Solar panel recycling.
America’s largest solar panel maker is also the world’s largest recycler of panels, with their program recovering 95% of materials for reuse.



I’m excited to welcome Clive Neal, a professor of planetary geology at the University of Notre Dame in South Bend, Indiana, and an expert on lunar science and the Apollo Moon rock samples. A former Chair of NASA’s Lunar Exploration Analysis Group, Neal will talk about why the Moon is so crucial to our understanding of the inner solar system. Please stay tuned!

President Xi Jinping, also general secretary of the Communist Party of China (CPC) Central Committee, has stressed the importance and urgency of advancing the development of quantum science and technology. Xi made the remarks while presiding over a group study session of the Political Bureau of the CPC Central Committee on Friday. Quantum mechanics is a fundamental theory which has been used successfully in explaining microscopic phenomena in all branches of physics. Experts believe the whole world is on the brink of a quantum revolution. Xi noted that China has made breakthroughs in some of the key areas, but still faces multiple challenges. He stressed the need to develop self-reliant technology in order to secure a stable supply chain. More support should be given to the industry in areas including development policy, talent recruiting, academic environment and so on, said Xi.
Elon Musk has warned many times about the dangers of AI. He sees strong artificial intelligence as an existential risk. Musk therefore wants to develop a brain machine interface or BMI device so we can merge with AI and hopefully develop a symbiotic relationship with artificial intelligence thus solve the AI control problem. Elon Musk has founded the neurotechnology company Neuralink. the company is focused on developing implantable brain machine interfaces. Neuralink has made recent headlines for its newest BMI device presented by Elon Musk.
In the short term, Neuralink’s BMI may be used to fix neurological problems and disorders. As Elon Musk has pointed out, over time, virtually everyone who gets old will suffer at least one if not multiple common neurological issues such as: Memory loss, hearing loss, seizures, strokes, brain damage etc.
With the development of Neuralink’s device, these problems may be a thing of the past. Better yet, the integration of Neuralink’s device with the human brain may advertently solve the artificial intelligence alignment problem by achieving a symbiotic relationship between humans and machines.
This is because there are many cases where an AI and a biological intelligence could benefit from each other’s actions; the AI receiving data from the human brain and the human brain receiving data from the AI. The benefits of this relationship would greatly outweigh the costs to both humans and AI systems; however, it is also very likely that AI systems and biological intelligences will at some point be in conflict.
Elon Musk has commented on the dangers of AI saying it is the greatest risk we face as a civilization. However, in order to prove that Neuralink can solve this problem, two things will need to become clear: how does Neuralink achieve symbiosis with the human brain? And what are the side effects and potential drawbacks of this symbiosis?
#ElonMusk #Neuralink #AI
It’s been almost 20 years since the Concorde was retired, putting an end to commercial supersonic flight for the very rich. But out in Colorado, the startup Boom Technology has raised $160 million in its quest to build a replacement, one that should be cheaper, more comfortable and able to fly more routes. Here’s an exclusive first look at Boom’s prototype test plane, the XB-1.
#HelloWorld #Technology #Aviation
——-
Like this video? Subscribe: https://www.youtube.com/Bloomberg?sub_confirmation=1
QuickTake Originals is Bloomberg’s official premium video channel. We bring you insights and analysis from business, science, and technology experts who are shaping our future. We’re home to Hello World, Giant Leap, Storylines, and the series powering CityLab, Bloomberg Businessweek, Bloomberg Green, and much more.
Subscribe for business news, but not as you’ve known it: exclusive interviews, fascinating profiles, data-driven analysis, and the latest in tech innovation from around the world.
Visit our partner channel QuickTake News for breaking global news and insight in an instant.
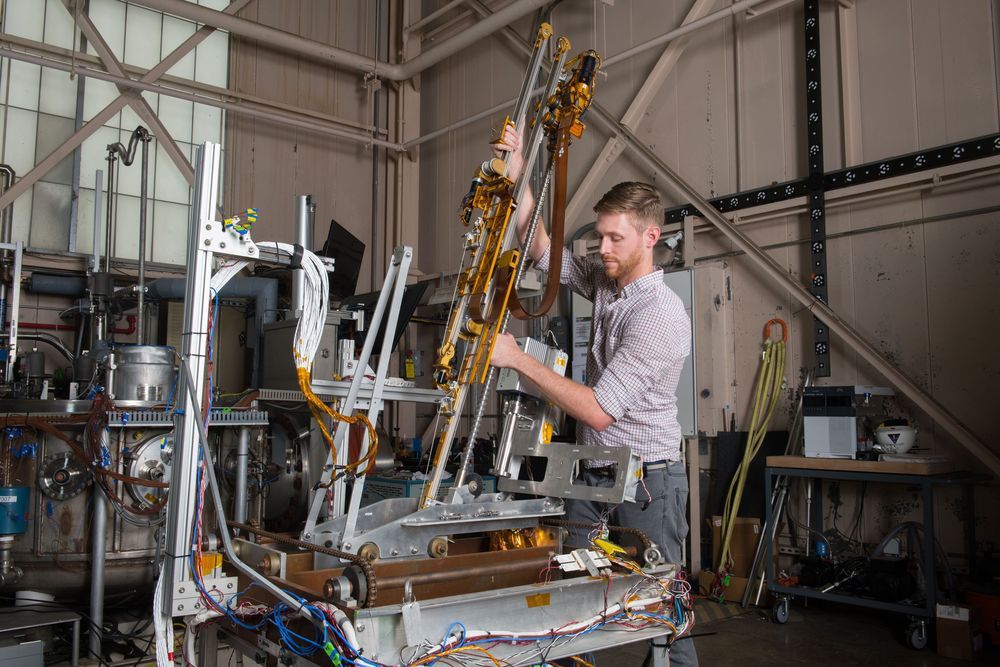

NASA has awarded Intuitive Machines of Houston approximately $47 million to deliver a drill combined with a mass spectrometer to the Moon by December 2022 under the agency’s Commercial Lunar Payload Services initiative. The delivery of the Polar Resources Ice Mining Experiment known as PRIME-1 will help NASA search for ice at the Moon’s South Pole and, for the first time, harvest ice from below the surface.
“We continue to rapidly select vendors from our pool of CLPS vendors to land payloads on the lunar surface, which exemplifies our work to integrate the ingenuity of commercial industry into our efforts at the Moon,” said NASA’s Associate Administrator for Science Thomas Zurbuchen. “The information we’ll gain from PRIME-1 and other science instruments and technology demonstrations we’re sending to the lunar surface will inform our Artemis missions with astronauts and help us better understand how we can build a sustainable lunar presence.”
PRIME-1 will land on the Moon and drill up to 3 feet (approximately 1 meter) below the surface. It will measure with a mass spectrometer how much ice in the sample is lost to sublimation as the ice turns from a solid to a vapor in the vacuum of the lunar environment. Versions of PRIME-1’s drill and the Mass Spectrometer Observing Lunar Operations, or MSolo, will also fly on VIPER, a mobile robot that also will search for ice at the lunar South Pole in 2023. NASA will land the first woman and next man on the Moon’s South Pole the following year.
SpaceX CEO Elon Musk shared a photo that shows just how far the company has come in terms of preparation for its upcoming tests.
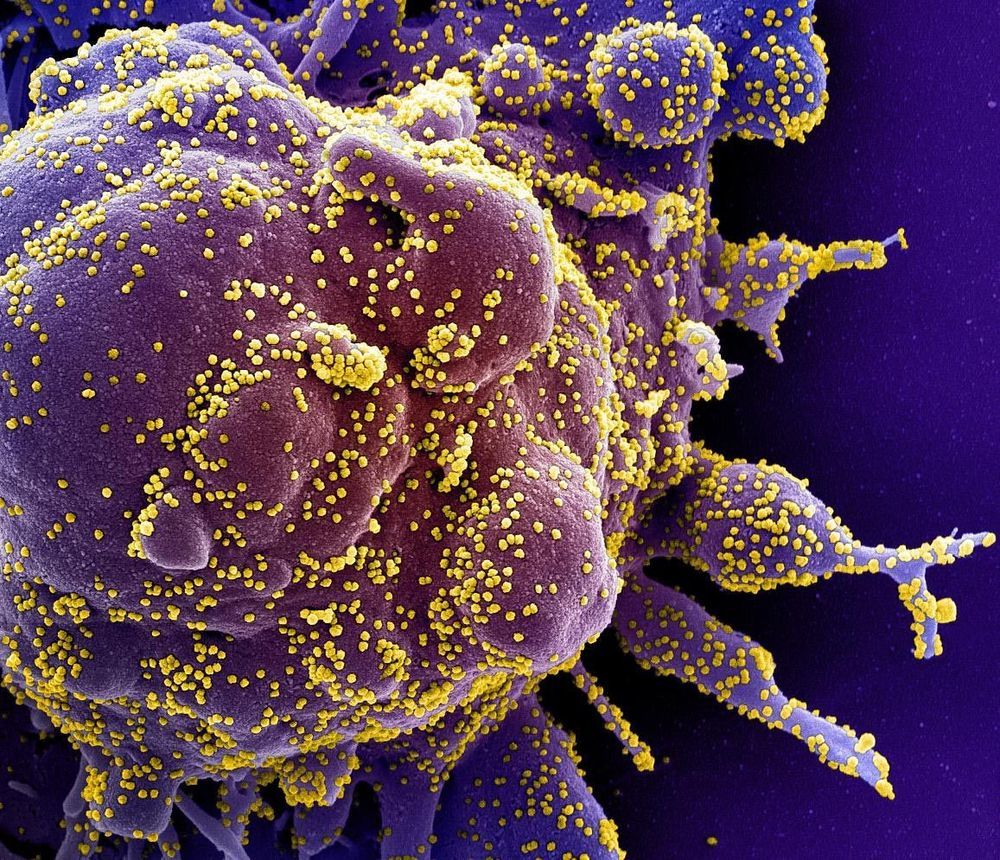
Blocking Immune System Pathway May Stop COVID-19 Infection, Prevent Severe Organ Damage
While the world waits eagerly for a safe and effective vaccine to prevent infections from severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), the virus behind the COVID-19 pandemic, researchers also are focusing on better understanding how SARS-CoV-2 attacks the body in the search for other means of stopping its devastating impact. The key to one possibility — blocking a protein that enables the virus to turn the immune system against healthy cells — has been identified in a recent study by a team of Johns Hopkins Medicine researchers.
Based on their findings, the researchers believe that inhibiting the protein, known as factor D, also will curtail the potentially deadly inflammatory reactions that many patients have to the virus.
