The US reportedly kept the test a secret for weeks for fear of spooking Moscow, following Russia’s own hypersonic use.



SpaceX’s first upgraded 33-engine Super Heavy booster appears to have passed a crucial test with surprising ease, boding well for a smooth qualification process.
Attempting that test so early on did not appear to be SpaceX’s initial plan. Instead, shortly before Super Heavy Booster 4’s third and likely final removal from Starbase’s ‘orbital launch mount’ (OLM) on March 24th, SpaceX transported a massive structural test stand from a Starbase storage yard to the orbital launch site (OLS), where technicians have focused on modifying nearby ground systems to support apparent structural testing of Super Heavy Booster 7. As of March 31st, all available evidence suggested that SpaceX was preparing that stand to verify Booster 7’s mechanical strength and simulate the major stresses it might experience before investing a significant amount of time and resources in qualification testing.
However, SpaceX appeared to change its plans at the last minute.
Ahead of the Tesla Gigafactory unveil party Thursday, the company’s large presence in Austin has opened doors to new education and job opportunities for locals.

Oxford spinoff First Light Fusion says its novel “projectile” approach offers “the fastest, simplest and cheapest route to commercial fusion power.” The company is now celebrating a significant breakthrough with its first confirmed fusion reaction.
The nuclear fusion space is heating up, if you’ll pardon the pun, as the world orients itself toward a clean energy future. Where current nuclear power plants release energy by splitting atoms in fission reactions, fusion reactors will release energy in the same way the Sun does – by smashing atoms together so hard and so fast that they fuse into higher elements.
Most of the big tokamak and stellarator-based fusion projects in progress now intend to create monstrously high temperatures, higher than in the core of the Sun, in magnetically confined plasma, hoping to get those atoms moving fast enough to overcome the powerful repulsion between two nuclei.

Using a “laser pincer,” scientists can generate their own antimatter, simulations show.
An international team of physicists have come up with a way to generate antimatter in the lab, allowing them to recreate conditions that are similar to those near a neutron star.
This setup, at Helmholtz-Zentrum Dresden-Rossendorf (HZDR) research laboratory in Germany, involves two high-intensity laser beams that can generate a jet of antimatter, as outlined in a paper published earlier this summer in the journal Communications Physics. That could make antimatter-based research far more accessible for scientists around the world.
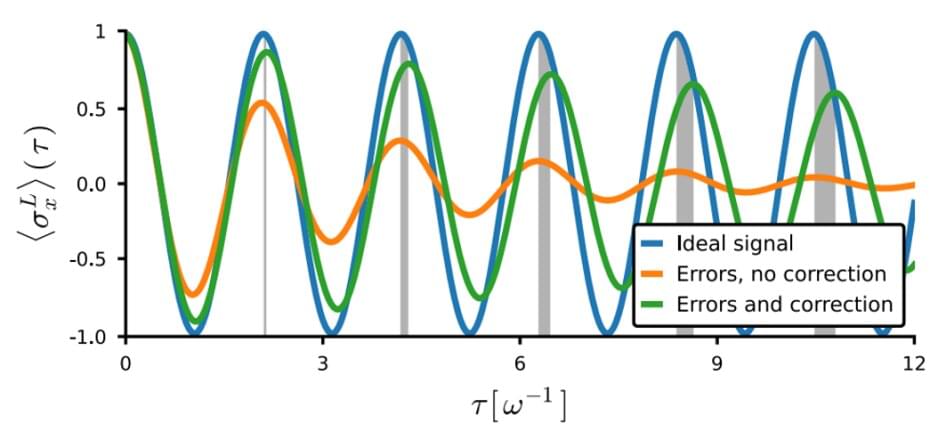
It is well established that quantum error correction can improve the performance of quantum sensors. But new theory work cautions that unexpectedly, the approach can also give rise to inaccurate and misleading results—and shows how to rectify these shortcomings.
Quantum systems can interact with one another and with their surroundings in ways that are fundamentally different from those of their classical counterparts. In a quantum sensor, the particularities of these interactions are exploited to obtain characteristic information about the environment of the quantum system—for instance, the strength of a magnetic and electric field in which it is immersed. Crucially, when such a device suitably harnesses the laws of quantum mechanics, then its sensitivity can surpass what is possible, even in principle, with conventional, classical technologies.
Unfortunately, quantum sensors are exquisitely sensitive not only to the physical quantities of interest, but also to noise. One way to suppress these unwanted contributions is to apply schemes collectively known as quantum error correction (QEC). This approach is attracting considerable and increasing attention, as it might enable practical high-precision quantum sensors in a wider range of applications than is possible today. But the benefits of error-corrected quantum sensing come with major potential side effects, as a team led by Florentin Reiter, an Ambizione fellow of the Swiss National Science Foundation working in the group of Jonathan Home at the Institute for Quantum Electronics, has now found. Writing in Physical Review Letters, they report theoretical work in which they show that in realistic settings QEC can distort the output of quantum sensors and might even lead to unphysical results.
Whether a computer could ever pass for a living thing is one of the key challenges for researchers in the field of Artificial Intelligence. There have been vast advancements in AI since Alan Turing first created what is now called the Turing Test—whether a machine could exhibit intelligent behavior equivalent to, or indistinguishable from, that of a human. However, machines still struggle with one of the fundamental skills that is second nature for humans and other life forms: lifelong learning. That is, learning and adapting while we’re doing a task without forgetting previous tasks, or intuitively transferring knowledge gleaned from one task to a different area.
Now, with the support of the DARPA Lifelong Learning Machines (L2M) program, USC Viterbi researchers have collaborated with colleagues at institutions from around the U.S. and the world on a new resource for the future of AI learning, defining how artificial systems can successfully think, act and adapt in the real world, in the same way that living creatures do.
The paper, co-authored by Dean’s Professor of Electrical and Computer Engineering Alice Parker and Professor of Biomedical Engineering, and of Biokinesiology and Physical Therapy, Francisco Valero-Cuevas and their research teams, was published in Nature Machine Intelligence, in collaboration with Professor Dhireesha Kudithipudi at the University of Texas at San Antonio, along with 22 other universities.

ABOUT PETER DIAMANDIS
Peter is the founder and executive chairman of the XPRIZE Foundation, and has started over 20 companies in the areas of longevity, space, venture capital and education. He is also the New York Times bestselling author of several books, including his latest, Life Force, which he published early in 2020 with Tony Robbins.
Peter joined host Robert Glazer on the Elevate Podcast to discuss transformational changes needed in education, how the pandemic accelerated global trends, and the astonishing medical and health technologies he believes will be widely available, sooner than you think.
