disease patients after just two months of treatment using a wearable head device. Electromagnetic waves emitted by the device appear to penetrate the brain to break up amyloid-beta and tau deposits.
Click on photo to start video.
What about what happens when two black holes collide?
Goddard Scientist Roopesh Ojha sheds light on the supermassive and stellar mass black holes within our galaxy. Scientists believe one supermassive black hole exists at the center of every galaxy and that many, many more of their much smaller siblings, the stellar mass black holes, surround it.
From the Peak District to John O’Groats, nearly 1,300 kilometres of off-road ups and downs, forest trails and canal paths await two-wheeled adventurers in the UK. The newly launched Great North Trail creates a continuous route linking England and Scotland in a bid to open up the countryside to cyclists. Passing through the Peak District, the Yorkshire Dales and Kielder Forest in England, up to Loch Lomond, the Trossachs National Park and Loch Ness in Scotland, the route takes in some of the UK’s best-known beauty spots. In Scotland, cyclists can branch towards Cape Wrath, the most north-westerly part of the UK, or John O’Groats on the northeast tip.
Wangari Maathai for years told people to plant trees. She is the reason Kenyans plant trees in protected forests, and will continue for a very long time.
Trees are a low-tech, high-efficiency way to offset much of humankind’s negative impact on the climate. What’s even better, we have plenty of room for a lot more of them.
A new study conducted by researchers at Switzerland’s ETH-Zürich, published in Science, details how Earth could support almost an additional billion hectares of trees without the new forests pushing into existing urban or agricultural areas. Once the trees grow to maturity, they could store more than 200 billion metric tons of carbon.
Great news indeed, but it still leaves us with some huge unanswered questions. Where and how are we going to plant all the new trees? What kind of trees should we plant? How can we ensure that the new forests become a boon for people in those areas?
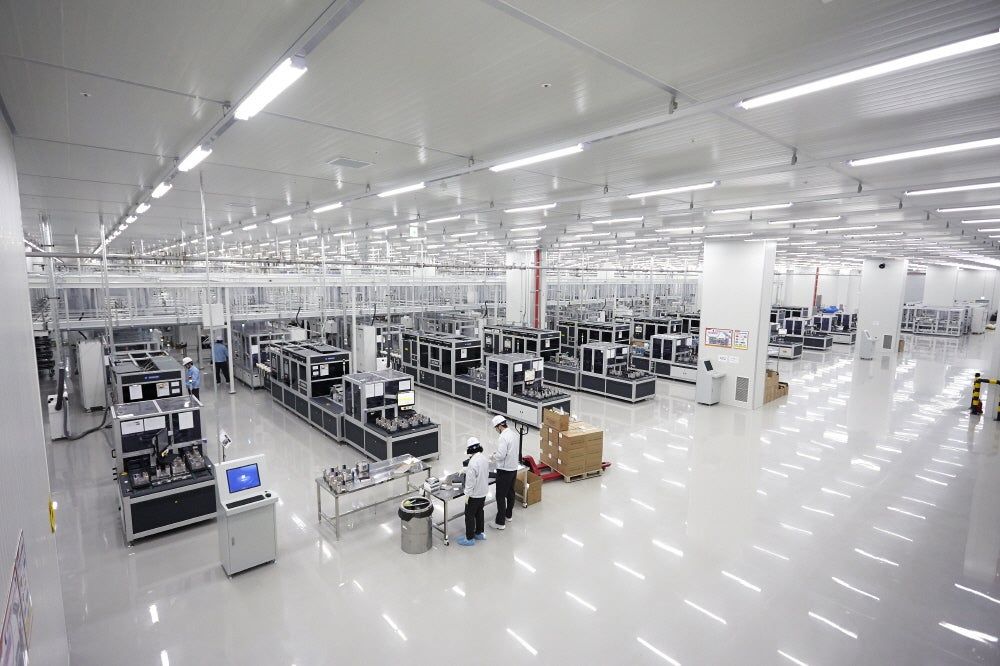
Hanwha Q Cells officially opened its 300,000 square foot solar panel factory in Dalton, Georgia last week, claiming it is the largest such manufacturing facility in the western hemisphere. The $200 million factory employs more than 650 workers and is capable of producing 12,000 solar panels a year — enough to generate 1.7 GW of electricity. Its standard production panel features six bus bars, has an efficiency of about 19%, and an output of up to 345 watts.