Researchers at Nanyang Technological University, Singapore (NTU Singapore) have developed a quantum communication chip that is 1,000 times smaller than current quantum setups, but offers the same superior security quantum technology is known for.
Most leading security standards used in secure communication methods—from withdrawing cash from the ATM to purchasing goods online on the smartphone—does not leverage quantum technology. The electronic transmission of the personal identification number (PIN) or password can be intercepted, posing a security risk.
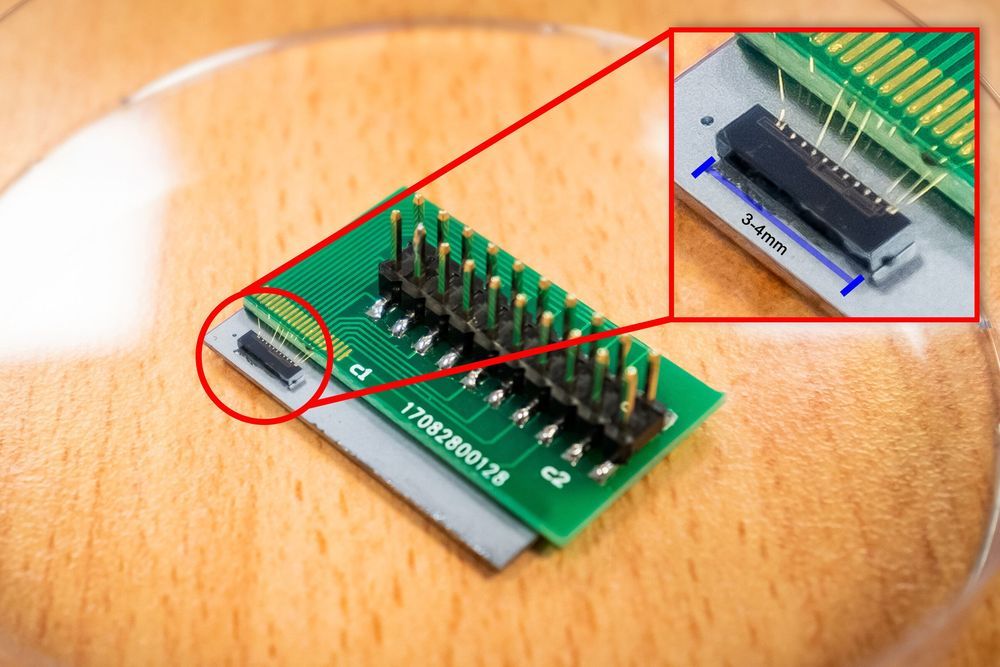
Roughly three millimeters in size, the tiny chip uses quantum communication algorithms to provide enhanced security compared to existing standards. It does this by integrating passwords within the information that is being delivered, forming a secure quantum key. After the information is received, it is destroyed along with the key, making it an extremely secure form of communication.