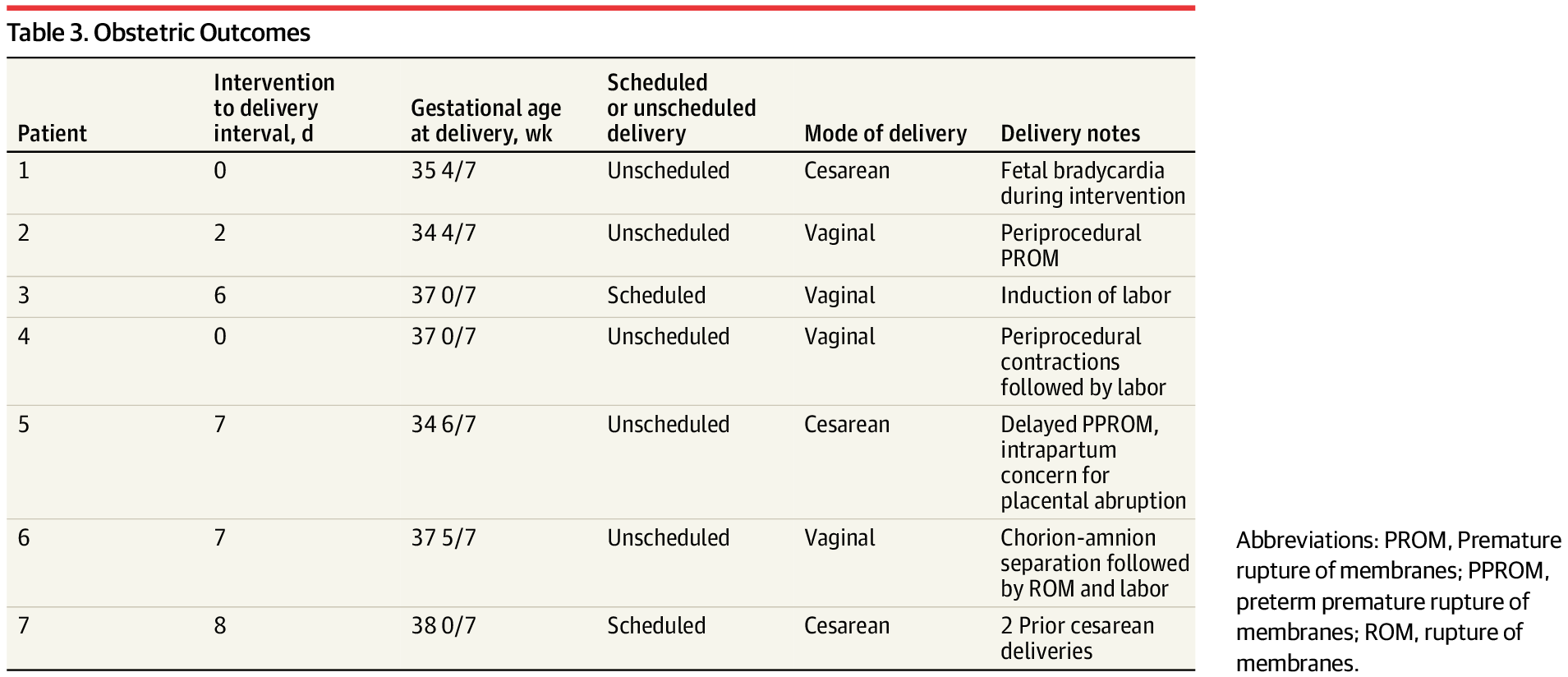
This intervention study evaluates in utero embolization in fetuses with vein of Galen malformation.

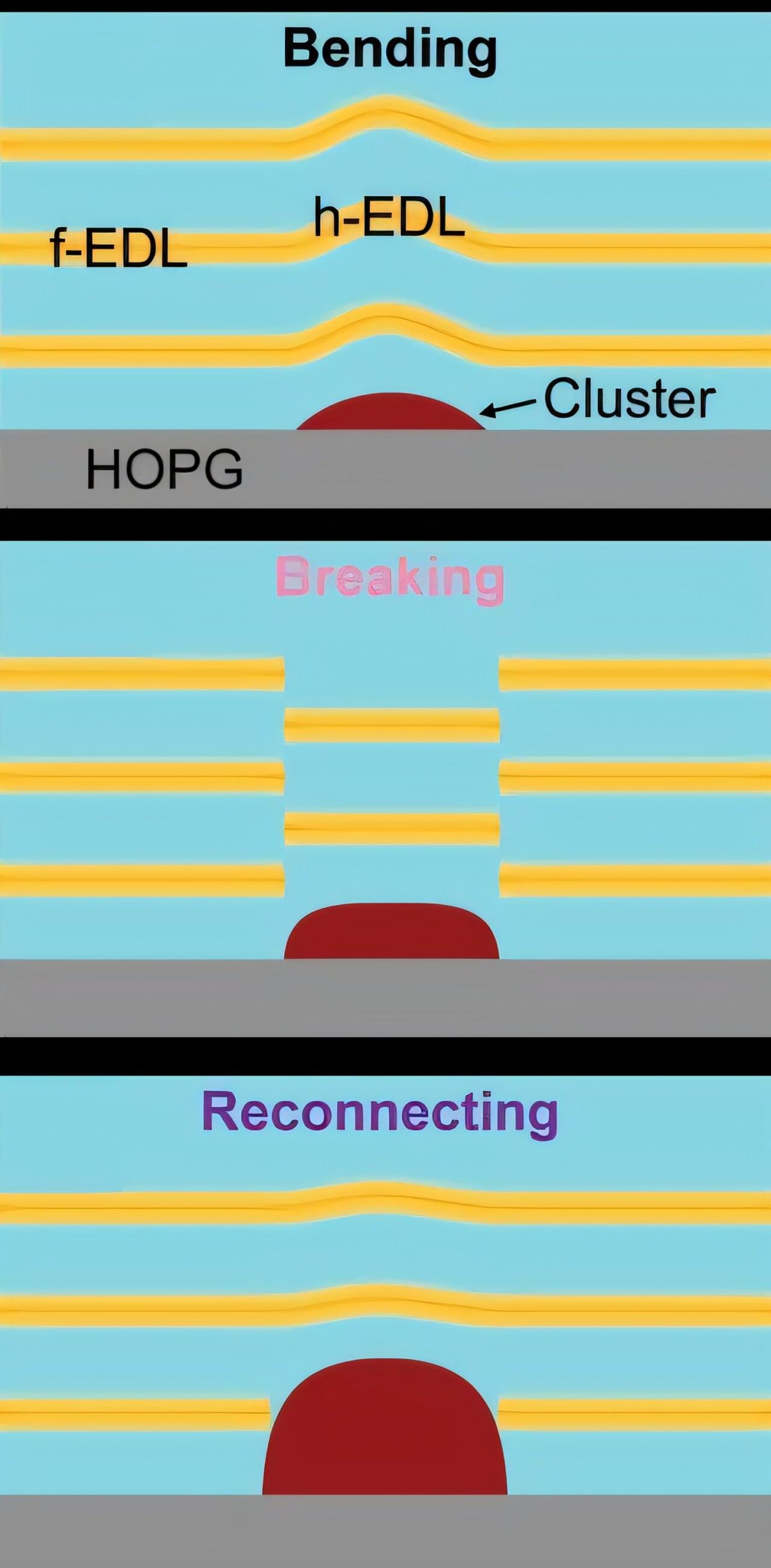
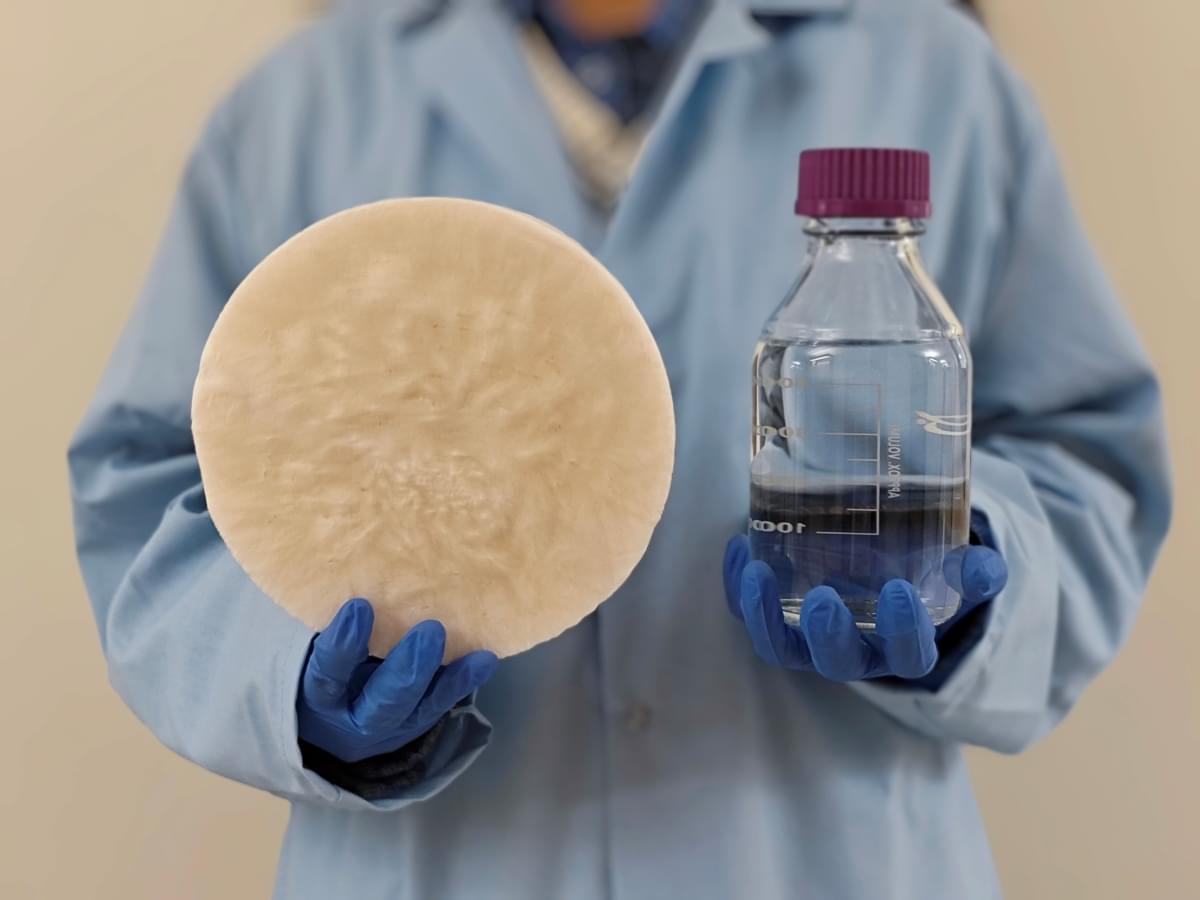
Electrochemical cells—or batteries, as a well-known example—are complex technologies that combine chemistry, physics, materials science and electronics. More than power sources for everything from smartphones to electric vehicles, they remain a strong motivation for scientific inquiry that seeks to fully understand their structure and evolution at the molecular level.
A team led by Yingjie Zhang, a professor of materials science and engineering in The Grainger College of Engineering at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign, has completed the first investigation into a widely acknowledged but often overlooked aspect of electrochemical cells: the nonuniformity of the liquid at the solid-liquid interfaces in the cells.
As the researchers report in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, microscopic imaging revealed that these interfacial structures, called electrical double layers (EDLs), tend to organize into specific configurations in response to chemical deposition on the surface of the solid. The paper is titled “Nucleation at solid–liquid interfaces is accompanied by the reconfiguration of electrical double layers.”

Research led by Rutgers suggests there could be significant new possibilities for treating neurodegenerative diseases and brain injuries.
Researchers have uncovered how a specific protein supports the stability of connections between brain cells, which are essential for learning and memory.
According to the scientists, their findings, published in the journal Science Advances.


At the Large Hadron Collider, scientists from the University of Kansas achieved a fleeting form of modern-day alchemy — turning lead into gold for just a fraction of a second. Using ultra-peripheral collisions, where ions nearly miss but interact through powerful photon exchanges, they managed to knock protons out of nuclei, creating new, short-lived elements. This breakthrough not only grabbed global attention but could help design safer, more advanced particle accelerators of the future.
Philip Goff joins me to discuss panpsychism, cosmopsychism, and how these theories of consciousness have the potential to explain one of the most striking discoveries of modern science: the fine-tuning of the universe for intelligent life.
To purchase Philip’s book, \.

The global voluntary carbon market (VCM) is a critical tool for mobilizing finance for decarbonization efforts. As the market for carbon credits has grown, however, the value and effectiveness of the market has come under scrutiny.
To restore trust and increase confidence in the market, it is critical that carbon credits represent real, additional, verifiable emission reductions. The credibility and integrity of carbon credits rely heavily on the standards governing their creation and purchase. Strengthening market mechanisms, ensuring rigorous accounting standards, and increasing global cooperation are all essential to ensure that carbon markets contribute towards a low-carbon future.