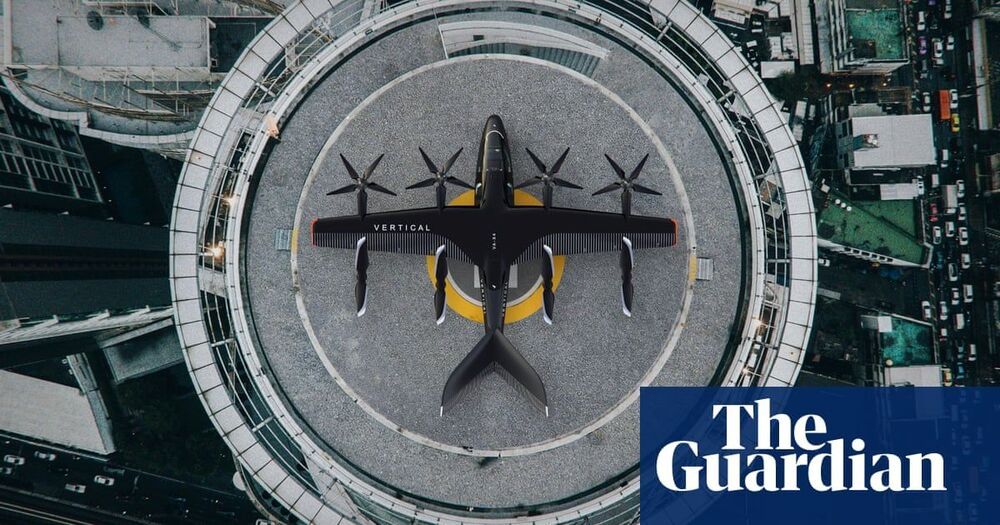
The aircraft could be used to transfer passengers between home and airports, Virgin believes. It would be able, for example, to make the 56-mile journey from Cambridge to Heathrow in 22 minutes, compared with a 90-minute drive.
The announcement represents another step in the race to making mass electric flight and air taxis a reality. Some analysts have predicted the sector could be worth £150bn by 2040 but significant hurdles remain, including regulation and safety certification. The VA-X4 has yet to take its first test flight. Dómhnal Slattery, the chief executive of Avolon, said its order would “accelerate the inevitable commercial rollout of zero-emissions aircraft. Before the end of this decade, we expect zero-emission urban air mobility, enabled by eVTOLs, to play an increasingly important role in the global commercial aviation market.”