Following on from the video last week all about mTOR, this week I have got one on AMPK. This is yet another protein that has an enzymatic role in the cellular energy systems that keeps us all alive and well, and it performs a natural balancing act with mTOR. As with all the systems in our body, a natural balance is essential for harmony, do we feast or fast, do we exercise hard or relax and meditate, do we sleep as many hours as possible or as few as we can get by on, should our body concentrate on growth or repair? It can all seem like a mine field, so it is often good to start with the essentials to make sure you have a good grasp of what they are, before you venture out of your depth. Hopefully this video will help shed some light these areas so you can find the right routine to help you strike a balance.
Get the latest international news and world events from around the world.


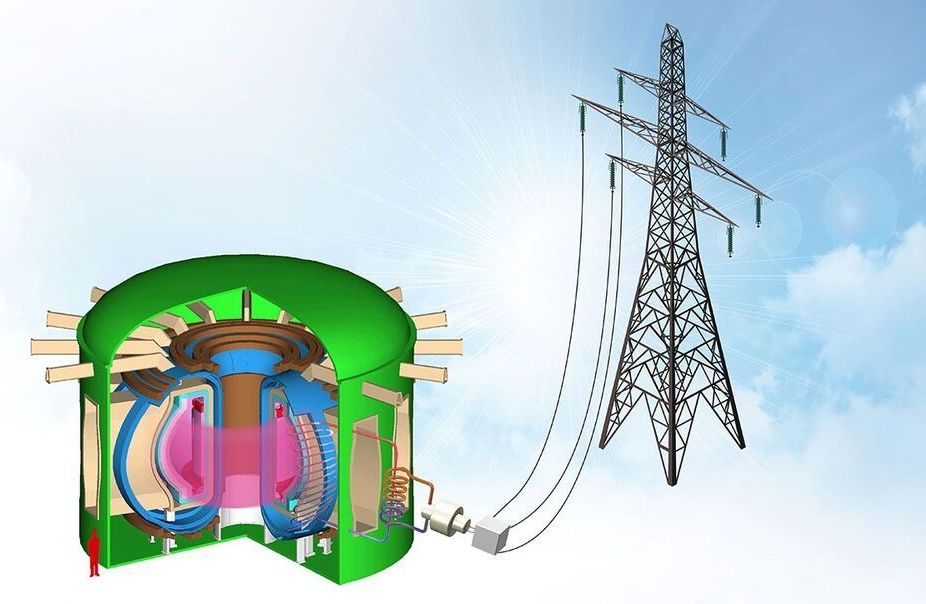
US Researchers Design Compact Fusion Power Plant
New concept delivers continuous electricity with an approach that reduces cost and risk
San Diego, March 29, 2021 – Fusion energy is heating up. In the past few months, both the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Fusion Energy Sciences Advisory Committee (FESAC) and the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine (NASEM) released reports calling for aggressive development of fusion energy in the U.S.
Now, scientists at the DIII-D National Fusion Facility have released a new design for a compact fusion reactor that can generate electricity and help define the technology necessary for commercial fusion power. The approach is based on the “Advanced Tokamak” concept pioneered by the DIII-D program, which enables a higher-performance, self-sustaining configuration that holds energy more efficiently than in typical pulsed configurations, allowing it to be built at a reduced scale and cost.
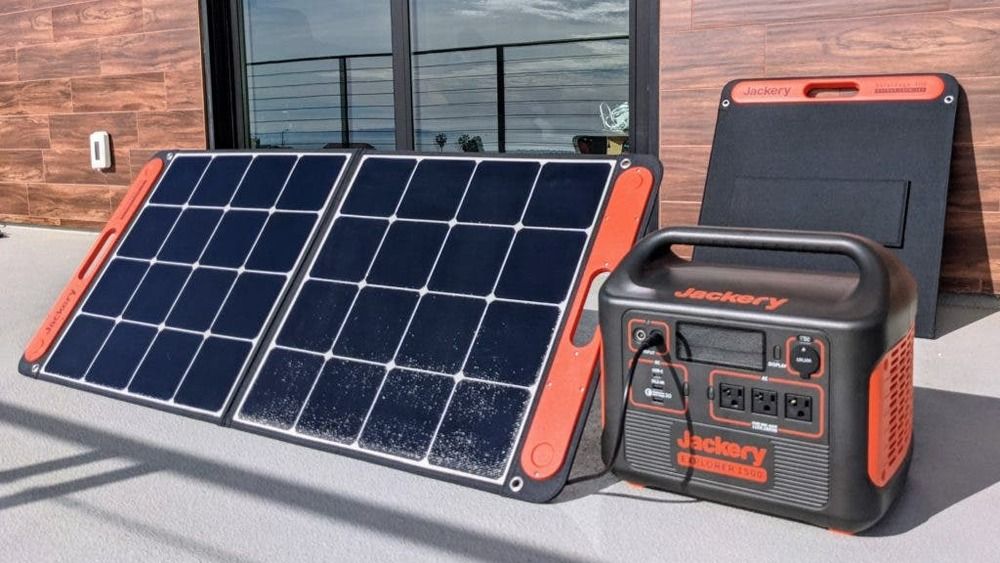

The Jackery Explorer 1500 Solar Generator Enables Exciting New Possibilities
The renewable energy experts at Jackery are up to their usual tricks and announced a new line of solar generator products on Jackery Day that open up a completely new range of possibilities.
They sent us their Solar Generator 1500 with two of their slick 100 watt folding Solar Saga panels to run through the paces. On paper, the new Jackery Explorer 1500 Portable Power Station battery was impressive, with its massive 1.5kWh capacity and increased power output capabilities.
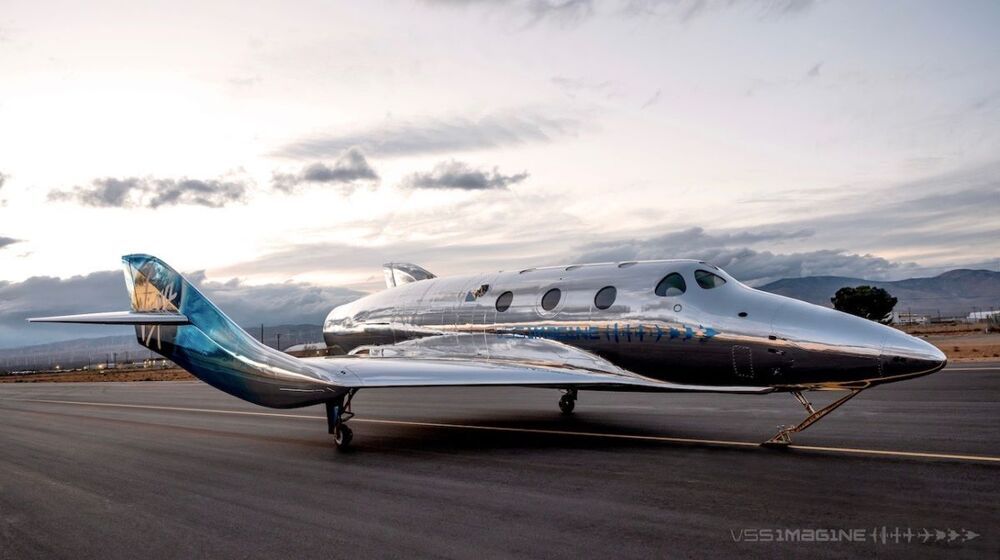

Meet VSS Imagine: Virgin Galactic unveils its first SpaceShip III spacecraft
Virgin Galactic passengers won’t circle Earth like astronauts aboard the International Space Station do. But they will get to experience a few minutes of weightlessness and see the curve of Earth against the blackness of space. More than 600 people have booked a ride to date, at a price (most recently) of $250000 per seat, company representatives have said.
VSS Unity has company.
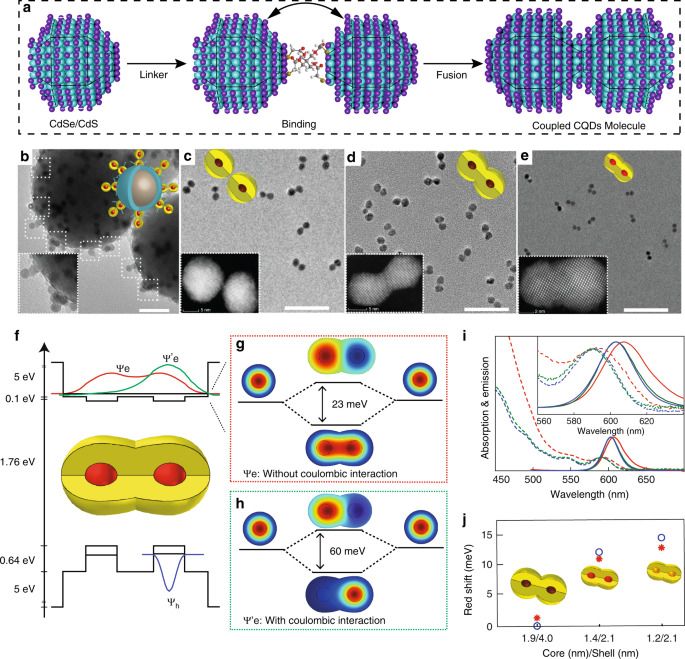
Colloidal quantum dot molecules manifesting quantum coupling at room temperature
Circa 2019 o.o
In analogy to the coupling of atoms into molecules, the authors fuse colloidal semiconductor nanocrystals into quantum dot dimers. These nanocrystal ‘molecules’ exhibit significant quantum coupling effects, making them promising for applications in devices and potential quantum technologies.
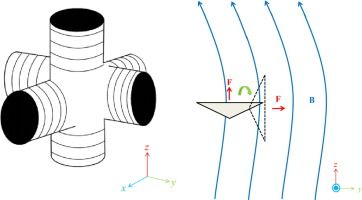
A propellant-free superconducting solenoid thruster driven by geomagnetic field
Space travel nowadays relies on physical ejection of propellants, which is challenged by reachable distance of a vehicle in desirable time. In contrast, electromagnetic propulsion was proposed to be a potential solution without need of carrying bulky mass of propellants, by using force interaction of local magnetic dipoles with the external natural magnetic field. Further development of this technique, however, has been daunted by extremely small magnetic induction that can be obtained.
To generate a significant thrust by a system with a reasonable scale, we propose an alternative concept of design, based on the variation of local magnetic dipole moments that has not been considered.
A magnetic dipole is created by wrapping a solenoid around an iron core. It is varied spatially by changing the cross-sectional area of the solenoid, hence giving a gradient of magnetic dipole moment. The interaction force is measured by an in-house force sensor based on a cantilever, which has a high sensitivity of one micro-Newton. In addition, numerical simulation is used to calculate the magnetic field and created force via the Maxwell stress tensor.

Opinion | How many aliens are out there? Why a new estimate is raising eyebrows
‘Humans are extraordinarily special’. Not new but well worth remembering.
Either way, their conclusion is that, like stick-shift cars, extraterrestrial civilizations are few and far between. The implication is that our nearest cosmic chums are at least several thousand light-years away.
You may wonder why this story has raised eyebrows. Well, it would make Homo sapiens extraordinarily special, despite the fact that the galaxy is stuffed with planets. It discomfits scientists (including me) because, historically, every time we’ve thought we occupy a privileged position in the universe, we were wrong. Remember that six centuries ago, learned folk would have assured you that Earth was the center of the cosmos.
FDA approves first test of CRISPR to correct genetic defect causing sickle cell disease
UC scientists and physicians hope to permanently cure patients of sickle cell disease by using CRISPR-Cas9 to replace a defective gene with the normal version.
In 2014, two years after her Nobel Prize-winning invention of CRISPR-Cas9 genome editing, Jennifer Doudna thought the technology was mature enough to tackle a cure for a devastating hereditary disorder, sickle cell disease, that afflicts millions of people around the world, most of them of African descent. Some 100000 Black people in the U.S. are afflicted with the disease.
Mobilizing colleagues in the then-new Innovative Genome Institute (IGI) — a joint research collaboration between the University of California, Berkeley, and UC San Francisco — they sought to repair the single mutation that makes red blood cells warp and clog arteries, causing excruciating pain and often death. Available treatments today typically involve regular transfusions, though bone marrow transplants can cure those who can find a matched donor.
After six years of work, that experimental treatment has now been approved for clinical trials by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration, enabling the first tests in humans of a CRISPR-based therapy to directly correct the mutation in the beta-globin gene responsible for sickle cell disease. Beta-globin is one of the proteins in the hemoglobin complex responsible for carrying oxygen throughout the body.