China has had some notable space successes in the past few years including sending an uncrewed mission to Mars and starting construction of its own space station.



The AI nanny is here! In a new feat for science, robots and AI can now be paired to optimise the creation of human life. In a Matrix-esque reality, robotics and artificial intelligence can now help to develop babies with algorithms and artificial wombs.
Reported by South China Morning Post, Chinese scientists in Suzhou have developed the new technology. However, there are worries surrounding the ethics of actually artificially growing human babies.
This video covers the world in 2080 and its future technologies. Watch this next video about the world in 2070: https://bit.ly/3nYXvjf.
► BlockFi: Get Up To $250 In Bitcoin: https://bit.ly/3rPOf1V
► Jarvis AI: Write 5x Faster With Artificial Intelligence: https://bit.ly/3HbfvhO
► M1 Finance: Open A Roth IRA And Get Up To $500: https://bit.ly/3KHZvq0
► Udacity: 75% Off All Courses (Biggest Discount Ever): https://bit.ly/3j9pIRZ
► Business Ideas Academy: Start A Business You Love: https://bit.ly/3KI7B1S
SOURCES:
• https://www.futuretimeline.net.
• The Future of Humanity (Michio Kaku): https://amzn.to/3Gz8ffA
• The Singularity Is Near: When Humans Transcend Biology (Ray Kurzweil): https://amzn.to/3ftOhXI
• Physics of the Future (Michio Kaku): https://amzn.to/33NP7f7
▶️ RECOMMENDED PLAYLISTS:
Future Technologies: https://youtube.com/playlist?list=PLiUrMrgIdon8afD1EtG3_mabSHLrfdKZJ
Technology Trends: https://youtube.com/playlist?list=PLiUrMrgIdon_H3FbJQFXqnjlyOYdHpY9q.
Business Tech: https://youtube.com/playlist?list=PLiUrMrgIdon-SUSL_8YQpO1Kqgsf5ZzyM
Business Innovation Tutorials: https://youtube.com/playlist?list=PLiUrMrgIdon97qKW3TaPO9TqC6U3zVC3W
Business Strategy Tutorials: https://youtube.com/playlist?list=PLiUrMrgIdon87F3Ads27NkSy47apAcOIH
💡 On this channel, I explain the following concepts:
• Future and emerging technologies.
• Future and emerging trends related to technology.
• The connection between Science Fiction concepts and reality.
SUBSCRIBE: https://bit.ly/3geLDGO
Disclaimer:

Just reminder, Google isn’t everything.
www.refseek.com — Academic Resource Search. More than a billion sources: encyclopedia, monographies, magazines.
www.wo… See more.
Sorry! The file you requested could not be found. Return to RefSeek
An error report has been generated and sent to the system administrator.

The Neuro-Network.
𝐇𝐨𝐰 ‘𝐃𝐨𝐫𝐦𝐚𝐧𝐭’ 𝐂𝐞𝐥𝐥𝐬 𝐈𝐧 𝐓𝐡𝐞 𝐀𝐠𝐢𝐧𝐠 𝐁𝐫𝐚𝐢𝐧 𝐂𝐨𝐧𝐭𝐫𝐢𝐛𝐮𝐭𝐞 𝐓𝐨 𝐂𝐨𝐠𝐧𝐢𝐭𝐢𝐯𝐞 𝐃𝐞𝐜𝐥𝐢𝐧𝐞
𝘾𝙤𝙜𝙣𝙞𝙩𝙞𝙫𝙚 𝙙𝙚𝙘𝙡𝙞𝙣𝙚 𝙖𝙣𝙙 𝙛𝙤𝙧𝙜𝙚𝙩𝙩𝙞𝙣𝙜 𝙩𝙝𝙞𝙣𝙜𝙨 𝙖𝙨 𝙬𝙚 𝙜𝙚𝙩 𝙤𝙡𝙙𝙚𝙧 𝙞𝙨 𝙖𝙡𝙢𝙤𝙨𝙩 𝙖 𝙧𝙞𝙜𝙝𝙩 𝙤𝙛 𝙥𝙖𝙨𝙨𝙖𝙜𝙚. 𝘼𝙡𝙡… See more.
Cellular senescence is a state where cells get stuck in a particular phase of their cell cycle, which can affect physiological function. In the brain this effect can block neuroregeneration. Clearing them may reverse certain aspects of cognitive decline associated with aging, including memory loss.
Power all the things.
YouTuber Handy Geng built a massive 27,000,000mAh power bank that is capable of recharging any device and even powering a washing machine.
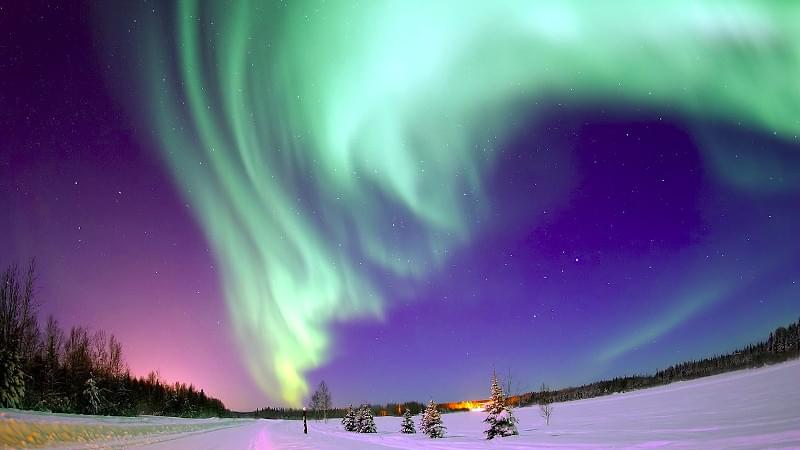

How do you look back over your life and divide it up? Maybe by decades, cultural moments, or geopolitical events. For radio amateurs with older callsigns there’s a temptation to do so by solar cycles, as the roughly 11-year period of the Sun’s activity had a huge effect on radio propagation through the charge it creates in the upper atmosphere. We’re now in solar cycle 25, numbered since the 18th century when the science of solar observation began, and as never before we’re surrounded by information from experts such as [Dr. Tamitha Skov], the so-called [Space Weather Woman]. When she says something is on the way we listen, so a recent Tweet predicting a direct hit from a solar storm with a good probability of auroras in lower latitudes is very much worth sharing.
We must extend our commiserations to readers in equatorial climes and ever through the lower half of the USA, southern Europe, the Middle East, India, Japan, and China. You won’t see the aurora we’ll catch in Europe along with our friends in New Zealand, Canada, Russia, and northern USA. But even then to those of us at moderate latitudes an aurora is a pretty rare event, so we’re hoping for clear skies on the 2nd of February and would advise you to look out too if you’re in the likely zone even if they won’t be quite as impressive as those in our header picture. Meanwhile radio amateurs everywhere don’t have to see pretty lights in the sky to reap the benefits in terms of propagation, so happy DX hunting! The Tweet is embedded below the break, so you can play the timeline for yourselves.
Direct Hit! NASA, NOAA & MetOffice predictions agree the #solarstorm launched Jan 29 will hit Earth by early Feb 2! This one is slow so expect #aurora only as far south as Netherlands, north USA, & up to north New Zealand & Tasmania. #GPS & HF #radio issues on Earth’s nightside! pic.twitter.com/Uua1LGMgJR
Accelerating Research To Prevent & Cure Disease — Dr. Kevin Perrott, Ph.D., Founder & CEO, OpenCures; Co-Founder & Treasurer, SENS Research Foundation
Dr. Kevin Perrott, Ph.D. is Founder and CEO, OpenCures (https://opencures.org/), Adjunct Professor, University of Alberta, Co-Founder and Advisor, Oisin Biotechnologies, President, of Global Healthspan Policy Institute, and Co-Founder and Treasurer, SENS Research Foundation.
Kevin is a successful entrepreneur and owner of the largest motorcycle and snowmobile dealership in Canada, Riverside Honda and Skidoo Sales in Edmonton, Alberta. He became a cancer survivor, an experience which clearly highlighted the deficiencies of the current health technology development paradigm where the customer has almost no input in the development of their own health solutions. Armed with the realization that nothing is more valuable than health and the time to enjoy it with those you love, Kevin resolved to put his energies towards addressing these deficiencies.
In 2003, Kevin joined Aubrey de Grey and David Gobel to form the Methuselah Foundation which offered competitive prizes for advances in longevity science. A few years later he became a co-founder with Aubrey de Grey and others of SENS Research Foundation to develop interventions able to repair or make harmless the damage that accumulates and underlies multiple age-related disorders. Mostly recently, Kevin formed OpenCures as a for-benefit corporation helping individuals perform self-directed research, generate data, and focus the value of data on the health solutions they are interested in.
Kevin has authored and co-authored several peer-reviewed articles all focused on accelerating the science underlying the development of therapies for degenerative diseases. He is a co-founder of multiple non-profit and for-profit entities whose missions are aligned with that purpose.