
Get the latest international news and world events from around the world.

Prometheism, Transhumanism & The Coming Singularity
We take a deep and necessary dive into the topics of robotics, transhumanism, singularity, and other apocalyptic tech – all to prepare for the endgame moves of the elite and their Breakaway Civilization. To win this game of digital thrones, we must tap into the myth and Gnosis of an ancient trickster egregore named Prometheus. We must steal fire from the gods before they burn civilization down very soon.
Astral Guest – Jason Reza Jorjani, author of Prometheism.
This is a partial show for nonmembers. For the second half of the interview, please become a member: http://thegodabovegod.com/members/subscription-levels/ or patron at Patreon: https://www.patreon.com/aeonbyte.
More information on Jason: https://jasonrezajorjani.com/
Get the book: https://amzn.to/32AWkfR
Download these and all other shows: http://thegodabovegod.com/

Elon Musk’s latest adventure
He hopes it will be a stepping stone to the Moon and Mars.
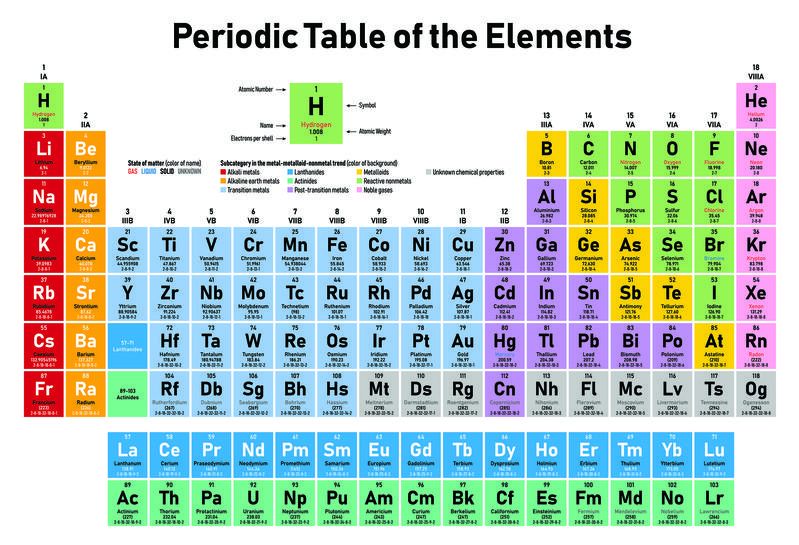
Periodic Table Of The Elements Turns 150
Maybe you’ve felt a certain chemistry with 2019 but don’t know why? Maybe it’s because this year marks the 150th anniversary of the Periodic Table of the Elements. It’s considered the founding document of modern chemistry, one you may have studied in school.
UW-Madison professor of chemistry Bassam Shakhashiri knows both the history of the table, and its modern relevance. He says the table came about through a collaboration of a few scientists but that Dmitri Mendeleev properly gets much of the credit.
“Dimitri Mendeleev, the Russian chemist, he proposed — sometimes people say he discovered — the pattern of similar behavior [of certain elements] and arranged them,” Shakhashiri explains.


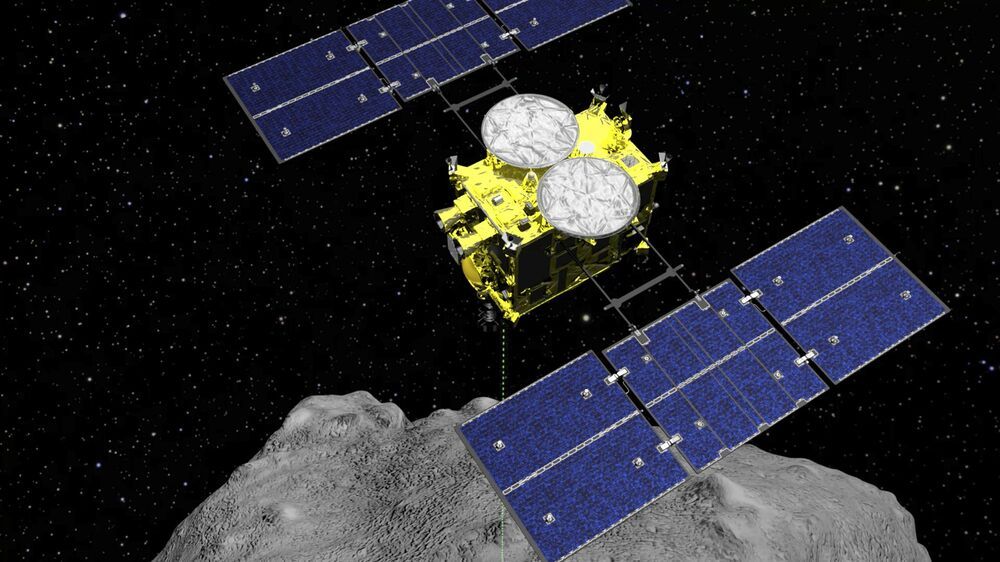
Japan spacecraft approaches Earth to drop asteroid samples
TOKYO (AP) — Japanese space agency officials said Friday the Hayabusa2 spacecraft is on its intended trajectory as it approaches Earth to deliver a capsule containing samples from a distant asteroid that could provide clues to the origin of the solar system and life on Earth.
The spacecraft left the asteroid Ryugu, about 300 million kilometers (180 million miles) away, a year ago. The capsule is to be released 220,000 kilometers (136,700 miles) away in space and land in a remote, sparsely populated area of Woomera, Australia, on Sunday.
Hayabusa2 is flying smoothly according to plan, Yuichi Tsuda, project manager at the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency, said at a briefing ahead of the critical separation of the capsule from the spacecraft on Saturday.
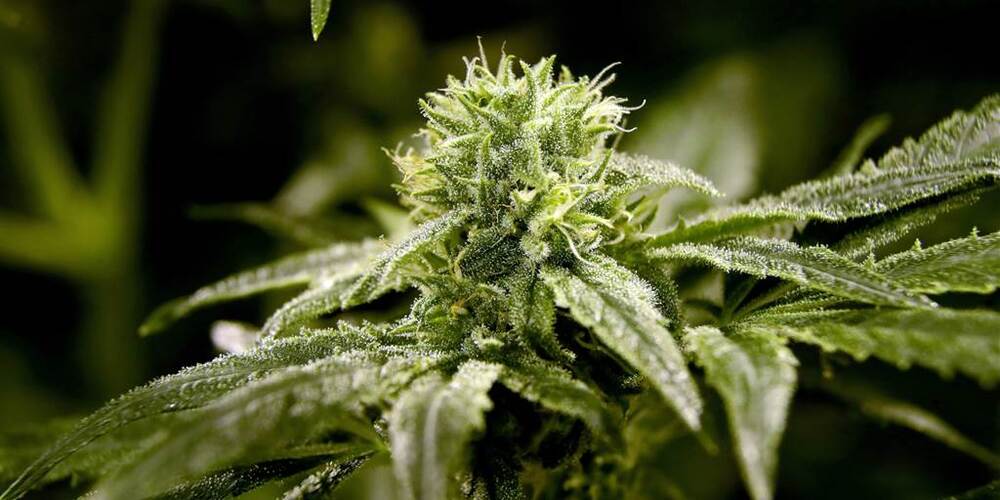


House passes historic bill to decriminalize cannabis
The proposal would end a federal ban on marijuana and create a pathway to expunge related criminal records.
As the cannabis industry continues to take root state by state, the House of Representatives voted in favor of removing marijuana from the federal Controlled Substances Act.
The House voted Friday on the Marijuana Opportunity Reinvestment and Expungement Act, or MORE Act, which decriminalizes cannabis and clears the way to erase nonviolent federal marijuana convictions. The Senate is unlikely to approve the bill.
The MORE Act also creates pathways for ownership opportunities in the emerging industry, allows veterans to obtain medical cannabis recommendations from Veteran Affairs doctors, and establishes funding sources to reinvest in communities disproportionately affected by the war on drugs.