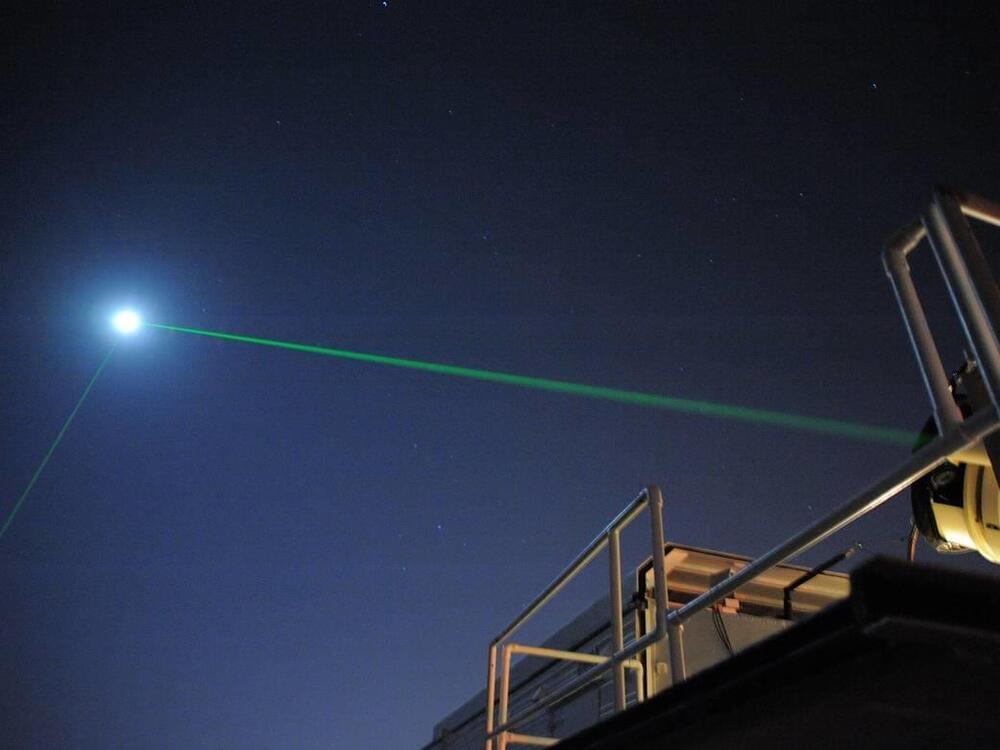
After a decade of failed attempts, scientists successfully bounced photons off of a reflector aboard the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter, some 240,000 miles from Earth.




As the number of electric cars on the road grows, so does the need for electric vehicle (EV) charging stations and the Internet-based managing systems within those stations. However, these managing systems face their own issues: cybersecurity attacks.
Elias Bou-Harb, director of the UTSA Cyber Center for Security and Analytics, and his colleagues — Claud Fachkha of the University of Dubai and Tony Nasr, Sadegh Torabi and Chadi Assi of Concordia University in Montreal — are shedding light on the vulnerabilities of these cyber systems. The researchers are also recommending measures that would protect them from harm.
The systems built into electric cars perform critical duties over the Internet, including remote monitoring and customer billing, as do a growing number of internet-enabled EV charging stations.

One possible application of interest to researchers is bone healing. The idea is that the soft material, powered by the electroactive polymer, will be able to maneuver in spaces of complicated bone fractures and expand. When the material hardens, it can form the basis for building new bones. In their study, the researchers demonstrate that the material can wrap itself around chicken bones, and the artificial bone that develops later grows along with the animal’s bone. The developed biohybrid variable-stiffness actuators can be used in soft (micro-)robotics and as potential tools for bone repair or bone tissue engineering.
“By controlling how the material turns, we can make the microrobot move in different ways, and also affect how the material unfurls in broken bones. We can embed these movements into the material’s structure, making complex programs for steering these robots unnecessary”, says Edwin Jager.
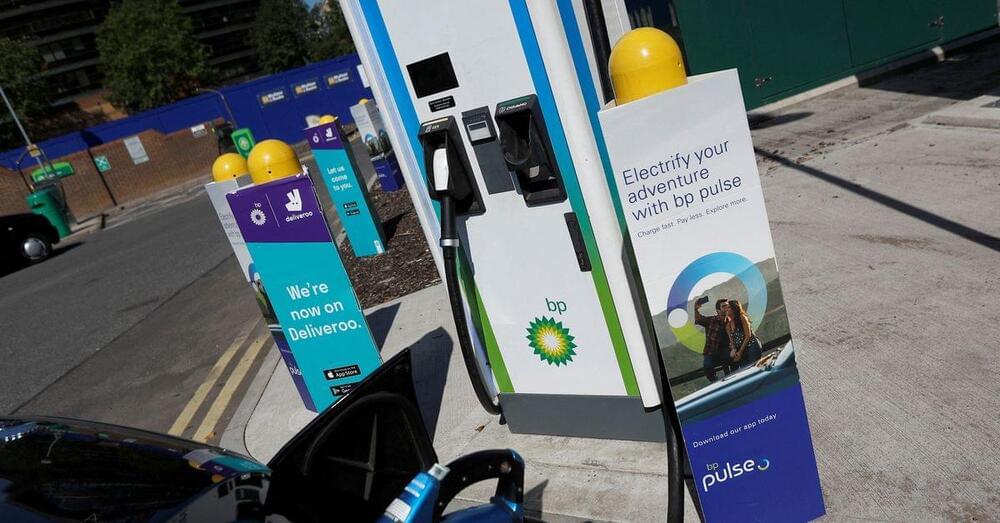

LONDON, Jan 14 (Reuters) — BP says its fast electric vehicle chargers are on the cusp of becoming more profitable than filling up a petrol car.
The milestone will mark a significant moment for BP which wants to shift away from oil and expand operations in power markets and around electric vehicles (EV).
EV charging has for years been a loss-making business as a whole for BP and rivals as they invest heavily in its expansion. The division is not expected to turn profitable before 2025 but on a margin basis, BP’s fast battery charging points, which can replenish a battery within minutes, are nearing levels they see from filling up with petrol.
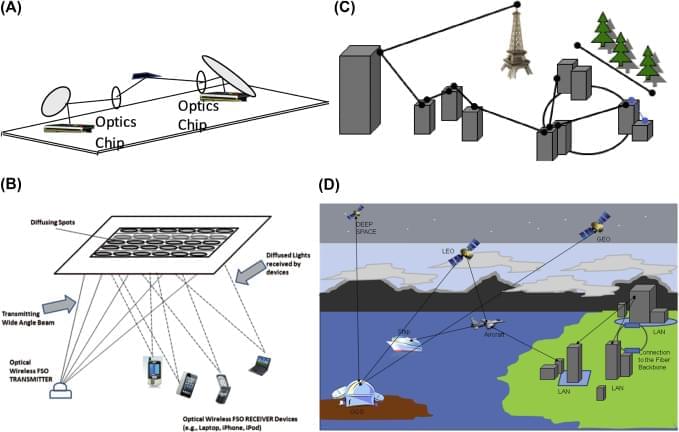
FSO communication systems are where free space acts as a communication channel between transceivers that are line-of-sight (LOS) for successful transmission of optical signals. The channel can be atmosphere, space, or vacuum, whose characteristics determine the transmission and reception of optical signals for designing reliable and efficient communication systems. Using FSO technology data is transmitted by propagation of light through atmospheric or space communication channels, allowing optical connectivity. FSO communication offers a high data rate to meet the tremendous increasing demand of broadband traffic mostly driven by Internet access and HDTV broadcasting services. Compared to fiber optics technology, FSO offers much more flexibility in designing optical network architectures at very high speeds, at tens and hundreds of Gbit/s rates. However, FSO communication is affected by atmospheric effects, which limits sensitivity and achievable data rates with acceptable BER. Some of these degradations are turbulence, absorption, and scattering, and various mitigation techniques exist for reliable and efficient data transmission [1] and to increase the communication performance. Both point-to-point, point-to-multipoint, multipoint-to-point, and multipoint-to-multipoint FSO communications are possible, depending on the different scenarios of establishing optical links. FSO communication is the most practical alternative to solve the bottleneck broadband connectivity problem. The data rates provided by FSO links continue to increase in both long-and short-range applications. FSO will be one of the most unique and powerful tools to address connectivity bottlenecks that have been created in high-speed networks during the past decade due to the tremendous success and continued acceptance of the Internet. The next generation of Internet connectivity will push the limits of existing infrastructure with high-bandwidth applications such as videoconferencing, streaming multimedia content, and network-enabled portable devices. Clearing these bottlenecks is crucial for the future growth and success of the contemporary Internet society. The bandwidth of optical communications access and edge networks will be needed to satisfy these demands. Communication systems are concerned with the transmission of information from a source to a user. The purpose of a communication system is therefore to transfer information. A very basic block diagram of any communication system (optical or radiofrequency (RF)) is shown in Fig. 4.1.
Fig. 4.1 shows a single point-to-point system, whereas in a multiplexed system there may be multiple input and output message sources and users (also called destinations). Fig. 4.2 shows other possible configurations and links for multipoint connections.
OWC is the next frontier for high-speed broadband connection and offers the following unique features and advantages: high bandwidth/capacity, ease of deployment, compact size, low power, and improved channel security. OWC can transmit and exchange voice and video communication data through the atmosphere/free-space at the rates of tens of Gbit/s and much more.
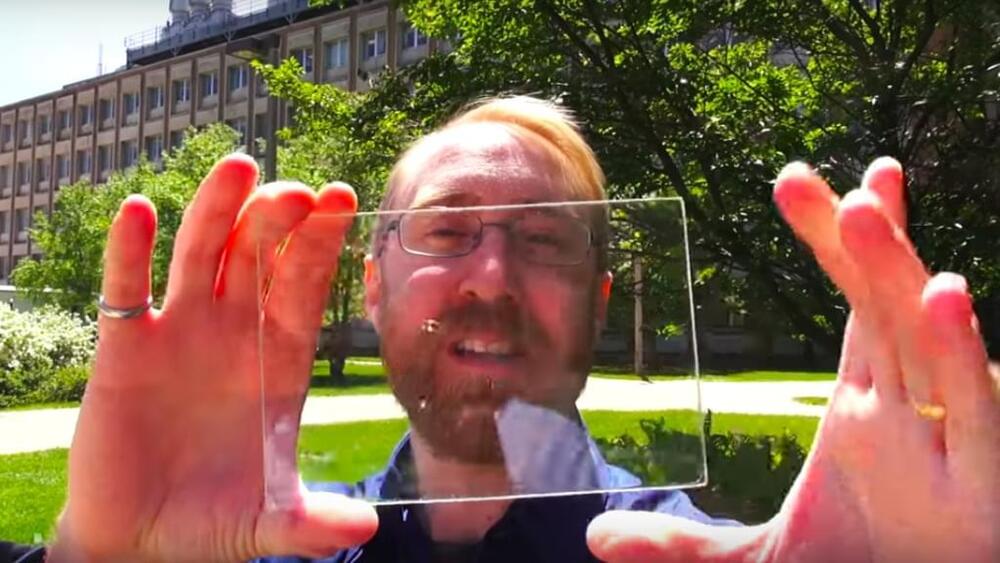


Building integrated solar provides businesses with new bottom line opportunities to leverage their properties to attract a new generation of sustainability-focused consumers, and that leaves little space for fossil energy to maneuver.
More than 20 billion square feet of windows are installed every year, and the leading firm Andersen Corporation apparently plans to make some of those billions into energy efficient, transparent solar energy generators that could kick the pace of global energy decarbonization into high gear. The well-known maker of windows and doors just chipped in for a $30 million Series B funding round that will help push the not-so-well-known transparent solar innovator Ubiquitous Energy out of the startup shadows and into the bright sunshine of the global building industries marketplace.
Ubiquitous Energy Hearts Transparent Solar Windows
The idea of transforming windows into fully transparent, see-through PV powerhouses has allured researchers for years. Conventional solar panels block the sun, so that’s out. Thin film PV technology offers an alternative route, but the problem is squeezing out enough clean kilowatts to make the endeavor worthwhile. Thin film is transparent, but overall the technology is not as efficient as conventional photovoltaic panels.
Inspired by the growth of bones in the skeleton, researchers at the universities of Linkoping in Sweden and Okayama in Japan have developed a combination of materials that can morph into various shapes before hardening. The material is initially soft but later hardens through a bone development process that uses the same materials found in the skeleton.
When we are born, we have gaps in our skulls that are covered by pieces of soft connective tissue called fontanelles. It is thanks to fontanelles that our skulls can be deformed during birth and pass successfully through the birth canal. Post-birth, the fontanelle tissue gradually changes to hard bone. Now, researchers have combined materials that together resemble this natural process. “We want to use this for applications where materials need to have different properties at different points in time. Firstly, the material is soft and flexible, and it is then locked into place when it hardens. This material could be used in, for example, complicated bone fractures. It could also be used in microrobots — these soft microrobots could be injected into the body through a thin syringe, and then they would unfold and develop their own rigid bones”, says Edwin Jager, associate professor at the Department of Physics, Chemistry and Biology (IFM) at Linkoping University.
The idea was hatched during a research visit in Japan when materials scientist Edwin Jager met Hiroshi Kamioka and Emilio Hara, who conduct research into bones. The Japanese researchers had discovered a kind of biomolecule that could stimulate bone growth under a short period of time. Would it be possible to combine this biomolecule with Jager’s materials research, to develop new materials with variable stiffness? In the study that followed, published in Advanced Materials, the researchers constructed a kind of simple “microrobot”, one which can assume different shapes and change stiffness. The researchers began with a gel material called alginate. On one side of the gel, a polymer material is grown. This material is electroactive, and it changes its volume when a low voltage is applied, causing the microrobot to bend in a specified direction.

Tech companies continued to draw criticism for their roles in political and social scandals, most notably when whisteblower and former Facebook employee Frances Haugen testified to lawmakers. Undeterred, Facebook rebranded itself Meta and said it would now focus on building the metaverse. Twitter CEO Jack Dorsey stepped down and likewise changed the name of his company Square to Block in a not-so-subtle nod to the blockchain.
Meanwhile, volatile cryptocurrencies set new records, their prices jumping and crashing on a tweet. NFTs, a once-obscure type of cryptoasset, went on an eye-watering tear as redditors pushed meme stocks skyward. It was also the year of ever-bigger AI. Machine learning models surpassed a trillion parameters, designed computer chips, and tackled practical problems in biology, math, and chemistry. Elsewhere, billionaires went to space, regular folks bought 3D printed houses, fusion power attracted billions in investment, gene editing trials hit their stride, and “flying car” companies hit the New York Stock Exchange.
For this year’s list of fascinating stories in tech and science, we sifted our Saturday posts and selected articles that looked back to where it all began, glanced ahead to what’s coming, or otherwise stood out from the chatter to stand the test of time.