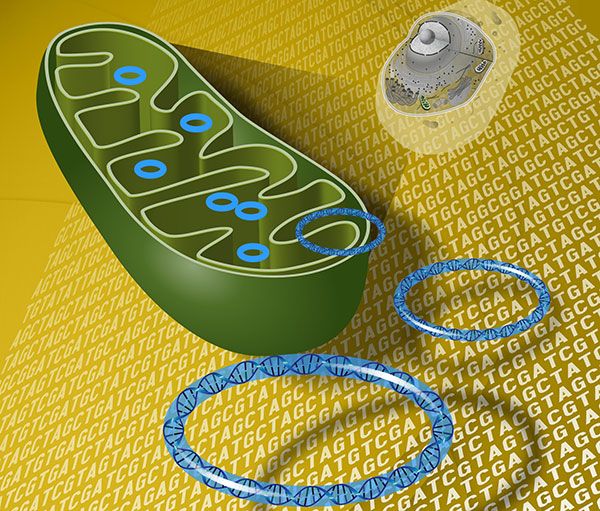
The solution was to split the protein into two harmless halves. Liu’s team, led by graduate student Beverly Mok, used 3D imaging data from the Mougous lab to work out how to divide the protein into two pieces. Each piece did nothing on its own, but when reunited, they reconstituted the protein’s full activity. The team fused each deaminase half to customizable DNA-targeting proteins that did not require guide RNAs. Those proteins bound to specific stretches of DNA, bringing the two halves of the deaminase together. That let the molecule regain its function and work as a precision gene editor—but only once it was correctly positioned.
Liu’s team used the technology to make precise changes to specific mitochondrial genes. Then, Mootha’s lab, which focuses on mitochondrial biology, ran tests to see whether the edits had the intended effect. “You could imagine that if you’re introducing editing machinery into the mitochondria, you might accidentally cause some sort of a catastrophe,” Mootha said. “But it was very clean.” The entire mitochondrion functioned well, except for the one part the scientists intentionally edited, he explained.
This mitochondrial base editor is just the beginning, Mougous suggested. It can change one of the four DNA letters into another. He hopes to find additional deaminases that he and Liu can develop into editors able to make other mitochondrial DNA alterations. Such tools could enable new strategies for treating mitochondrial diseases, as well as help scientists to model diseases and aid in drug testing. “The ability to precisely install or correct pathogenic mutations could accelerate the modeling of diseases caused by mtDNA mutations, facilitate preclinical drug candidate testing, and potentially enable therapeutic approaches that directly correct pathogenic mtDNA mutations,” the authors noted. “Bacterial genomes contain various uncharacterized deaminases, raising the possibility that some may possess unique activities that enable new genome-editing capabilities.”