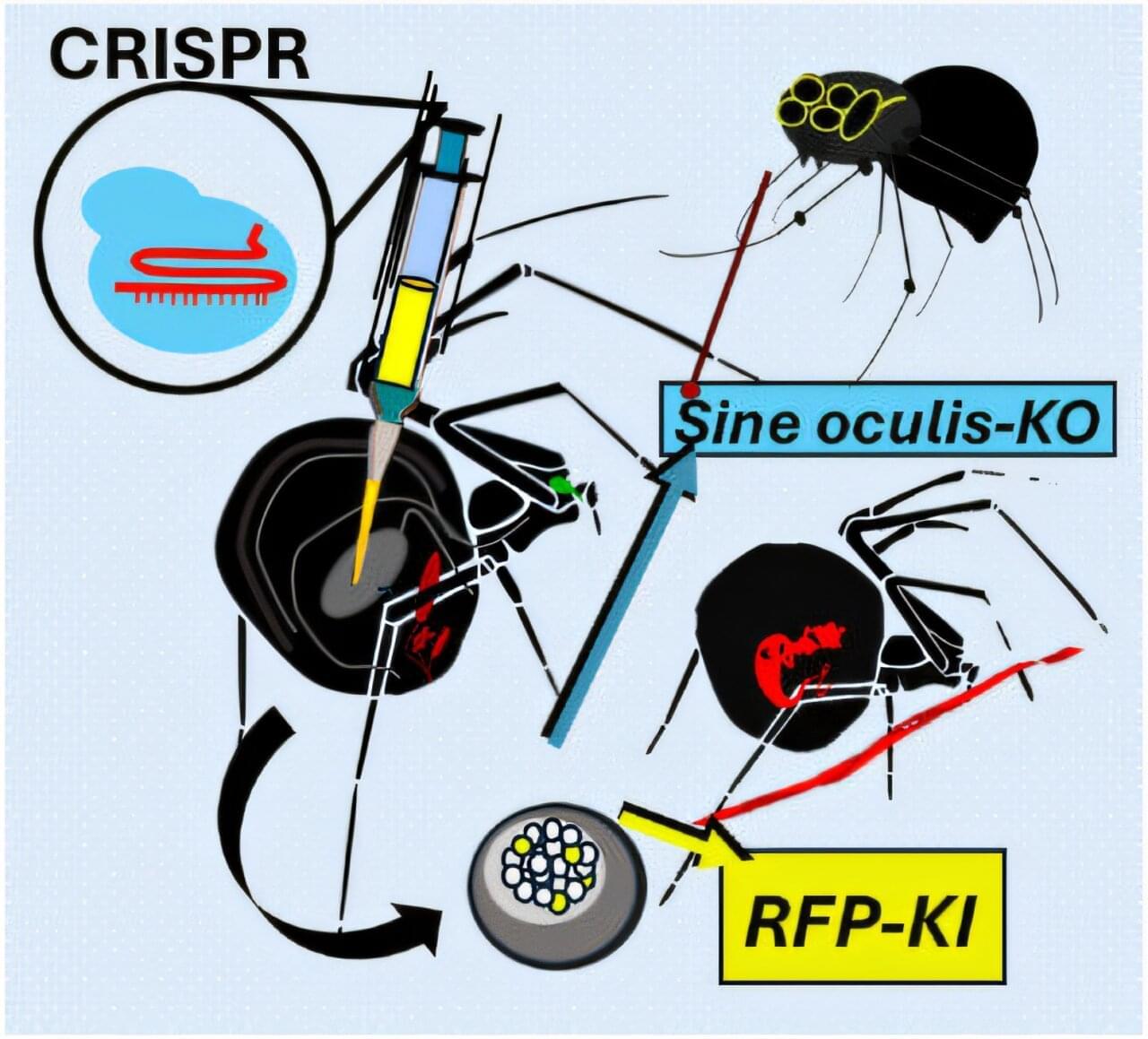
The University of Bayreuth’s Biomaterials research group has, for the first time, successfully applied the CRISPR-Cas9 gene-editing tool to spiders. Following the genetic modification, the spiders produced red fluorescent silk.
The findings of the study have been published in the journal Angewandte Chemie.
Spider silk is one of the most fascinating fibers in the field of materials science. In particular, its dragline thread is extremely tear-resistant, while also being elastic, lightweight and biodegradable. If scientists succeed in influencing spider silk production in vivo—in a living animal—and thereby gain insights into the structure of the dragline thread, it could pave the way for the development of new silk functionalities for a wide range of applications.