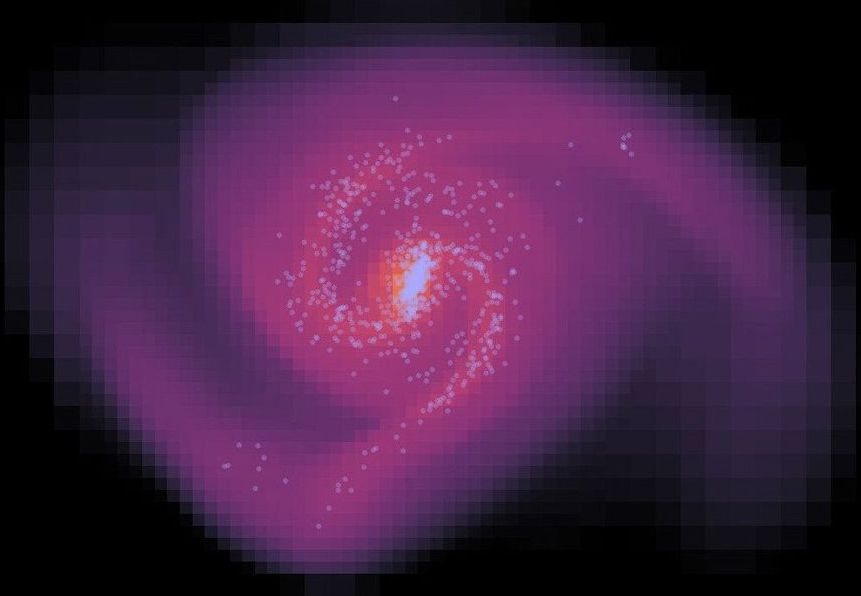
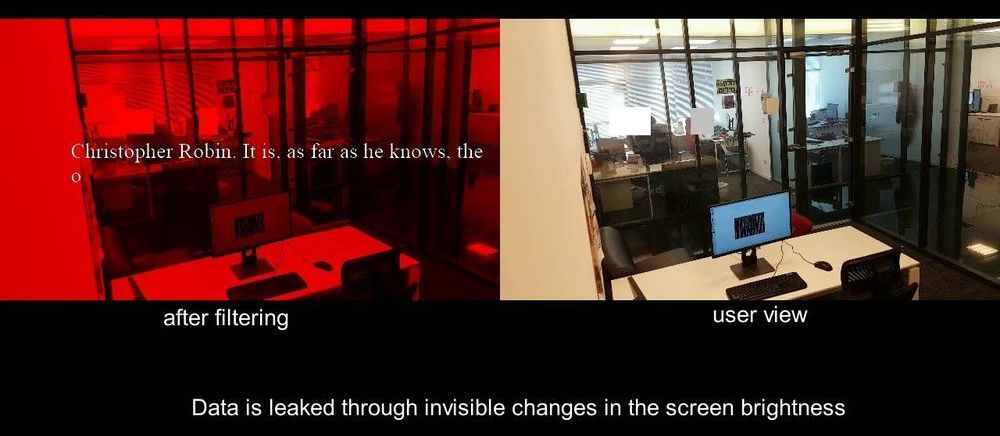
For the first time, researchers from the Universities of Bonn and Strasbourg have simulated the formation of galaxies in a universe without dark matter. To replicate this process on the computer, they have instead modified Newton’s laws of gravity. The galaxies that were created in the computer calculations are similar to those we actually see today. According to the scientists, their assumptions could solve many mysteries of modern cosmology. The results are published in the Astrophysical Journal.
Cosmologists today assume that matter was not distributed entirely evenly after the Big Bang. The denser places attracted more matter from their surroundings due to their stronger gravitational forces. Over the course of several billion years, these accumulations of gas eventually formed the galaxies we see today.
An important ingredient of this theory is the so-called dark matter. On the one hand, it is said to be responsible for the initial uneven distribution that led to the agglomeration of the gas clouds. It also explains some puzzling observations. For instance, stars in rotating galaxies often move so fast that they should actually be ejected. It appears that there is an additional source of gravity in the galaxies that prevents this—a kind of “star putty” that cannot be seen with telescopes: dark matter.