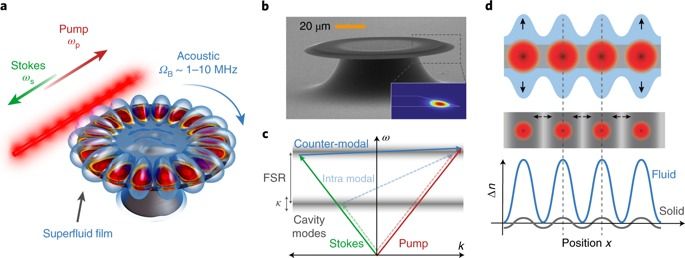
Brillouin scattering has applications ranging from signal processing1,2, sensing3 and microscopy4 to quantum information5 and fundamental science6,7. Most of these applications rely on the electrostrictive interaction between light and phonons3,7,8. Here we show that in liquids optically induced surface deformations can provide an alternative and far stronger interaction. This allows the demonstration of ultralow-threshold Brillouin lasing and strong phonon-mediated optical coupling. This form of strong coupling is a key capability for Brillouin-reconfigurable optical switches and circuits9,10, for photonic quantum interfaces11 and to generate synthetic electromagnetic fields12,13. While applicable to liquids quite generally, our demonstration uses superfluid helium. Configured as a Brillouin gyroscope14 this provides the prospect of measuring superfluid circulation with unprecedented precision, and exploring the rich physics of quantum fluid dynamics, from quantized vorticity to quantum turbulence15,16.
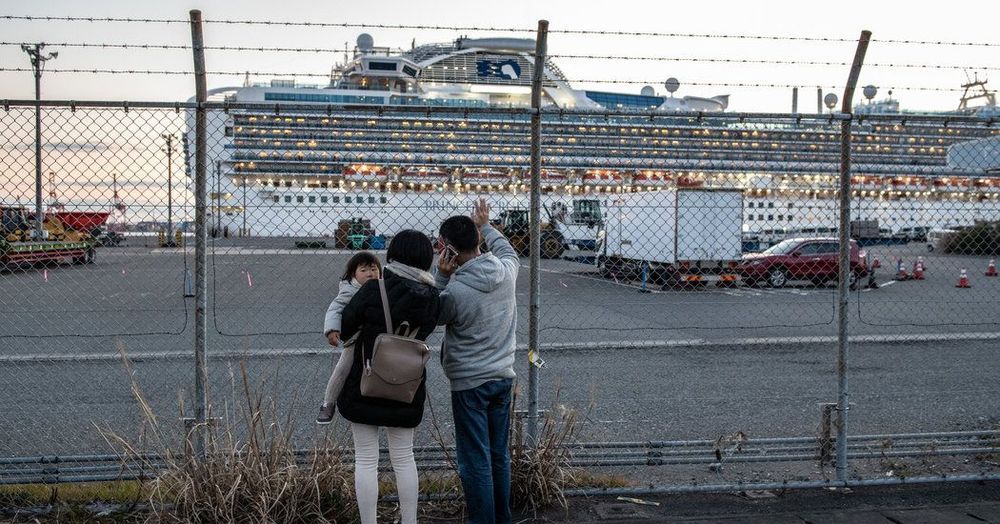
Critics say the government is making a coronavirus episode worse by not being more forthcoming.
An 18-year-old who was born without the left half of her brain scores well on IQ tests and plans to attend university, revealing our brain’s incredible adaptability.
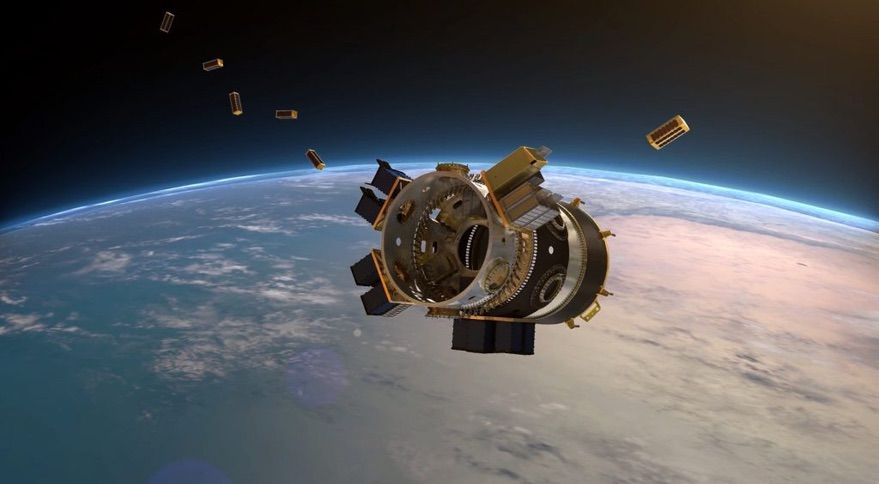
WASHINGTON — Spaceflight Industries announced Feb. 11 it will sell its smallsat rideshare launch business to a pair of Japanese companies, allowing it to focus on its BlackSky geospatial business.
Spaceflight Industries said that Mitsui & Co., Ltd. and Yamasa Co., Ltd. will acquire its rideshare business, known as Spaceflight, Inc., for an undisclosed sum. Mitsui & Co. and Yamasa will own Spaceflight as a 50/50 joint venture. The companies said that they expect the deal to close in the second quarter of this year, after a review by the Committee on Foreign Investment in the United States (CFIUS) to examine any national security implications of the sale.
Spaceflight Industries said it will use the proceeds from the deal to accelerate the growth of BlackSky, its geospatial intelligence business that is developing a constellation of high-resolution imaging satellites. BlackSky has four satellites in orbit currently with another eight scheduled for launch this year.
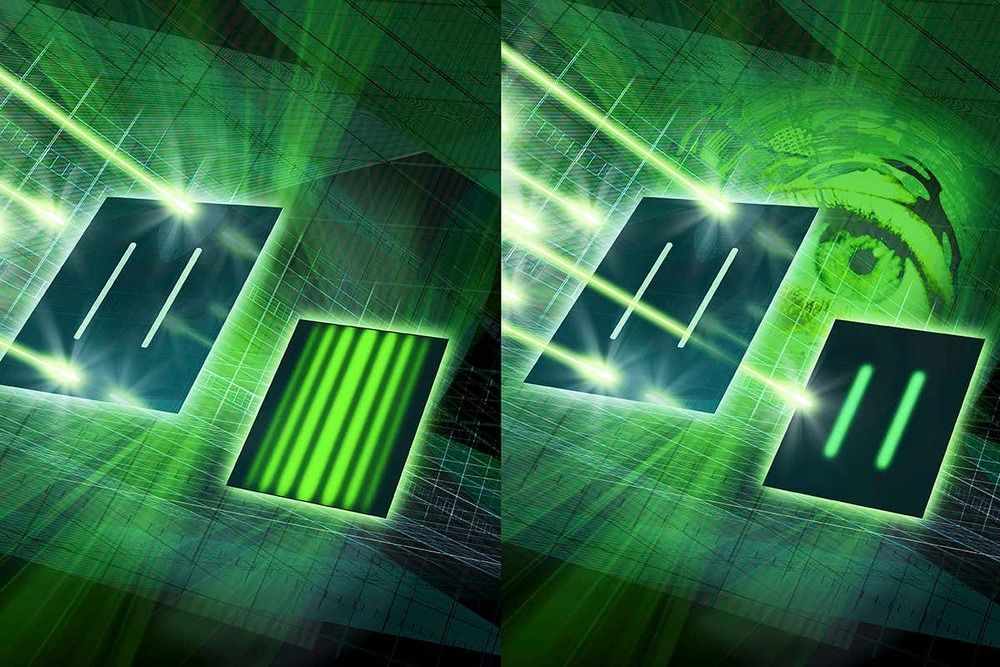
A basic rule of quantum physics is that knowing too much about an experiment will break quantum interference, but now physicists have discovered a way to bend that rule.
Researchers at the Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) in the US have uncovered the ‘Achilles’ heel’ of most viruses which plague mankind, and could soon develop a universal vaccine.
Vaccine research, development and testing takes a long time, as the ongoing coronavirus outbreak has shown, but that is because researchers devote their time, attention and resources to targeting specific viruses one-by-one. But now scientists at MGH have located what may prove to be a game-changing breakthrough for humanity which could strengthen our bodies and make them impervious to most viruses.
Apparently scientists at Massachusetts General Hospital are making some progress on identifying what they are calling a “universal vaccine” or the “Achilles heel” for viruses…
BOSTON — As the coronavirus outbreak shows, viruses are a constant threat to humanity. Vaccines are regularly developed and deployed against specific viruses, but that process takes a lot of time, doesn’t help everyone who needs protection, and still leaves people exposed to new outbreaks and new viruses.
Now, researchers at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) have uncovered a novel potential antiviral drug target that could lead to treatments protecting against a host of infectious diseases — creating a pan, or universal, treatment. Their work suggests that the protein Argonaute 4 (AGO4) is an “Achilles heel” for viruses.
AGO4 is one of a family of AGO proteins. Until now, there has been little evidence of whether they have individual roles. The researchers, led by Kate L. Jeffrey, PhD, and her collaborators found that AGO4 plays a key role protecting cells against viral infections.
We all know taking away screens and reading to our children during their formative years is the best thing for their brains. Now, there is new incredible science to back it up. We asked Jessica Ewing, CEO of subscription book club Literati and graduate of Stanford University in Cognitive Science, every question we could think of about kids, brains, and books.
The latest science, as explored by Literati CEO Jessica Ewing.
In a universe that unthinkingly follows the rules, human agency is an anomaly. Can physics ever make sense of our power to change the physical world at will?