Large language models (LLMs) are at the forefront of artificial intelligence (AI) and have been widely used for conversational interactions. However, assessing the personality of a given LLM remains a significant challenge.



Born and brought up in East Germany, Professor Franka Kalman is a much-respected figure in the field of separation sciences. Following undergraduate and postgraduate studies at the Technical University Budapest, Hungary, where she learned about the then emerging technique of high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), she applied that knowledge to complete her PhD looking at the analysis of novel opioid peptides at Martin Luther University Halle, Germany.
Her postdoctoral studies in the lab of the late, great Professor Csaba Horvath at Yale University, a placement that by all accounts provided both a grounding and springboard for her future career, were to be transformative and the techniques she developed there have gone on to be game-changing in the world of pharmaceutical development, analysis and quality control. Work for which she was recognized in 2012, when she was presented with the prestigious CEPharm Award from the Californian Separation Science Society (CASSS) for significant contributions to the practical application of capillary electrophoresis (CE) in the biotechnology and pharmaceutical industries.
After her time as a postdoc, she spent 13 very successful years in the pharmaceutical industry, working at the interface between science and industrial applications.
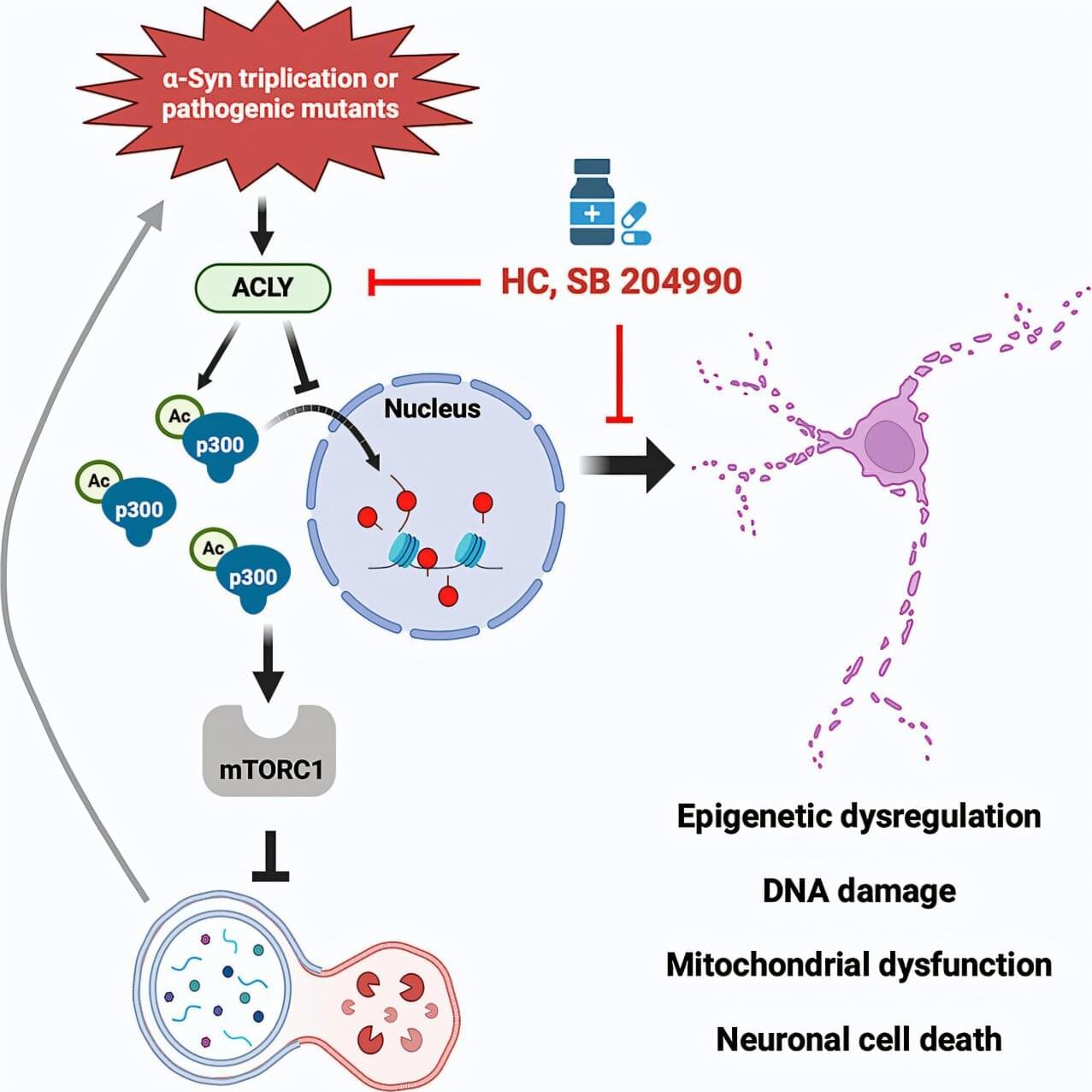
Researchers have identified a key enzyme driving forms of Parkinson’s disease, and have shown how blocking it restores normal function in animal and cell models, offering a promising new drug target for the condition.
The work is published in the journal Neuron.
In Parkinson’s, a protein known as alpha-synuclein builds up in clumps called Lewy bodies in nerve cells in the brain. These clumps of protein stop these cells from functioning normally, eventually leading the cells to die.
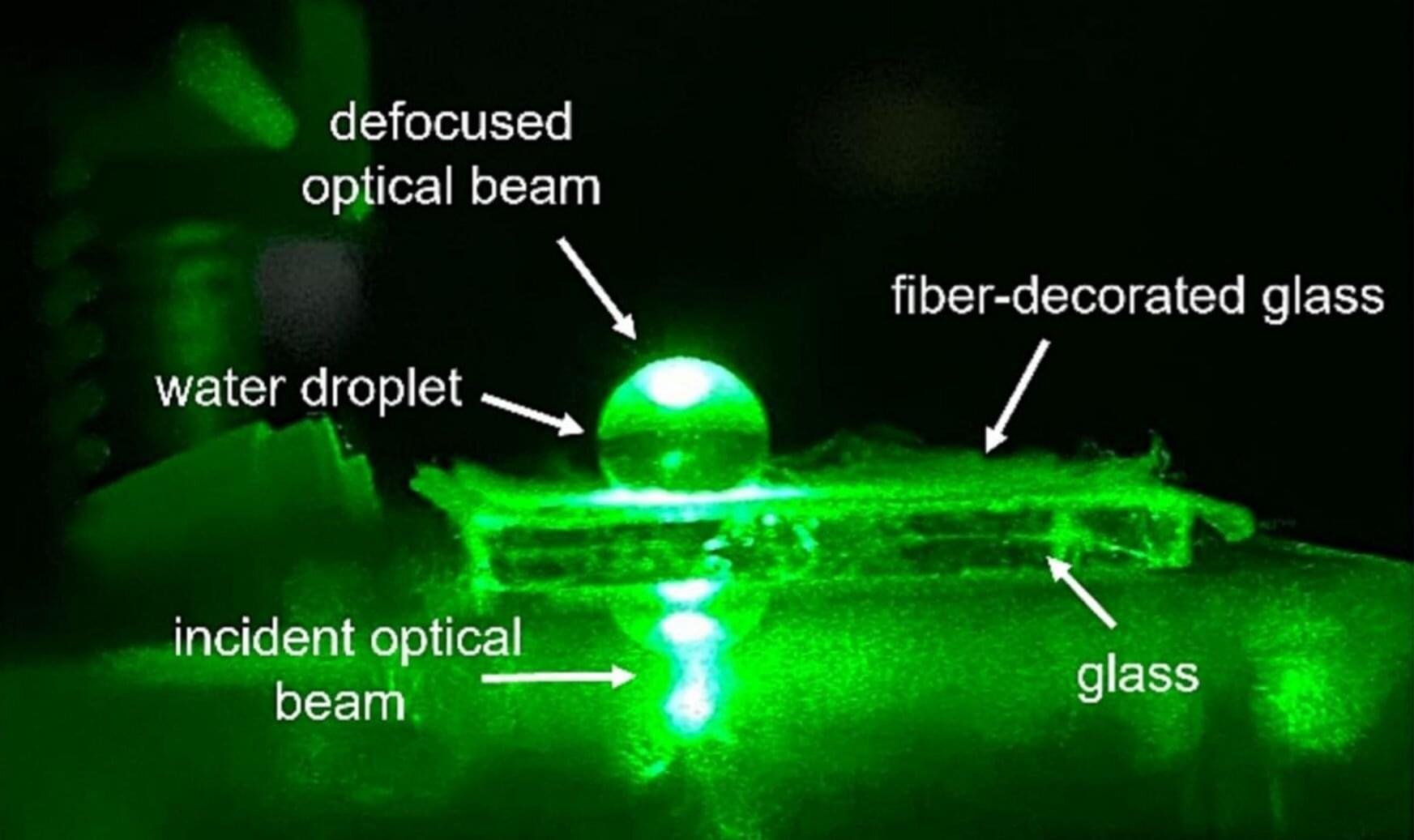
Filipino scientists have discovered a simple, affordable way to make dynamically adjustable water-based lenses that have a wide variety of potential future applications—from classrooms and research labs to cameras and even wearable gadgets. Their research is published in the journal Results in Optics.
By coating an ordinary glass slide with specially prepared polyvinyl chloride (PVC) plastic, the researchers were able to create a hydrophobic surface that could hold a water droplet in a dome shape similar to a magnifying glass. And by adding or removing water from the droplet, they were able to change and control the magnifying power of this liquid lens with minimal loss or distortion.
In a process called “electrospinning,” the researchers melted the PVC in an electric field, which stretches out and deposits the plastic onto the glass slide as very fine microfibers. This makes the surface of the slide more water repellent, and the result is that water droplets stay in a spherical dome shape instead of flattening out.

In a world-first, scientists have figured out how to reprogram cells to fight — and potentially reverse — brain diseases like Alzheimer’s.
Researchers at the University of California, Irvine created lab-grown immune cells that can track down toxic brain buildup and clear it away, restoring memory and brain function in mice.
They did this by turning stem cells — which can become any cell in the body — into brain immune cells called microglia.
A new brain-inspired AI model called TopoLM learns language by organizing neurons into clusters, just like the human brain. Developed by researchers at EPFL, this topographic language model shows clear patterns for verbs, nouns, and syntax using a simple spatial rule that mimics real cortical maps. TopoLM not only matches real brain scans but also opens new possibilities in AI interpretability, neuromorphic hardware, and language processing.
Join our free AI content course here 👉 https://www.skool.com/ai-content-acce… the best AI news without the noise 👉 https://airevolutionx.beehiiv.com/ 🔍 What’s Inside: • A brain-inspired AI model called TopoLM that learns language by building its own cortical map • Neurons are arranged on a 2D grid where nearby units behave alike, mimicking how the human brain clusters meaning • A simple spatial smoothness rule lets TopoLM self-organize concepts like verbs and nouns into distinct brain-like regions 🎥 What You’ll See: • How TopoLM mirrors patterns seen in fMRI brain scans during language tasks • A comparison with regular transformers, showing how TopoLM brings structure and interpretability to AI • Real test results proving that TopoLM reacts to syntax, meaning, and sentence structure just like a biological brain 📊 Why It Matters: This new system bridges neuroscience and machine learning, offering a powerful step toward *AI that thinks like us. It unlocks better interpretability, opens paths for **neuromorphic hardware*, and reveals how one simple principle might explain how the brain learns across all domains. DISCLAIMER: This video covers topographic neural modeling, biologically-aligned AI systems, and the future of brain-inspired computing—highlighting how spatial structure could reshape how machines learn language and meaning. #AI #neuroscience #brainAI
Get the best AI news without the noise 👉 https://airevolutionx.beehiiv.com/
🔍 What’s Inside:
• A brain-inspired AI model called TopoLM that learns language by building its own cortical map.
• Neurons are arranged on a 2D grid where nearby units behave alike, mimicking how the human brain clusters meaning.
• A simple spatial smoothness rule lets TopoLM self-organize concepts like verbs and nouns into distinct brain-like regions.
🎥 What You’ll See:
• How TopoLM mirrors patterns seen in fMRI brain scans during language tasks.
• A comparison with regular transformers, showing how TopoLM brings structure and interpretability to AI
• Real test results proving that TopoLM reacts to syntax, meaning, and sentence structure just like a biological brain.
📊 Why It Matters:


Lithium-ion batteries have been a staple in device manufacturing for years, but the liquid electrolytes they rely on to function are quite unstable, leading to fire hazards and safety concerns. Now, researchers at Penn State are pursuing a reliable alternative energy storage solution for use in laptops, phones and electric vehicles: solid-state electrolytes (SSEs).
According to Hongtao Sun, assistant professor of industrial and manufacturing engineering, solid-state batteries—which use SSEs instead of liquid electrolytes—are a leading alternative to traditional lithium-ion batteries. He explained that although there are key differences, the batteries operate similarly at a fundamental level.
“Rechargeable batteries contain two internal electrodes: an anode on one side and a cathode on the other,” Sun said. “Electrolytes serve as a bridge between these two electrodes, providing fast transport for conductivity. Lithium-ion batteries use liquid electrolytes, while solid-state batteries use SSEs.”
