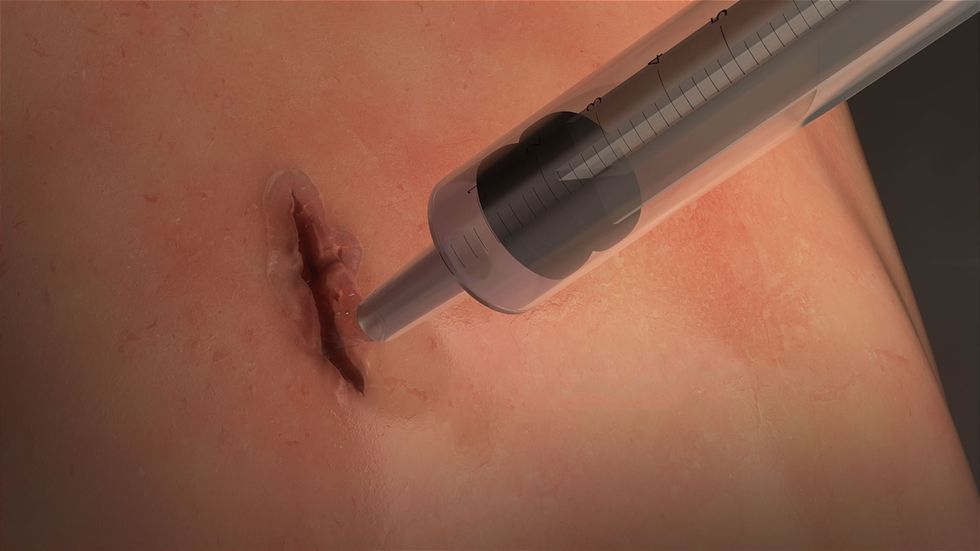
Another bit of science fiction is coming to life as scientists develop a highly elastic and adhesive surgical glue similar to the one Ryan Gosling used to seal his wound in Blade Runner 2049.
Surgeons use sutures, staples, and wires (sometimes in combination with adhesive substances) to facilitate healing of external and internal wounds. These methods, however, are not optimal, especially for reconnecting contracting tissues like those of lungs, arteries and the heart.
Sutures are also not ideal for preventing the leaking of liquids from incisions. In addition, piercing tissues to place sutures can further damage the surrounding wound area and can increase the risk for infection.