O.,o circa 2014.
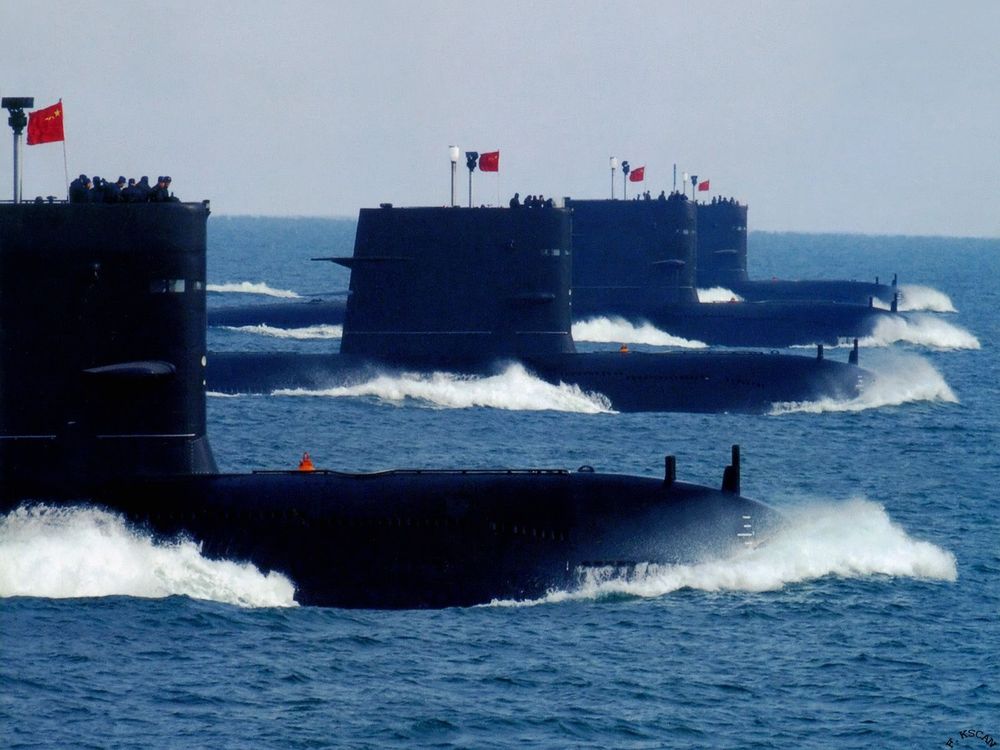
Researchers in China are reporting that they’ve taken a big step towards creating a supersonic submarine. This technology, which could just as easily be applied to weaponized torpedoes as military or civilian submarines, could theoretically get from Shanghai to San Francisco — about 6,000 miles — in just 100 minutes. If all this doesn’t sound crazy enough, get this: This new advance by the Chinese is based on supercavitation, which was originally developed by the Soviets in the ’60s, during the Cold War.
As you may already know, it’s a lot harder for an object to move quickly through water than air. This is mostly due to increased drag. Without getting into the complexities of fluid dynamics, water is simply much thicker and more viscous than air — and as a result it requires a lot more energy for an object to push through it. You can experience the increased drag of water yourself next time you’re in a swimming pool: Raise your hand above your head, and then let it fall towards the water. (Or alternatively, if there are people sunbathing nearby, do a belly flop.)
Anyway, much like a small-engined car is ultimately limited by its ability to cut through wind resistance (drag), a submarine or torpedo needs insane amounts of power to achieve high velocity through water. This is why, even in 2014, most submarines and torpedoes can’t go much faster than 40 knots (~46 mph). Higher speeds are possible, but it requires so much power that it’s not really feasible (torpedoes only have so much fuel).