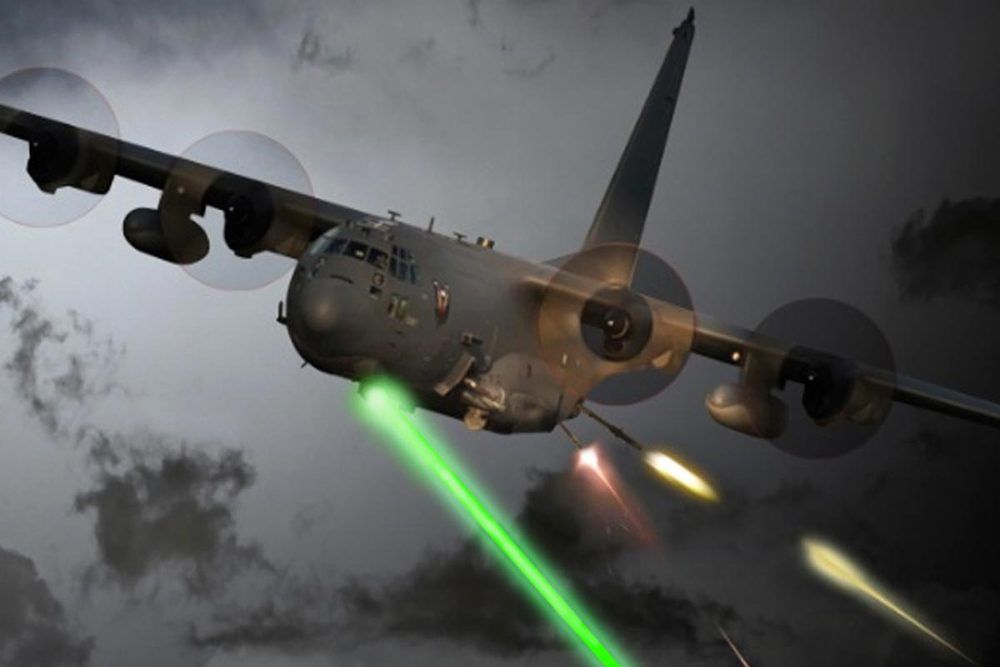
The Air Force is short of funding to speed development of a laser weapon for what is already one of the most lethal platforms in the U.S. arsenal — the Special Operations AC-130J Ghostrider gunship, Air Force Lt. Gen. Marshall Webb testified Wednesday.
“We’re $58 million short of having a full program that would get us a 60-kilowatt laser flying on an AC-130 by 2022,” Webb, commander of Air Force Special Operations Command, said at a hearing of the Senate Armed Services Subcommittee on Emerging threats.
Webb was responding to questions from Sen. Martin Heinrich, D-New Mexico, who said at the current pace of testing and funding, a laser weapon for the AC-130 would not be operational until 2030.