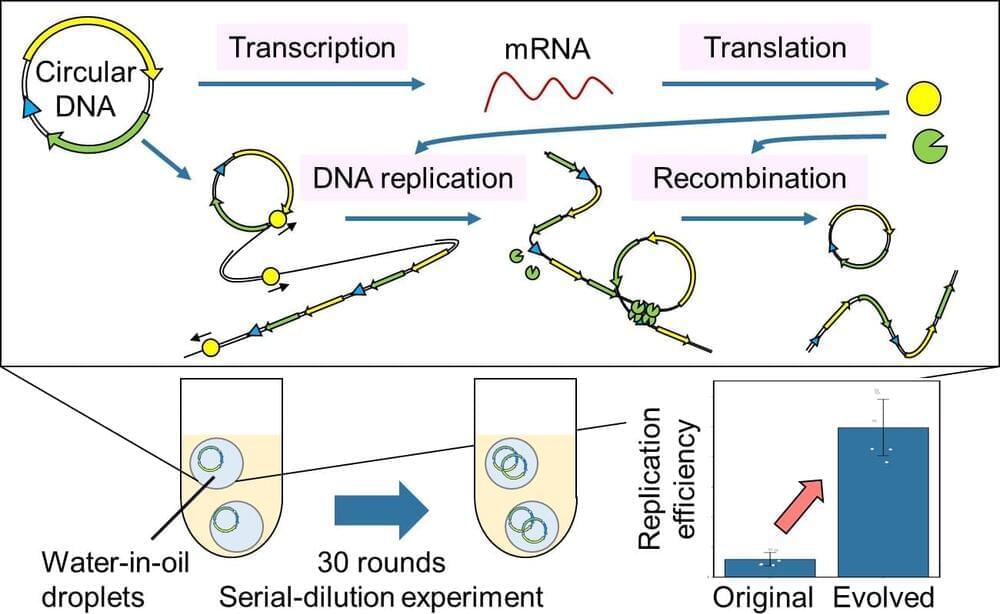
Professor Norikazu Ichihashi and his colleagues at the University of Tokyo have successfully induced gene expression from a DNA, characteristic of all life, and evolution through continuous replication extracellularly using cell-free materials alone, such as nucleic acids and proteins for the first time.
The ability to proliferate and evolve is one of the defining characteristics of living organisms. However, no artificial materials with these characteristics have been created. In order to develop an artificial molecular system that can multiply and evolve, the information (genes) coded in DNA must be translated into RNA, proteins must be expressed, and the cycle of DNA replication with those proteins must continue over a long period in the system. To date, it has been impossible to create a reaction system in which the genes necessary for DNA replication are expressed while those genes simultaneously carry out their function.
The group succeeded in translating the genes into proteins and replicating the original circular DNA with the translated proteins by using a circular DNA carrying two genes necessary for DNA replication (artificial genomic DNA) and a cell-free transcription-translation system. Furthermore, they also successfully improved the DNA to evolve to a DNA with a 10-fold increase in replication efficiency by continuing this DNA replication cycle for about 60 days.
By adding the genes necessary for transcription and translation to the artificial genomic DNA developed by the group, it could be possible to develop artificial cells that can grow autonomously simply by feeding them low-molecular-weight compounds such as amino acids and nucleotides, in the future. If such artificial cells can be created, we can expect that useful substances currently produced using living organisms (such as substances for drug development and food production) will become more stable and easier to control.
This research has been led by Professor Norikazu Ichihashi, a research director of the project “Development of a self-regenerative artificial genome replication-transcription-translation system” in the research area “Large-scale genome synthesis and cell programming” under the JST’s Strategic Basic Research Programs CREST (Team type). In this research area, JST aims to elucidate basic principles in relation to the structure and function of genomes for the creation of a platform technology for the use of cells.