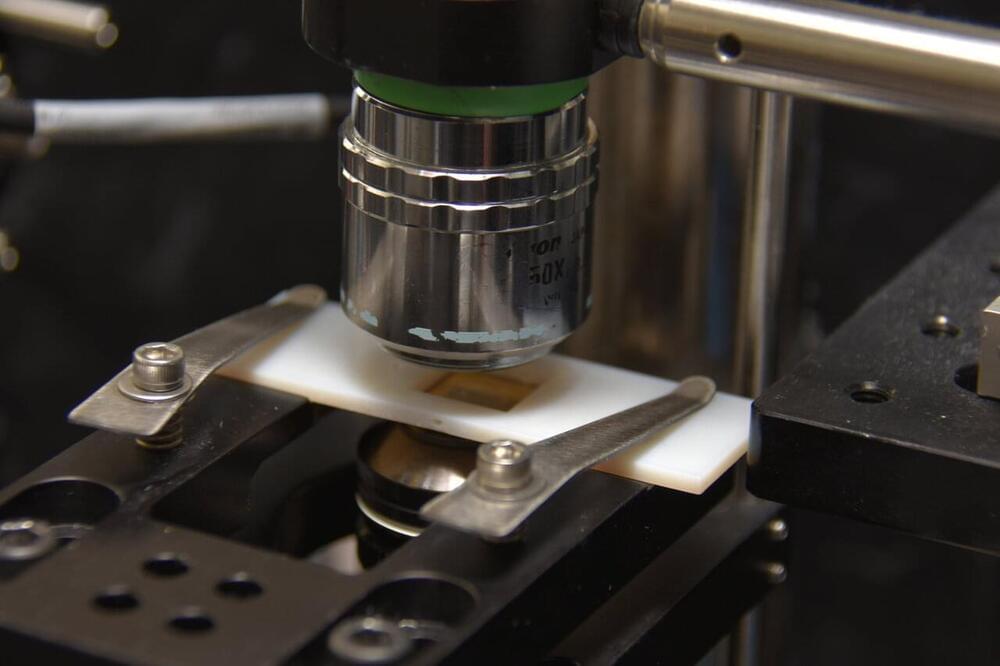
At just 1/1000th of a millimeter, nanoparticles are impossible to see with the naked eye. But, despite being small, they’re extremely important in many ways. If scientists want to take a close look at DNA, proteins, or viruses, then being able to isolate and monitor nanoparticles is essential.
Trapping these particles involves tightly focusing a laser beam to a point that produces a strong electromagnetic field. This beam can hold particles just like a pair of tweezers but, unfortunately, there are natural restrictions to this technique. Most notable are the size restrictions—if the particle is too small, the technique won’t work. To date, optical tweezers have been unable to hold particles like individual proteins, which are only a few nanometers in diameter.
Now, due to recent advances in nanotechnology, researchers in the Light-Matter Interactions for Quantum Technologies Unit at the Okinawa Institute of Science and Technology Graduate University (OIST) have developed a technique for precise nanoparticle trapping. In this study, they overcame the natural restrictions by developing optical tweezers based on metamaterials —a synthetic material with specific properties that do not occur naturally. This was the first time that this kind of metamaterial had been used for single nanoparticle trapping.