It’s a web of endless possibilities, but there’s a chance we might find ourselves interwoven in the same old web of Big Tech.
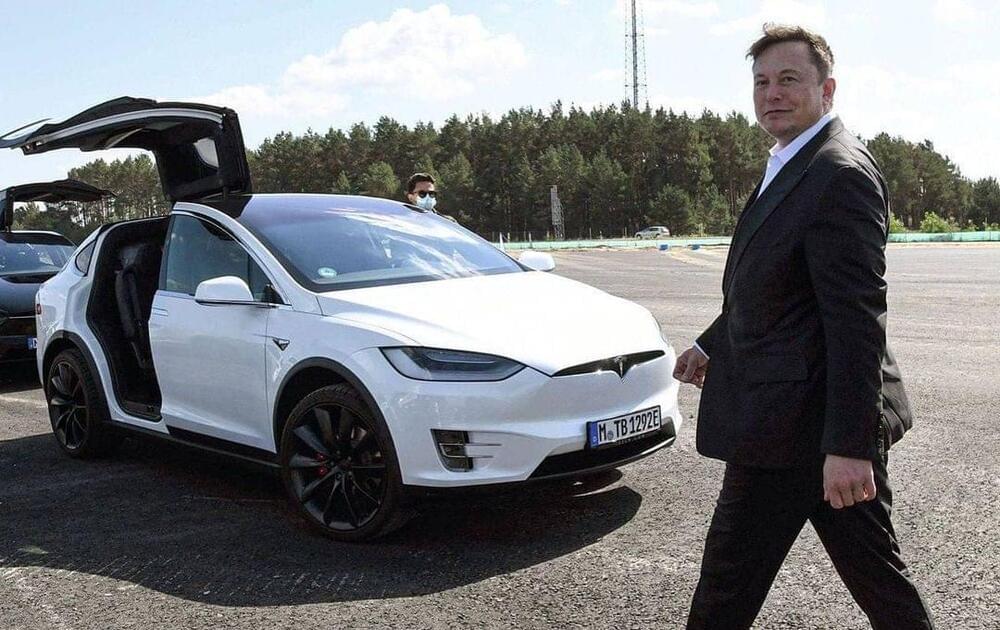
The emergence of blockchain-based technologies such as cryptocurrency, NFTs, metaverse, blockchain, and distributed ledger technology, etc is being seen as the herald of a new era of the internet — a more transparent and open version of the web that would be collectively controlled by users, instead of tech giants like Google and Facebook.
Some experts believe this decentralized Web, which is also referred to as Web 3.0, will bring more transparency and democratization to the digital world. Web 3.0 may establish a decentralized digital ecosystem where users will be able to own and control every aspect of their digital presence. Some hope that it will put an end to the existing centralized systems that encourage data exploitation and privacy violation.
More than 30 years have passed since the World Wide Web first came into existence, and over this course of time, the world of the internet has gone through various stages of development. There is no textbook definition of Web 3.0, but by going through these stages, you can have an idea of how Web 3.0 may shape the future of the internet experience.
Full Story: