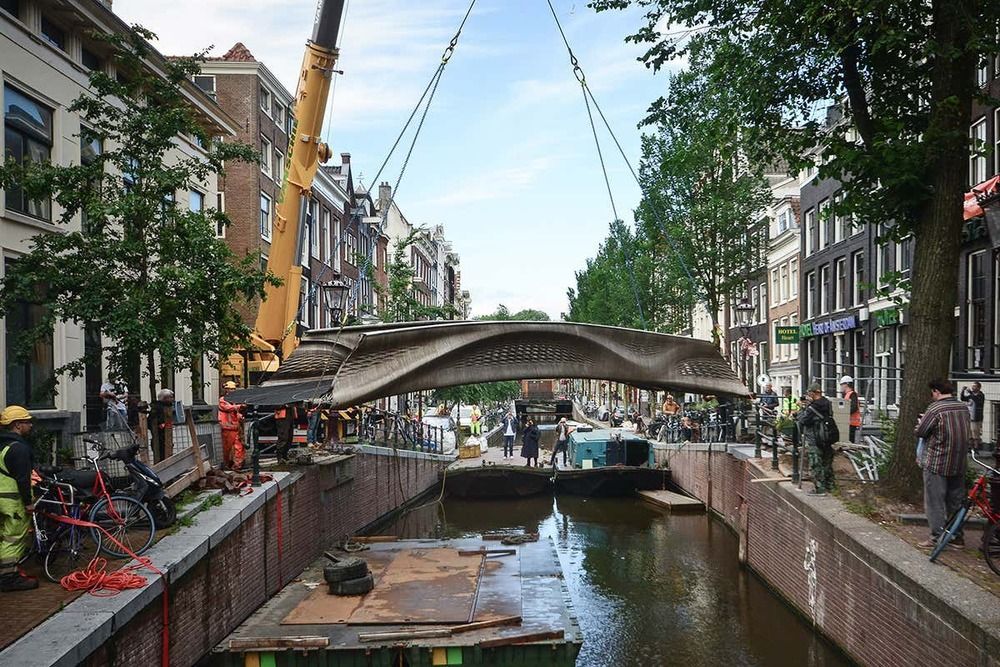
The world’s first 3D-printed steel bridge has opened in Amsterdam. It was created by robotic arms using welding torches to deposit the structure of the bridge layer-by-layer using 4500 kilograms of stainless steel.
The first ever 3D-printed steel bridge has opened in Amsterdam, the Netherlands. It was created by robotic arms using welding torches to deposit the structure of the bridge layer by layer, and is made of 4500 kilograms of stainless steel.
The 12-metre-long MX3D Bridge was built by four commercially available industrial robots and took six months to print. The structure was transported to its location over the Oudezijds Achterburgwal canal in central Amsterdam last week and is now open to pedestrians and cyclists.
More than a dozen sensors attached to the bridge after the printing was completed will monitor strain, movement, vibration and temperature across the structure as people pass over it and the weather changes. This data will be fed into a digital model of the bridge.