Move over, Hollywood—science fiction is getting ready to leap off the big screen and enter the real world. While recent science fiction movies have demonstrated the power of artificially intelligent computer programs, such as the fictional character J.A.R.V.I.S. in the Avenger film series, to make independent decisions to carry out a set of actions, these imagined movie scenarios could now be closer to becoming a reality.
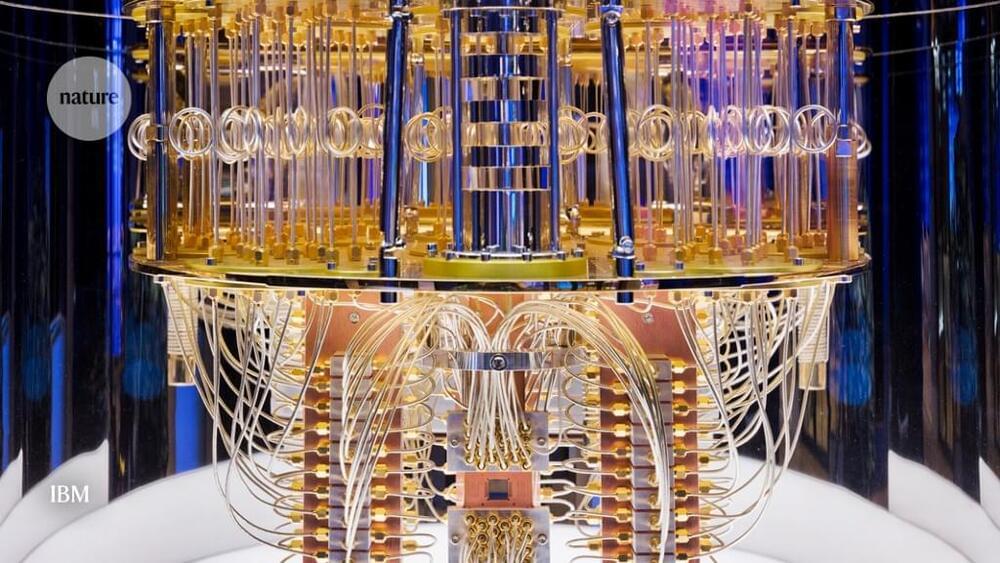
In a recent study published in Nature Communications, a journal of Nature, researchers at the University of Missouri and University of Chicago have developed an artificial material, called a metamaterial, which can respond to its environment, independently make a decision, and perform an action not directed by a human being. For example, a drone making a delivery might evaluate its environment including wind direction, speed or wildlife, and automatically change course in order to complete the delivery safely.
Guoliang Huang, Huber and Helen Croft Chair in Engineering, and co-author on the study, said the mechanical design of their new artificial material incorporates three main functions also displayed by materials found in nature—sensing; information processing; and actuation, or movement.