New governance models and new ways for us to interact are needed to help address existential challenges like climate change.



Summary: Histone H4 mutations in the spool cause intellectual disabilities and developmental delays, a new study reports.
Source: University of Otago.
University of Otago-led research has identified a new rare genetic mutation which will finally give families around the world answers as to what is affecting their loved one.


The plan is there is no plan.
So it turns out we may be America’s worst-designed city. Lack of “official” zoning. Messy roads and meager public transportation options. Complete chaos. We get it, our predecessors sucked at design. But that may not necessarily be a bad thing. In fact, there are a bunch of ways in which the city totally (and unintentionally) came out ahead in the whole “the plan is there is no plan” deal.
Love it or hate it, Houston’s lack of zoning may actually be what shielded it from the popped housing bubble that rocked the rest of the country. Picture Margot Robbie explaining this all whilst in a bubble bath drinking champagne. While housing prices soared as the national bubble inflated, Houston’s costs remained modest; and when all hell broke loose when the bubble burst, H-town remained largely unaffected.
As discussed in an article from the Chron, senior economist Bill Gilmer found that zoning regulations were partly to blame. First, the laws constricted supply, which resulted in raising the cost of new home construction. As housing demand increased, cities with strict zoning laws saw prices increase due to the lack of supply. In turn, the high housing prices extinguished demand and — BOOM — the mortgage market collapsed and chaos consumed the majority of the country — minus Houston, where the increase in demand was met with an increase in construction/supply. Or something like that. Whatever. Margot Robbie in a bubble bath.

Over the past decade or so, many researchers worldwide have been trying to develop brain-inspired computer systems, also known as neuromorphic computing tools. The majority of these systems are currently used to run deep learning algorithms and other artificial intelligence (AI) tools.
Researchers at Sandia National Laboratories have recently conducted a study assessing the potential of neuromorphic architectures to perform a different type of computations, namely random walk computations. These are computations that involve a succession of random steps in the mathematical space. The team’s findings, published in Nature Electronics, suggest that neuromorphic architectures could be well-suited for implementing these computations and could thus reach beyond machine learning applications.
“Most past studies related to neuromorphic computing focused on cognitive applications, such as deep learning,” James Bradley Aimone, one of the researchers who carried out the study, told TechXplore. “While we are also excited about that direction, we wanted to ask a different and complementary question: can neuromorphic computing excel at complex math tasks that our brains cannot really tackle?”
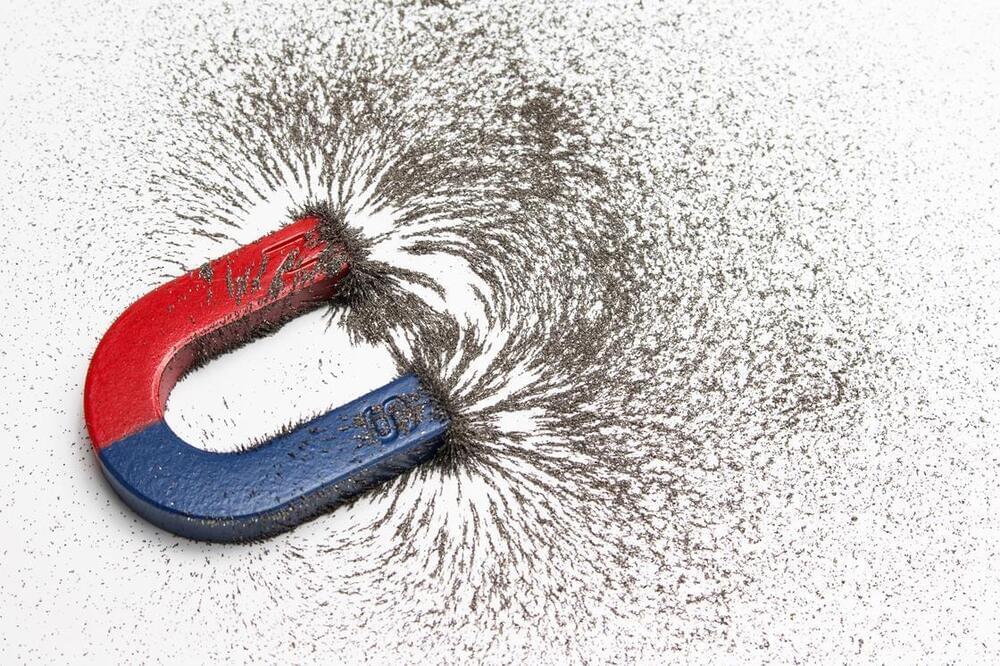


Probability of a reaction occurring increases 100-fold and points to quantum control of chemistry.
A new step towards quantum control of chemistry has been achieved by researchers in the US, who found that tuning the magnetic field applied to colliding ultracold molecules could alter the probability of them reacting or undergoing inelastic scattering a 100-fold.1 The work could potentially prove useful for producing large ensembles of molecules in the same state and investigating their properties.
At room temperature, the random thermal motion of atoms and molecules blurs the quantum nature of chemistry. In an ultracold regime, however, this thermal motion is stilled, revealing chemical interactions as quantum interference processes between matter waves. Remarkable phenomena have been seen in ultracold atomic gases, such as the creation of Bose–Einstein condensates, in which atoms all enter the quantum ground state of a trap, allowing a macroscopic view of their quantum wavefunction. Wolfgang Ketterle at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT), whose group performed the new research, shared the 2001 physics Nobel prize for the creation of this condensate.
Cooling molecules to the ground state of a trap is much trickier than cooling atoms because they can contain thermal energy in so many internal degrees of freedom, and was only achieved by Jun Ye of JILA in the US and colleagues recently.2 In 2020, Ye’s group applied an electric field to potassium–rubidium molecules, which decay into diatomic potassium and rubidium molecules. The researchers showed that, at a specific field, the molecules were excited into states forbidden by quantum mechanics and could get close enough to react. This drastically slowed the decay rate. ‘For our system, we typically think that, if the two molecules get very close together, there is close to a 100% chance that they will undergo a chemical reaction,’ explains Kyle Matsuda, Ye’s PhD student and the 2020 paper’s lead author.
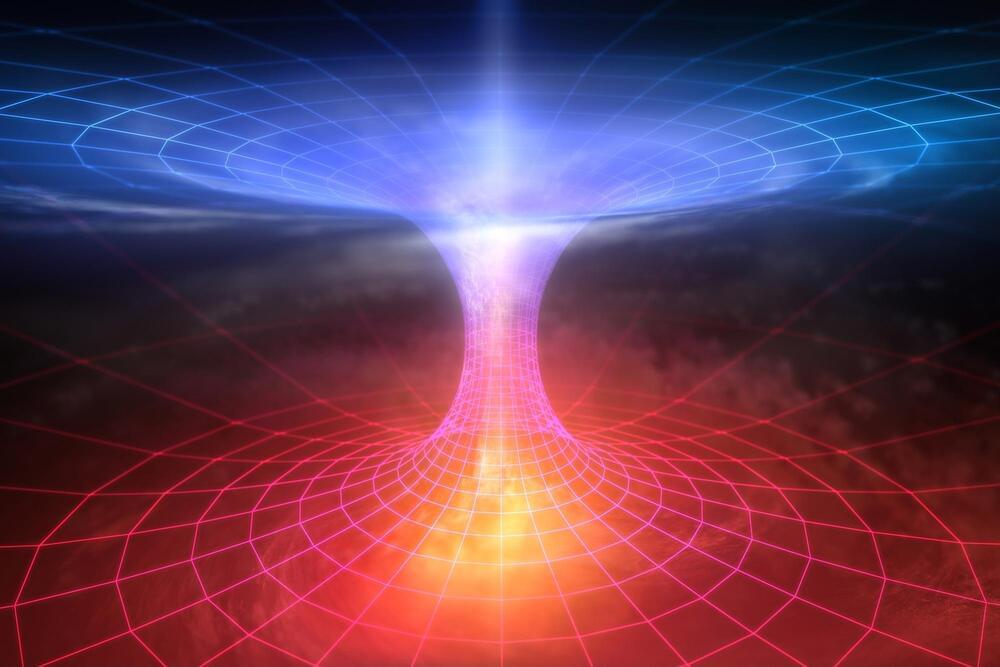


A mathematical analysis helps illuminate the puzzle over how information escapes from a black hole.
A RIKEN physicist and two colleagues have found that a wormhole—a bridge connecting distant regions of the Universe—helps to shed light on the mystery of what happens to information about matter consumed by black holes.
Einstein’s theory of general relativity predicts that nothing that falls into a black hole can escape its clutches. But in the 1970s, Stephen Hawking calculated that black holes should emit radiation when quantum mechanics, the theory governing the microscopic realm, is considered. “This is called black hole evaporation because the black hole shrinks, just like an evaporating water droplet,” explains Kanato Goto of the RIKEN Interdisciplinary Theoretical and Mathematical Sciences.