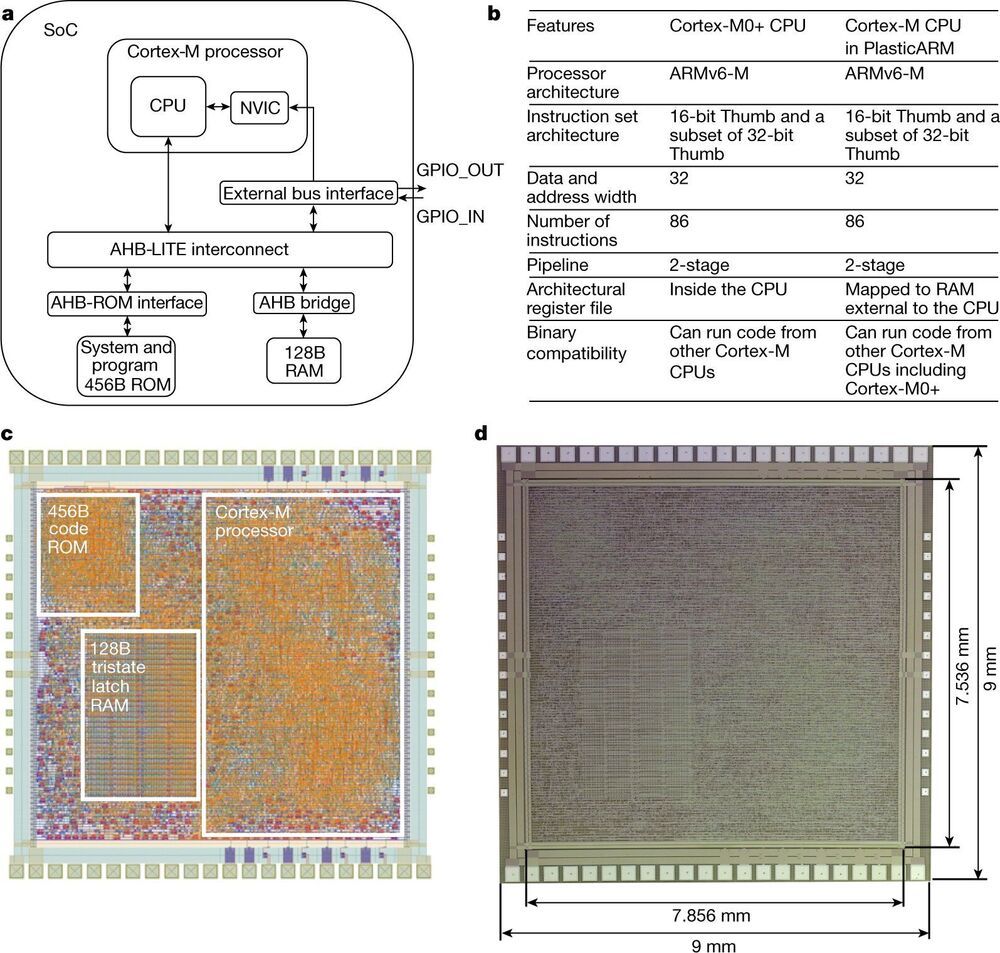
A team of researchers at ARM Inc., has developed a 32-bit microprocessor on a flexible base which the company claims could pave the way to fully flexible smart integrated systems. In their paper published in the journal Nature, the group describes how they used metal−oxide thin-film transistors along with a type of plastic to create their chip and outline ways they believe it could be used.
Microprocessors power a wide range of products, but what they all have in common is their stiffness. Almost all of them are made using silicon wafers, which means that they have to be hard and flat. This inability to bend, the researchers with this new effort contend, is what is preventing the development of products such as smart clothes, smart labels on foods, packaging and even paper products. To meet that need, the team has created what they describe as the PlasticARM—a RISC-based 32-bit microprocessor set on a flexible base. In addition to its flexibility, the new technique allows for printing a microprocessor onto many types of materials, all at low cost.
To create their bendy microprocessor, the researchers teamed with a group at PragmatIC Semiconductor to create a bendable version of the Cortex M0+ microprocessor, which was chosen for its simplicity and small size. To make their chip, (which includes ROM, RAM and interconnections) the team used amorphous silicon fabricated (in the form of metal-oxide thin-film transistors) onto flexible polymers.