However, the $799 product can still run PC games, thanks to the integrated graphics on the CPU.


Face is pretty impressive, and not CGI as far as i know. The BIG challenge in robotics remains building robotic hands that can match human level hands.
Ameca, a new humanoid robot from a company in the UK, has taken the internet by storm with its ultra-realistic movements and expressions.

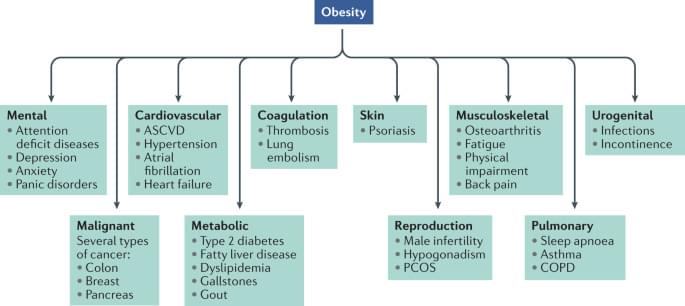
The development of therapies that are capable of safely achieving sizeable and sustained body weight loss has proved tremendously challenging. Here, Müller et al. provide an overview of the history of anti-obesity drug development, focusing on lessons learned, ongoing challenges and recent advances in the field.
In this episode, I talk to world-renowned biologist David Sinclair about aging and longevity. David rejects the notion that the deterioration of health is a natural part of growing old and asserts that aging is a disease itself that we need to reverse. But how will a reset of our biological clocks affect our interactions, responses to adversity, morality, and how we live our lives? We discuss the ethical implications of limitless lifespans and also touch on the topics of death, evolution, genetics, medicine, and data tracking.
Bio.
Dr. David Sinclair is a professor in the department of genetics and co-director of the Paul F. Glenn Center for Biology of Aging Research at Harvard Medical School and co-founder of the scientific journal Aging. He is best known for his work on understanding why we age and how to slow its effects. In addition to being a co-founder of several biotechnology companies, he’s the author of the book Lifespan: Why We Age – and Why We Don’t Have To. Dr. Sinclair was listed by TIME magazine as one of the “100 most influential people in the world”.
Website: sinclair.hms.harvard.edu.
Twitter: @davidasinclair.
Topics.
00:02:26 David’s “sticky beak” personality.
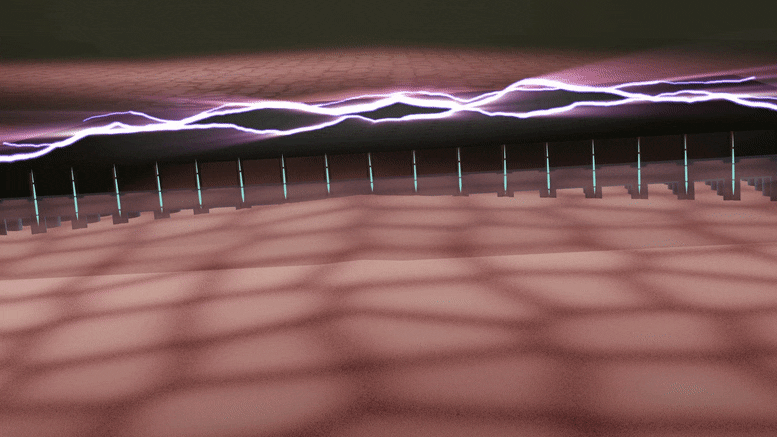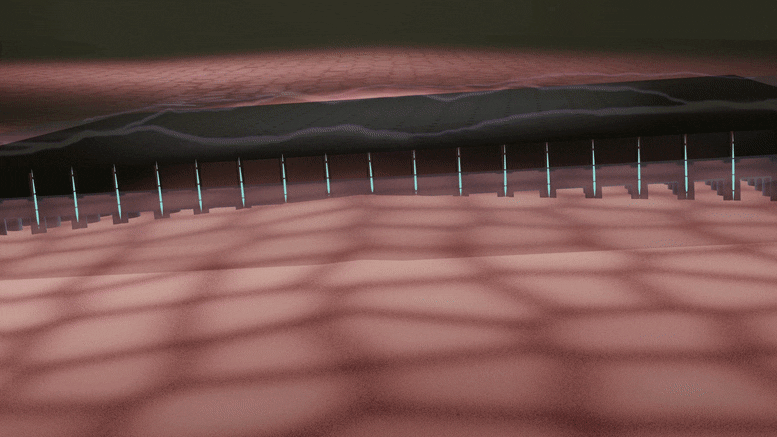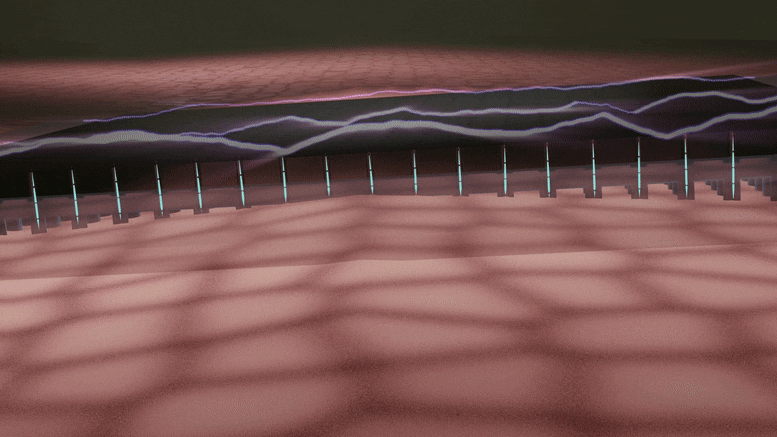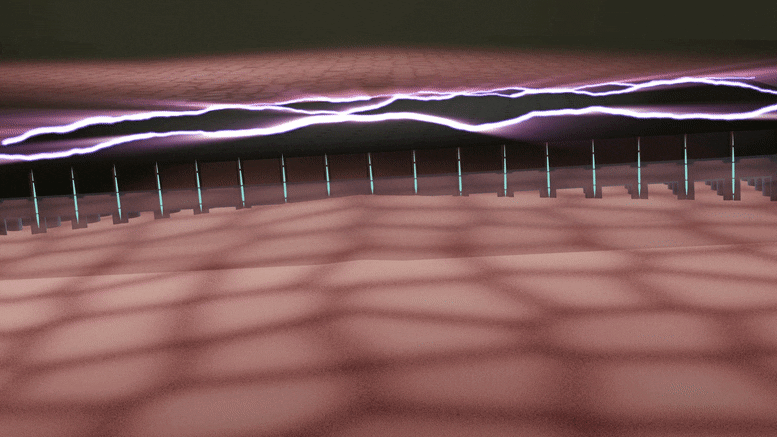
A silicon device that can change skin tissue into blood vessels and nerve cells has advanced from prototype to standardized fabrication, meaning it can now be made in a consistent, reproducible way. As reported in Nature Protocols, this work, developed by researchers at the Indiana University School of Medicine, takes the device one step closer to potential use as a treatment for people with a variety of health concerns.
The technology, called tissue nanotransfection, is a non-invasive nanochip device that can reprogram tissue function by applying a harmless electric spark to deliver specific genes in a fraction of a second. In laboratory studies, the device successfully converted skin tissue into blood vessels to repair a badly injured leg. The technology is currently being used to reprogram tissue for different kinds of therapies, such as repairing brain damage caused by stroke or preventing and reversing nerve damage caused by diabetes.
SPARC is aiming to be the first experimental device to achieve an energy-positive fusion reaction. New research suggests that this goal may soon be within reach.
» Subscribe to Seeker! http://bit.ly/subscribeseeker.
» Watch more Elements! http://bit.ly/ElementsPlaylist.
» Visit our shop at http://shop.seeker.com.
With construction slated to begin in spring 2021, the team predicts it could be built within 3 to 4 years from that. Their goal is to achieve a Q factor of at least 2, basically meaning SPARC will pump out twice the energy needed to power it.
Actually, by the calculations in their papers, SPARC could possibly achieve a Q ratio of 10! But the researchers are cautious about overpromising, and are just focused on achieving the lower figure.
It’s still impressive, considering any net gain would be a first for human created controlled fusion.
Assuming it gets built along that predicted 3–4 year timeline and actually gets flipped on, there’s still several steps between SPARC and limitless clean energy.
#sparc #climatechange #fusion #technology #physics.
We’ve Long Waited for Fusion. This Reactor May Finally Deliver It—Fast.

Because leviathan black holes would never fit in a lab, Jeff Steinhauer and his research team created a mini one right here on Earth.
When something rips physics apart, you cross over into the quantum realm, a place inhabited by black holes, wormholes and other things that have been the stars of multiple sci-fi movies. What lives in the quantum realm either hasn’t been proven to exist (yet) or behaves strangely if it does exist.
Black holes often venture into that realm. With these collapsed stars — at least most of them are — being impossible to fly a spacecraft into (unless you never want to see it again), one physicist decided that the best way to get up close to them was under a literal microscope. Jeff Steinhauer wanted to know whether black holes radiate particles like the late Stephen Hawking theorized they would. Because one of these leviathans would never fit in a lab, he and his research team created one right here on Earth.
“We have to understand how we see the Hawking radiation sound waves falling in and coming out,” Steinhauer, who co-authored a study recently published in Nature Physics, told SYFY WIRE. “They should be very slight. Seeing this radiation from a real black hole is too weak and would be totally overpowered by other sources of radiation, which is why we want to see it in an analog system.”

😀
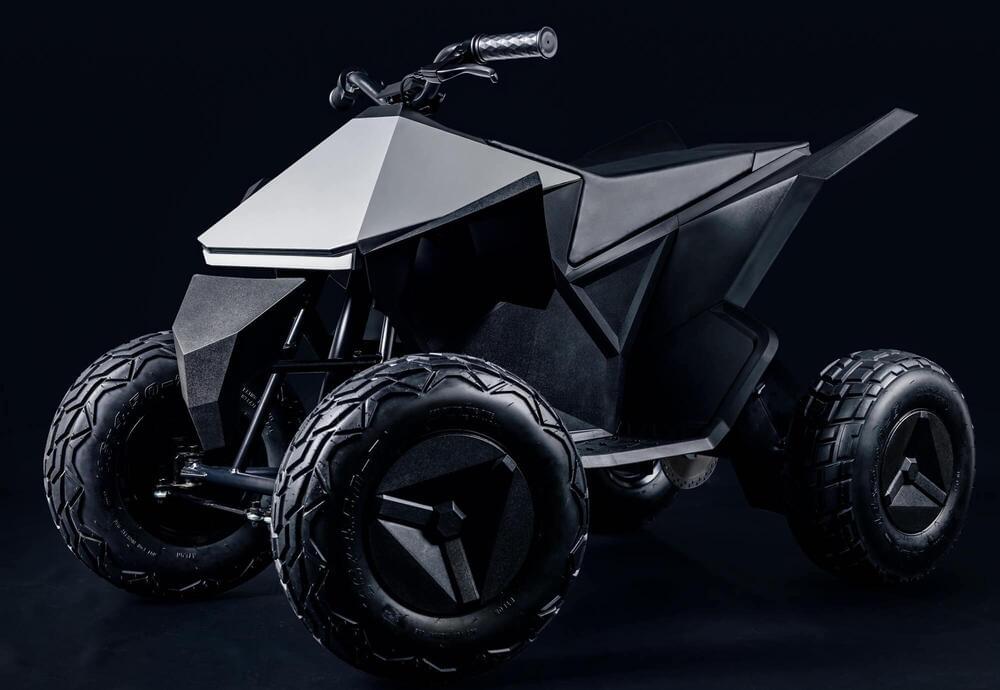
Tesla hasn’t yet shipped the Cybertruck, or the full-size Cyberquad that made a splashy debut at the introduction of its Blade Runner-esque pickup truck, but you can get a mini Cyberquad designed for the kiddos starting in 2–4 weeks if you order one right now from its website.
The Tesla “Cyberquad for Kids” is available to purchase on Tesla’s site for $1,900 — a steep price relative to your average Power Wheels, but the lowest-priced vehicle in Tesla’s existing lineup by far. And the Cyberquad’s materials are a cut above your average battery electric kid car, with a “full steel frame,” along with cushioned seating and fully adjustable suspension.
It may be the cheapest Tesla you can buy, but it’s also the most limited when it comes to range: You’ll get up to around 15 miles on a full charge, which takes five hours, according to the company. It’s also not going to break any land speed records, with a speedometer that tops out at 10 mph (which you can limit to a max of 5 mph for safety, if desired). That’s still plenty fast for a kid’s ride-on vehicle, which is probably why Tesla labels this one as designed for kids at least 8 and up, with a max weight of 150 lbs.

Bongard said they found that the xenobots, which were initially sphere-shaped and made from around 3,000 cells, could replicate. But it happened rarely and only in specific circumstances. The xenobots used “kinetic replication” — a process that is known to occur at the molecular level but has never been observed before at the scale of whole cells or organisms, Bongard said.
The US scientists who created the first living robots say the life forms, known as xenobots, can now reproduce — and in a way not seen in plants and animals.
Formed from the stem cells of the African clawed frog (Xenopus laevis) from which it takes its name, xenobots are less than a millimeter (0.04 inches) wide. The tiny blobs were first unveiled in 2020 after experiments showed that they could move, work together in groups and self-heal.
Now the scientists that developed them at the University of Vermont, Tufts University and Harvard University’s Wyss Institute for Biologically Inspired Engineering said they have discovered an entirely new form of biological reproduction different from any animal or plant known to science.