Scientists have discovered the first fast radio burst that beats at a steady rhythm, and the mysterious repeating signal is coming from the outskirts of another galaxy.
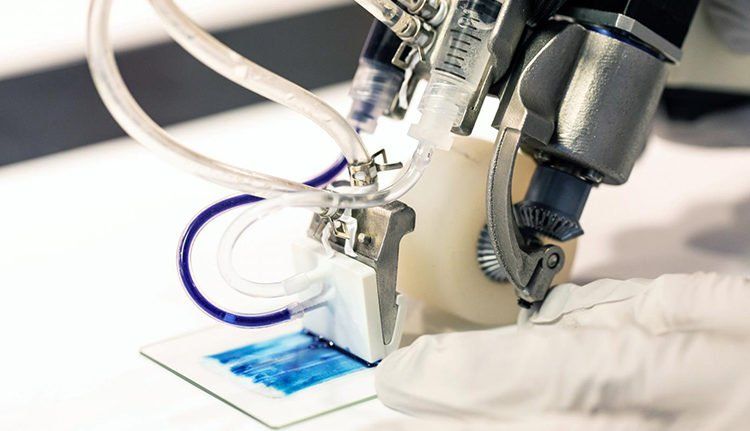
A burn that is over 25% of the human body area can be life threatening. However a burn that is only 1 percent but on a visible area of the body can be life-worsening. That is why advancements in the area of wound care and burns treatment are so important from patient perspective. Being a doctor of the future will include having a point-of-care device such as a 3D-Bioprinter that will scan the lesions in dept and width and print a gel imbued with cells and prolo-factors.
Forgive me my conservatism… we already have such clinics that are on the clinical trials for such treatments.
Read more in the article. Stay tuned for more topics through the Academy blog. Gain more knowledge in Regenerative Medicine and practical experience with biologics through the Annual Congress — Global Regenerative Congress 18–20 September 2020 in Dubai. Registrations are open: www.grc2020dubai.com
Researchers from the University of Toronto (ON, Canada) have reported success in trials of a handheld bioprinter for treating serious burns and wounds.
One of the biggest problems in the sneaker resale market may now be more manageable.
Product authentication technology provider Entrupy on Wednesday released its Legit Check Tech (LCT) solution, a device that uses artificial intelligence to determine whether a sneaker is counterfeit or not — and it only takes about a minute to use.
Fake pairs of popular Nike and Adidas sneakers are rampant in the resale sector. Authorities recently busted a counterfeiting operation that shipped $470 million worth of fake Nikes to the US.
This handheld 3D printer deposits layers of skin tissue, and could one day help to heal deep wounds. Instead of waiting for skin patches to grow in a Petri dish, you apply it directly.
A team of Canadian scientists has successfully applied skin tissue to burn wounds using a handheld 3D printer. This technology may become a game-changer in the way severe burn victims are treated.
The handheld skin 3D printer, the work of scientists at the University of Toronto Engineering and Sunnybrook Hospital, was first shown back in 2018. Since then it has undergone a major redesign that improves upon the initial model’s functionality.
More than a year ago, the world was shocked by Chinese biophysicist He Jiankui’s attempt to use CRISPR technology to modify human embryos and make them resistant to HIV, which led to the birth of twins Lulu and Nana.
Now, crucial details have been revealed in a recent release of excerpts from the study, which have triggered a series of concerns about how Lulu and Nana’s genome was modified.
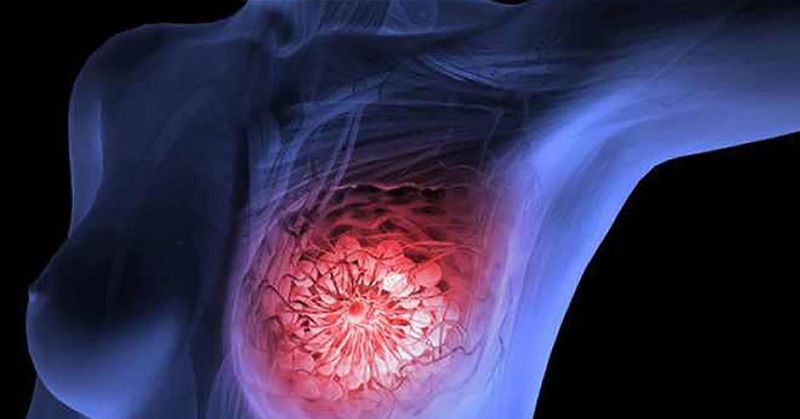
HER2-positive breast cancer is a type of aggressive cancer marked by uncontrolled production of breast cells. About 20% of women and men diagnosed with breast cancer have HER2-positive cancer, specifically.
Currently, oncologists treat HER2-positive breast cancer patients with surgery, radiation, chemotherapy, or targeted treatments like Herceptin (trastuzumab), Kadcyla (Ado-trastuzumab-emtansine), Perjeta (Pertuzumab), and Tykerb (Lapatinib).
These targeted treatments work by interfering with the protein that signals breast cell production, and they’re often used in conjunction with chemotherapy, which undoubtedly, can be a very arduous treatment process.
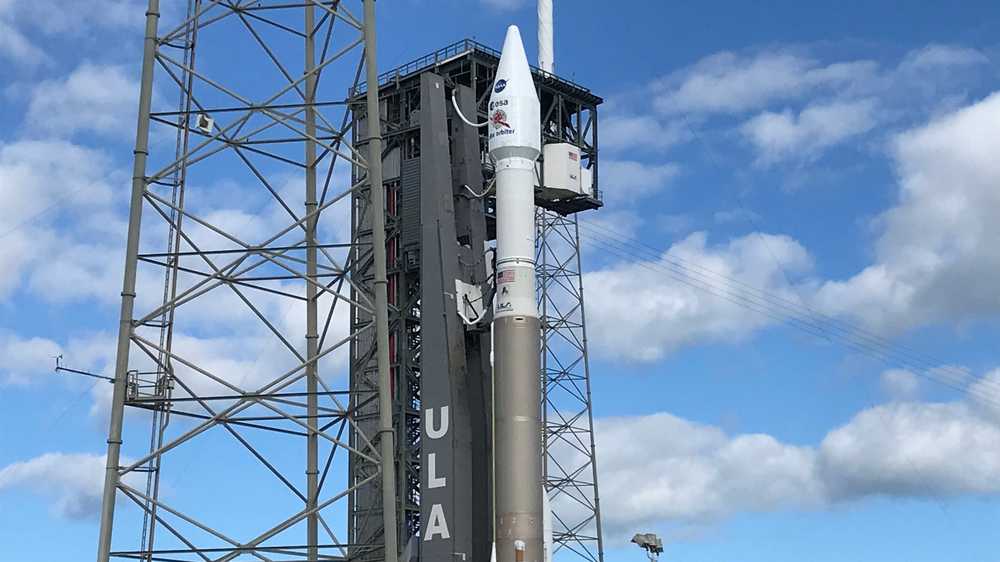
A United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket launches from Cape Canaveral with the Solar Orbiter probe on Sunday, Feb. 9, 2020. Florida Today.
Connect tweet linkedin comment email more
Update: LIFTOFF of Atlas V at 11:03 p.m. with Solar Orbiter!
Follow live as Solar Orbiter, a probe slated to study the sun, takes flight on a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral. Liftoff is planned for 11:03 p.m. Eastern time. Teams have two hours to launch.
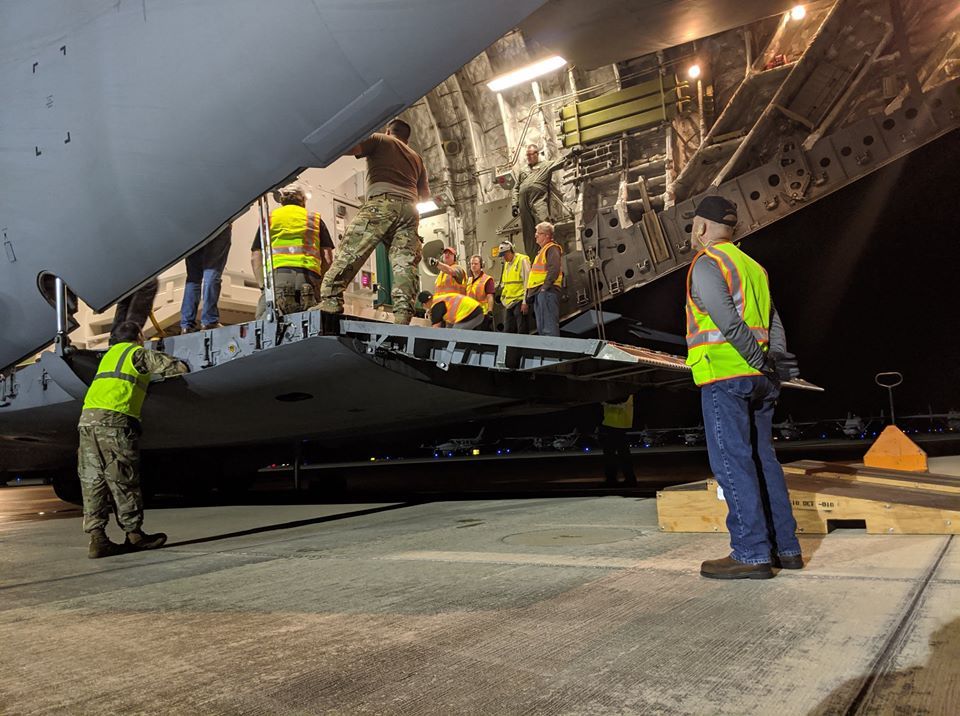
WASHINGTON — The third satellite of the GPS 3 constellation arrived Feb. 5 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station, Florida, where it will undergo final testing and checkout before its scheduled launch in April aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket.
The GPS 3 satellite was flown from Lockheed Martin’s assembly line in Colorado aboard a U.S. Air Force C-17 cargo aircraft.
In a news release on Friday, the U.S. Space Force Space and Missile Systems Center said the next steps are to prepare the GPS 3 SV-3 for propellant loading and fairing encapsulation before it’s horizontally integrated with a Falcon 9 launch vehicle.
TrackML was a Kaggle competition in 2018 with $25 000 in cash prizes where the challenge was to reconstruct particle tracks from 3D points left in silicon detectors. CERN (the European Organization for Nuclear Research) provided data over particles collision events. The rate at which they occur over there is in the neighborhood of hundreds of millions of collisions per second, or tens of petabytes per year. There is a clear need to be as efficient as possible when sifting through such an amount of data, and this is where machine learning methods may be of help.
Particles, in this case protons, are boosted to high energies inside the Large Hadron Collider (LHC) — each beam can reach 6.5 TeV giving a total of 13 TeV when colliding. Electromagnetic fields are used to accelerate the electrically charged protons in a 27 kilometers long loop. When the proton beams collide they produce a diverse set of subatomic byproducts which quickly decay, holding valuable information for some of the most fundamental questions in physics.
Detectors are made of layers upon layers of subdetectors, each designed to look for specific particles or properties. There are calorimeters that measure energy, particle-identification detectors to pin down what kind of particle it is and tracking devices to calculate the path of a particle. [1] We are of course interested in the tracking, tiny electrical signals are recorded as particles move through those types of detectors. What I will discuss is methods to reconstruct these recorded patterns of tracks, specifically algorithms involving machine learning.