Serious Science — http://serious-science.org.
Neuroscientist Karl Friston on functional specialization of different brain areas, brain hierarchy, and the connectome.
Serious Science — http://serious-science.org.
Neuroscientist Karl Friston on functional specialization of different brain areas, brain hierarchy, and the connectome.

The two billionaires are locked in a race to send humans to space, with Musk’s SpaceX far in front of Bezos’ Blue Origin venture. But the two differ on what to do when humanity arrives in space: Musk wants to establish a self-sustaining city on Mars, while Bezos would rather see humans orbiting Earth in giant space stations.
Musk’s vision receives a lot of publicity, but space consultant Rand Simberg tells Inverse that Bezos’ goal is the “more expansive.”
“Elon is what [science fiction writer Isaac] Asimov would have called a planetary chauvinist,” he says. “He thinks people need to be on planets. He wants to be a multi-planet species. That’s nice, I guess. But Bezos actually has a more expansive vision.”


Nov 30 (Reuters) — Amazon.com Inc’s (AMZN.O) cloud computing unit on Tuesday introduced two new custom computing chips aimed at helping its customers beat the cost of using chips from Intel Corp (INTC.O) and Nvidia Corp (NVDA.O).
With $45.37 billion in sales in 2020, Amazon Web Services (AWS) is the world’s biggest cloud computing provider and one of the biggest buyers of data center chips, whose computing power AWS rents out to its customers. Ever since buying a startup called Annapurna Labs in 2015, AWS has worked to develop its own custom chips.
On Tuesday, the company released the third generation of its Graviton chip that is designed to compete with central processors from Intel and Advanced Micro Devices (AMD.O). The Graviton3 is 25% faster than its predecessor, and Dave Brown, vice president of Elastic Compute Cloud at Amazon, told Reuters that the company expects it to provide a better performance per dollar than Intel’s chips.
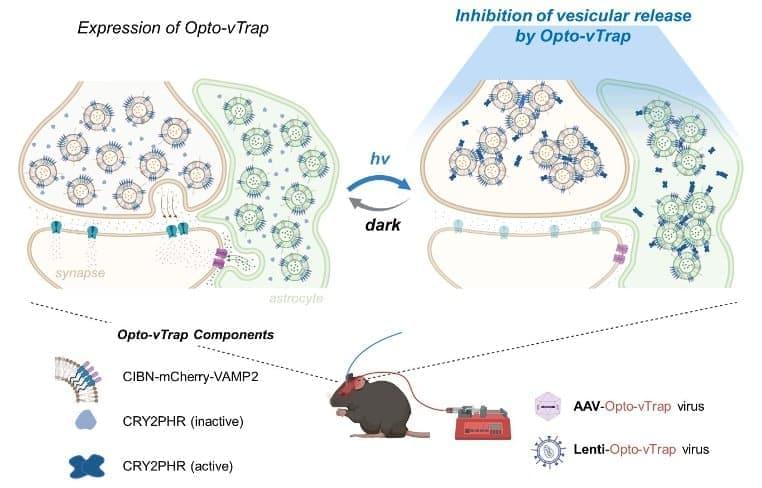
Summary: A newly developed system dubbed Opto-vTrap can temporarily trap vesicles from being released from brain cells.
Source: Institute for Basic Science.
Controlling signal transmission and reception within the brain circuits is necessary for neuroscientists to achieve a better understanding of the brain’s functions. Communication among neuron and glial cells is mediated by various neurotransmitters being released from the vesicles through exocytosis. Thus, regulating vesicular exocytosis can be a possible strategy to control and understand brain circuits.

Our hunter-gatherer ancestors are huddled around a campfire when they suddenly hear the nearby bushes rustling. They have two options: investigate if the movement was caused by small prey such as a rabbit, or flee, assuming there was a predator such as a saber-tooth tiger. The former could lead to a nutritious meal, while the latter could ensure survival. What call do you think our ancestors would have made?
Evolution ensured the survival of those who fled the scene on the margin of safety rather than those who made the best decision by analyzing all possible scenarios. For thousands of years, humans have made snap decisions in fight-or-flight situations. In many ways, the human race learned to survive by jumping to conclusions.
“In modern context, such survival heuristics become myriad cognitive biases,” said Eric Colson, Chief Algorithms Officer at Stitch Fix. Let’s look at the most common biases or shortcut decisions that influence organizational leaders and how decision intelligence can come to their rescue.

It feels a bit like a headline ripped from the plotline of the 2013 flick “Gravity” — NASA astronauts suddenly find themselves having to worry more about the threat of space debris whipping around Earth at over 17,000 miles per hour.
Just two weeks after the current crew of the International Space Station had to take emergency shelter in the Russian Soyuz and SpaceX Crew Dragon capsules that are docked to the ISS, NASA has now postponed a planned spacewalk because of the threat.
One source of the increased threat is Russia’s recent anti-satellite missile test that created hundreds, if not thousands, of new pieces of debris in low-earth orbit. On November 15 it was reported that Russia blasted one of its own defunct satellites to smithereens, a move that drew global condemnation.

Most times when we think of deepfakes, we think of the myriad negative applications. From pornography to blackmail to politics, deepfakes are a product of machine learning. They create a lie that is so realistic that it is hard to believe it is not the real thing. In a society plagued by fake news, deepfakes have the potential to do a substantial amount of harm.
But a recent team of researchers found another use for deepfakes — to deepfake the mind. And using machine learning to simulate artificial neural data in this way may make a world of difference for those with disabilities.
For people with full body paralysis, the body can seemingly become a prison. Communicating and the simplest of tasks may appear to be an insurmountable challenge. But even if the body is frozen, the mind may be very active. Brain-computer interfaces (BCIs) offer a way for these patients to interact with the world.
BCIs do not rely on muscle or eye movements. Instead, the user is trained to manipulate an object using the power of thought alone. BCIs can allow a fully paralyzed person to operate a wheelchair by just thinking, to move a cursor on a computer screen, or even play pinball by moving the paddles with their mind. BCIs can be freeing for people with this type of paralysis. It can also be used to treat depression or to rehabilitate the brain.
Full Story:

And it uses components already commercially available.
Engineers at Stanford University have demonstrated a new, simpler design for a quantum computer that could help practical versions of the machine finally become a reality, a report from New Atlas reveals.
The new design sees a single atom entangle with a series of photons, allowing it to process and store more information, as well as run at room temperature — unlike the prototype machines being developed by the likes of Google and IBM.
Quantum computers rely on qubits rather than the ones and zeroes, or bits, of classical computing. Qubits can exist in three different states — a one, a zero, or a superposition of one and zero simultaneously — meaning they can, in theory, carry out computations it would take classical computers thousands of years to achieve.
Though quantum computers have the capacity to perform such complex tasks, they have so far been hindered by their sensitivity to heat and vibrations — a problem that means they have to be kept at temperatures close to absolute zero.
Full Story: