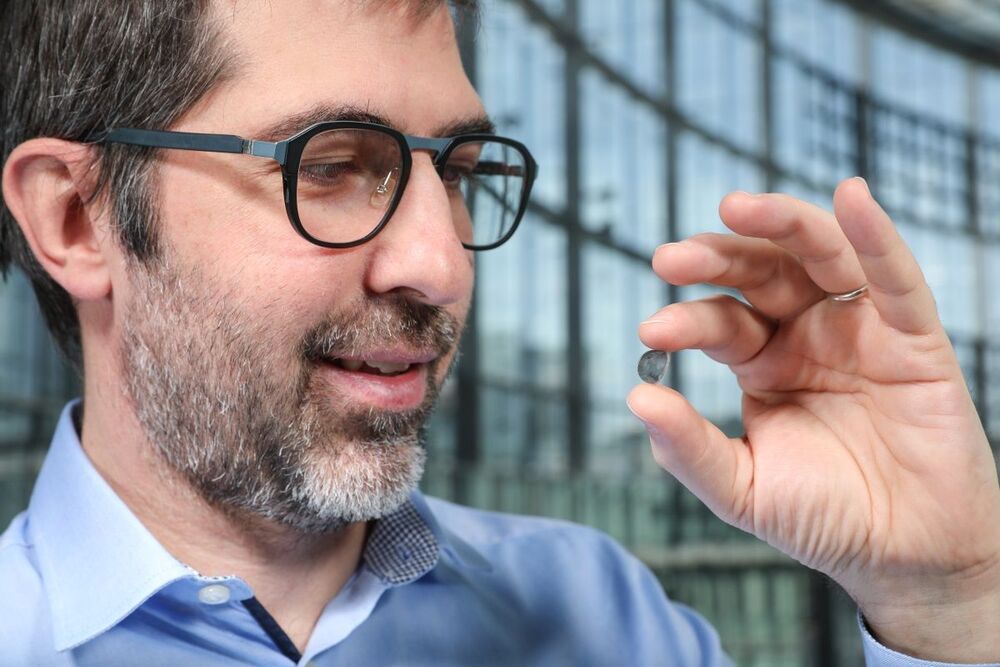
A new retinal implant uses thousands of electrodes to stimulate retinal cells in the blind and produce dotted images.



In a recent paper, Bell argues that the principles of Mario Kart—especially the parts of it that make it so addictive and fun for players—can serve as a helpful guide to create more equitable social and economic programs that would better serve farmers in low-resource, rural regions of the developing world. That’s because, even when you’re doing horribly in Mario Kart—flying off the side of Rainbow Road, for example—the game is designed to keep you in the race.
“Farming is an awful thing to have to do if you don’t want to be a farmer,” Bell says. “You have to be an entrepreneur, you have to be an agronomist, put in a bunch of labor…and in so many parts of the world people are farmers because their parents are farmers and those are the assets and options they had.” This is a common story that Bell has come across many times during research trips to Pakistan, Bangladesh, Cambodia, Malawi, and other countries in southern Africa, and is what largely inspired him to focus his research on policies that could aid in development.
In his new paper, Bell argues that policies that directly provide assistance to farmers in the world’s poorest developing regions could help reduce poverty overall, while increasing sustainable and environmentally friendly practices. Bell says the idea is a lot like the way that Mario Kart gives players falling behind in the race the best power-ups, designed to bump them towards the front of the pack and keep them in the race. Meanwhile, faster players in the front don’t get these same boosts, and instead typically get weaker powers, such as banana peels to trip up a racer behind them or an ink splat to disrupt the other players’ screens. This boosting principle is called “rubber banding,” and it’s what keeps the game fun and interesting, Bell says, since there is always a chance for you to get ahead.

There has not been enough progress in our understanding of the basic mechanisms underlying psychosis. Studying psychotic disorders in animal models is difficult because the diagnosis relies on self-reported symptoms that can only be assessed in humans. Schmack et al. developed a paradigm to probe and rigorously measure experimentally controlled hallucinations in rodents (see the Perspective by Matamales). Using dopamine-sensor measurements and circuit and pharmacological manipulations, they demonstrated a brain circuit link between excessive dopamine and hallucination-like experience. This could potentially be useful as a translational model of common psychotic symptoms described in various psychiatric disorders. It may also help in the development of new therapeutic approaches based on anatomically selective modulation of dopamine function.
Science, this issue p. see also p. [33][2]
### INTRODUCTION


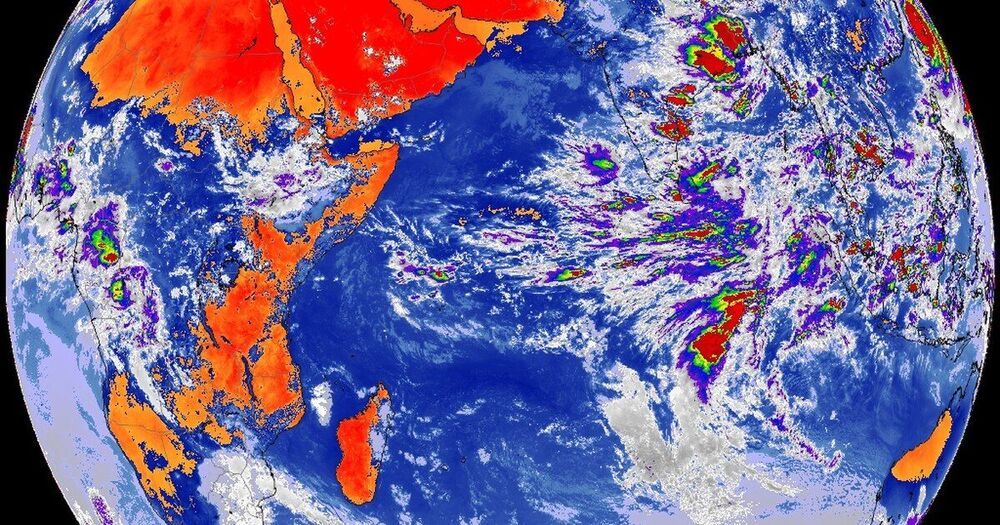
Based on the recommendations of weather forecasters, Operation Overlord’s June 5 D-Day was postponed due to a weather front. However, the operation was launched one day later when analysis projected a short period of acceptable weather. Germany’s forecasters missed this break, and the results were cataclysmic for German forces.
The Korean and Vietnam conflicts highlighted a growing need for “weather superiority” as enemy forces learned to take advantage of periods of bad weather that limited the effectiveness of U.S. air forces. Even in Desert Storm, the first item in planning the daily air operations began with a weather forecast.
Today, superior knowledge of environmental conditions is a force multiplier for all the services in an era where concepts like Joint All-Domain Command and Control are accelerating the speed and precision at which war is conducted. The outcome of future conflict will depend on rapid, accurate and more fully informed decisions. If a commander lacks an assured source of high-fidelity intelligence about the environment, then tools, tactics and timing cannot be aligned to achieve desired outcomes.
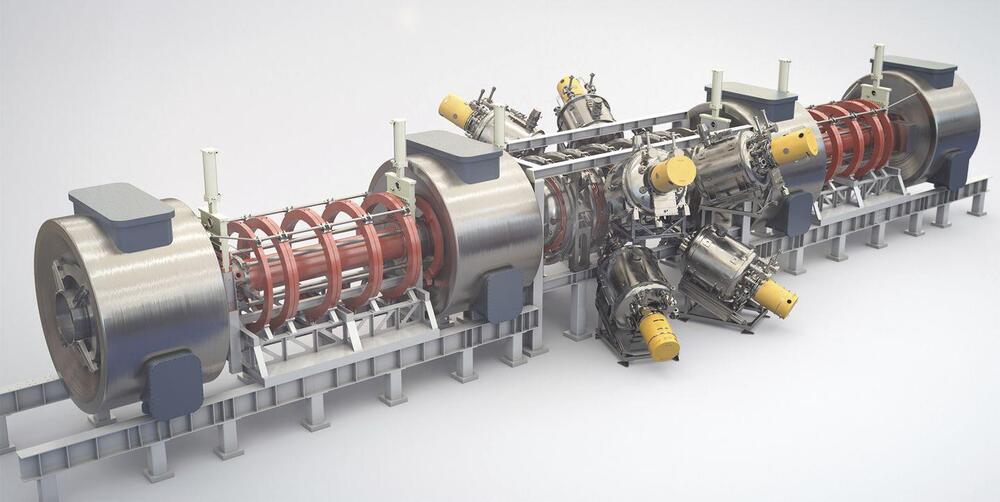
This means 6 years after TAE began to reach “long enough,” Norman has finally reached “hot enough” frequently enough that it can begin to scale up for commercial power plants. And this is why the company says it feels it can build that kind of power plant by the end of the decade in 2030.
Nuclear fusion has long felt like decades away. Today, the timeline accelerates.
Developing ultra high bandwidth brain-machine interfaces to connect humans and computers.
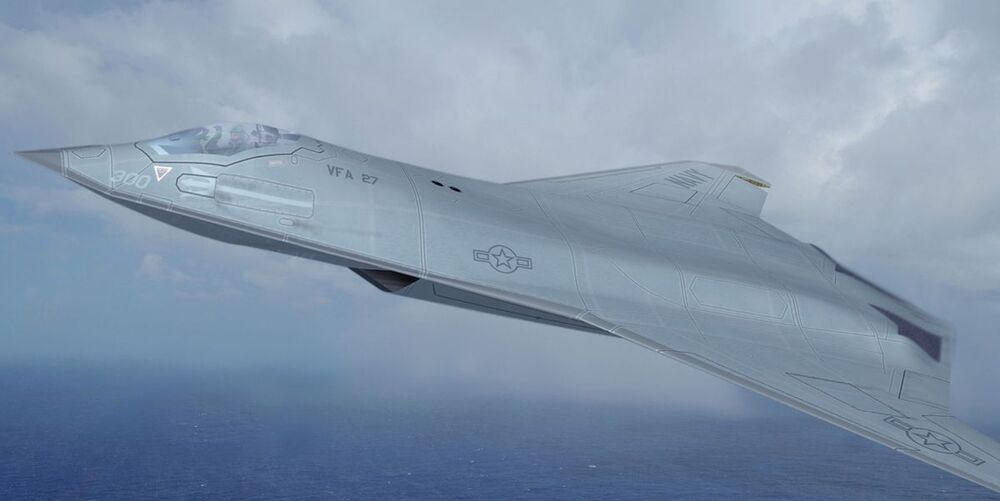

NGAD is the Navy’s effort to replace the Super Hornet. Note: It’s a completely separate program from the Air Force’s own NGAD—which recently designed, tested, and flew a secret new fighter jet—and will produce a completely separate plane. The two aircraft will almost certainly be quite different, with the Air Force’s jet more optimized for air superiority. It’s likely the two fighters, developed roughly within the same time period, will share much of the same technology.
The U.S. Navy elaborated on its plans to replace the F/A-18E/F Super Hornet, saying the service’s next strike fighter will “most likely be manned.” The jet will probably fly alongside robotic allies, and remotely crewed aircraft could eventually account for six out of 10 planes on a carrier flight deck.
“As we look at it right now, the Next-Gen Air Dominance [NGAD] is a family of systems, which has as its centerpiece the F/A-XX—which may or may not be manned—platform. It’s the fixed-wing portion of the Next-Gen Air Dominance family of systems,” said Rear Adm. Gregory Harris, the head of the Chief of Naval Operations’ air warfare directorate, during a Navy League event.
The F/A-18E/F Super Hornet dominates Navy’s strike fighter fleet, made up of fighters that can execute both fighter and attack missions. Although the Navy is buying the F-35C Joint Strike Fighter, it’s only purchasing enough of the planes to replace one or two of the four strike fighter squadrons per deployed aircraft carrier. The Navy believes it needs to replace the Super Hornet and its electronic warfare variant, the EA-18G Growler, in the 2030s.