Credit: SpaceX.
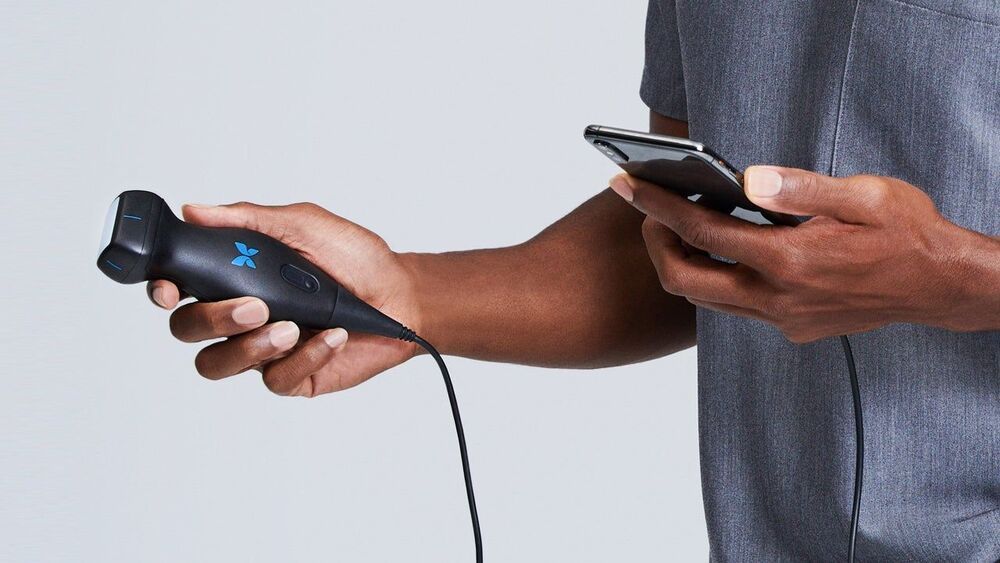
Doctors can triage and monitor patients faster—and sometimes more accurately—with the aid of the pocket-size machines.
Drexel University researchers are one step closer to offering a new treatment for the millions of patients who suffer from slow-healing, chronic wounds. The battery-powered applicator — as small and light as a watch — is the first portable and potentially wearable device to heal wounds with low-frequency ultrasound.
The National Institutes of Health (NIH) has awarded the research team an estimated $3 million to test the therapy on 120 patients over the next five years. By using diagnostic monitoring of blood flow in the wound tissue, the clinical trial will also determine how nutrition and inflammation impact wound closure, making treatment customization a possibility.
The project is an interdisciplinary collaboration between Drexel’s School of Biomedical Engineering, Science and Health Systems, the College of Medicine and the College of Nursing and Health Professions.
Circa 2008
Three independent research teams have successfully performed organ transplantations that do not require the recipient to face a lifetime of immunosuppressant drugs to prevent rejection. Instead, the new techniques prevent rejection by training the immune system to recognize the new organ as its own.
The three studies, published this week in the New England Journal of Medicine, are preliminary and involve only a few patients. But if the techniques can be reproduced in a larger population, they could eliminate one of the most enduring scars of the operation: the need to continue taking sometimes-dangerous immunosuppressant drugs.
Thousands of kidney transplantations are performed every year, and nearly 99% of patients in the United States are still alive a year after the surgery. But even when the organ donor is a close relative, the transplant recipient often needs to take immunosuppressant drugs for the rest of their lives to guard against organ rejection. But although the drugs help to prevent rejection, they also increase the risk of infection and are very pricey.
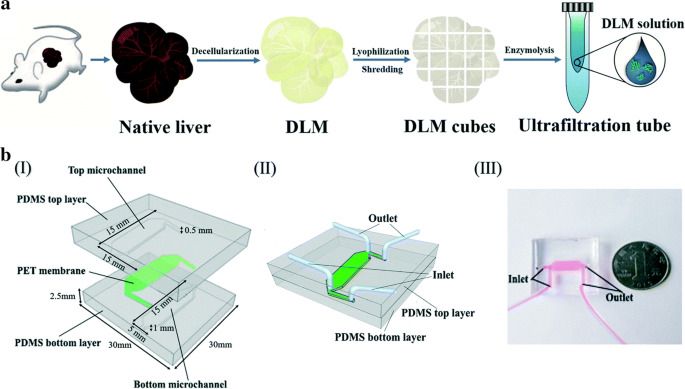
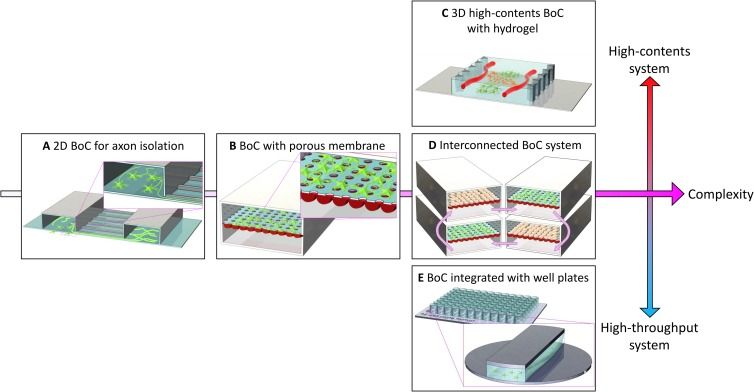
The organ-on-a-chip (OOAC) is in the list of top 10 emerging technologies and refers to a physiological organ biomimetic system built on a microfluidic chip. Through a combination of cell biology, engineering, and biomaterial technology, the microenvironment of the chip simulates that of the organ in terms of tissue interfaces and mechanical stimulation. This reflects the structural and functional characteristics of human tissue and can predict response to an array of stimuli including drug responses and environmental effects. OOAC has broad applications in precision medicine and biological defense strategies. Here, we introduce the concepts of OOAC and review its application to the construction of physiological models, drug development, and toxicology from the perspective of different organs. We further discuss existing challenges and provide future perspectives for its application.
Brain on a chip for drug discovery.
Since the advent of organ-on-a-chip, many researchers have tried to mimic the physiology of human tissue on an engineered platform. In the case of brain tissue, structural connections and cell–cell interactions are important factors for brain function. The recent development of brain-on-a-chip is an effort to mimic those structural and functional aspects of brain tissue within a miniaturized engineered platform. From this perspective, we provide an overview of trace of brain-on-a-chip development, especially in terms of complexity and high-content/high-throughput screening capabilities, and future perspectives on more in vivo-like brain-on-a-chip development.
With the advent of an aging society, the disease incidence rate is increasing, and the cost of drug development and disease treatment is expanding exponentially.1,2 According to the World Health Organization (WHO), nearly one billion people in the world suffer from neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s (AD) and Parkinson’s diseases.3 Despite decades of research on neurodegenerative diseases by many biologists and pharmaceutical companies, the underlying mechanism of their onset and progression is still largely unknown. The resolution of these diseases has a long way to go, and such steps are limited due to the lack of a suitable in vitro model system for mechanism study and drug development. In particular, the complex tissue structures and cell–cell interactions of the in vivo system make it challenging to unravel the underlying mechanism of the diseases and to predict the efficacy of clinical medicine.
Japan’s government to join forces with industry to supercharge development.
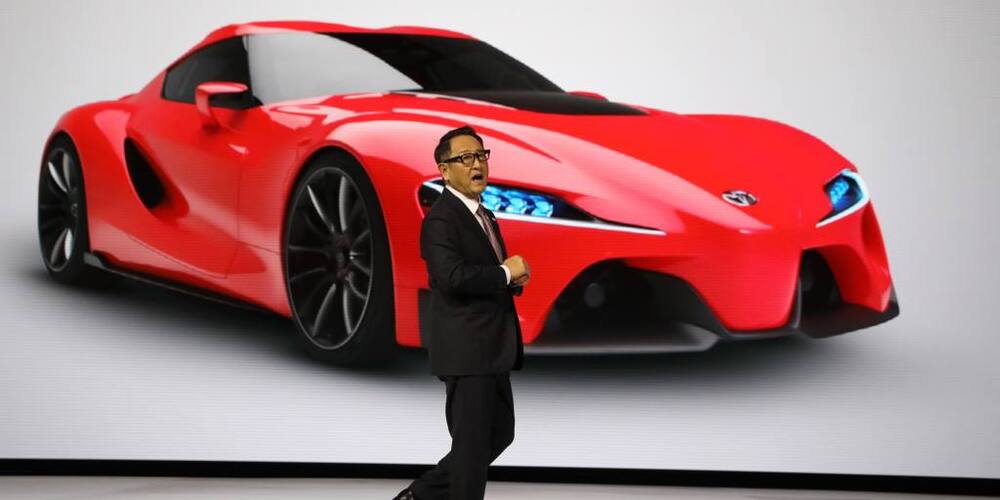
TOKYO — A trip of 500 km on one charge. A recharge from zero to full in 10 minutes. All with minimal safety concerns. The solid-state battery being introduced by Toyota promises to be a game changer not just for electric vehicles but for an entire industry.
The technology is a potential cure-all for the drawbacks facing electric vehicles that run on conventional lithium-ion batteries, including the relatively short distance traveled on a single charge as well as charging times. Toyota plans to be the first company to sell an electric vehicle equipped with a solid-state battery in the early 2020s. The world’s largest automaker will unveil a prototype next year.
The electric vehicles being developed by Toyota will have a range more than twice the distance of a vehicle running on a conventional lithium-ion battery under the same conditions. All accomplished without sacrificing interior space in even the most compact vehicle.
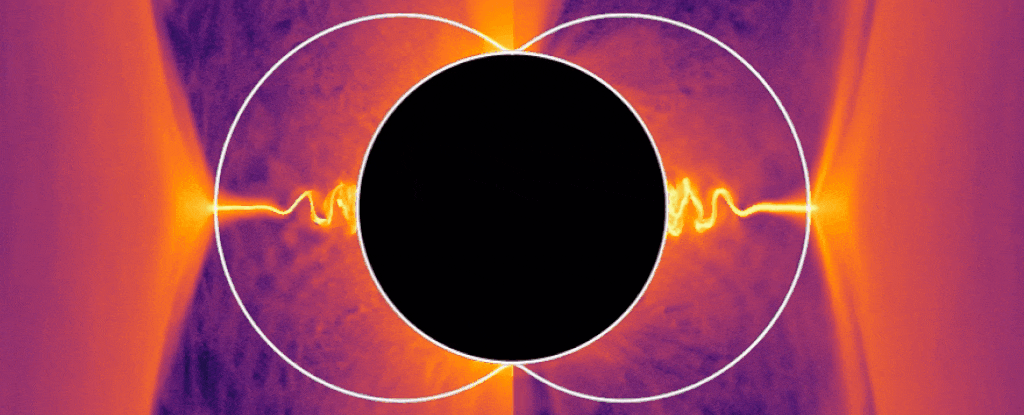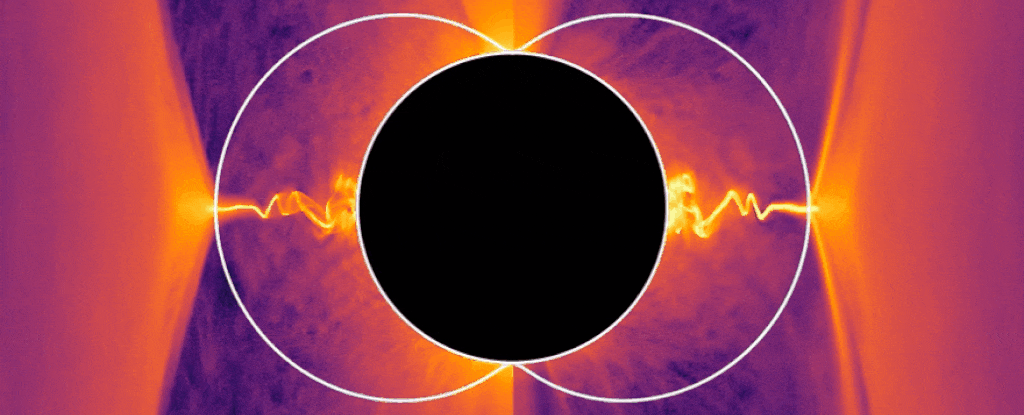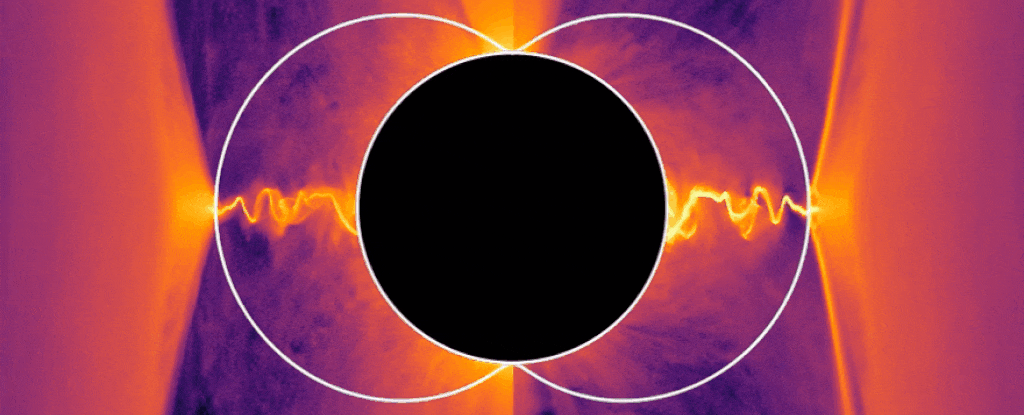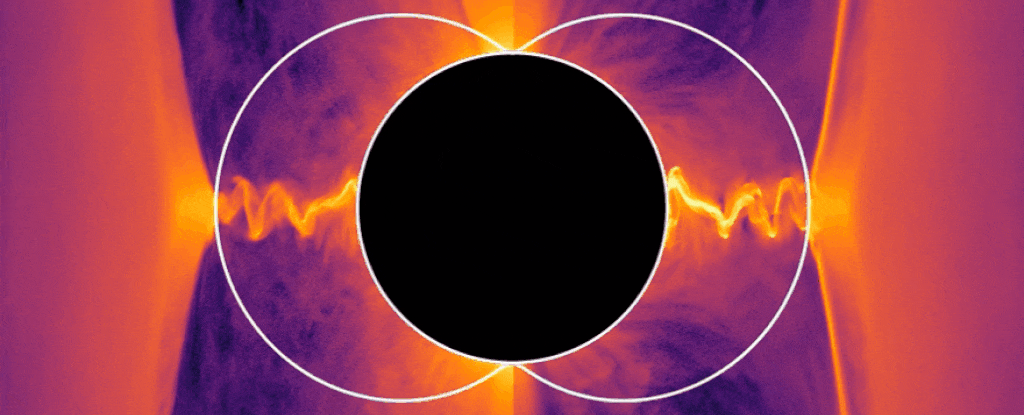
When a black hole is actively feeding, something strange can be observed: enormously powerful jets of plasma shoot from its poles, at velocities approaching light speed.
Given the intense gravitational interactions at play, exactly how those jets form is a mystery. But now, using computer simulations, a team of physicists has hit upon an answer — particles seeming to have “negative energy” extract energy from the black hole and redirect it to the jets.
And this theory has, for the first time, united two different and seemingly irreconcilable theories about how energy can be extracted from a black hole.
Circa 2014
We propose the new dark matter particle candidate—the “black hole atom,” which is an atom with the charged black hole as an atomic nucleus and electrons in the bound internal quantum states. As a simplified model we consider the central Reissner-Nordström black hole with the electric charge neutralized by the internal electrons in bound quantum states. For the external observers these objects would look like the electrically neutral Schwarzschild black holes. We suppose the prolific production of black hole atoms under specific conditions in the early universe.
Slaughter-free meat is finally starting to make the jump from the lab to the factory line.
As Singapore becomes the first country to allow the sale of cultured meat, more startups around the world are preparing to test production of lab-grown meats like beef and chicken in factories. While there’s a long way to go, it’s a crucial step in getting cell-based products ready for supermarket shelves.