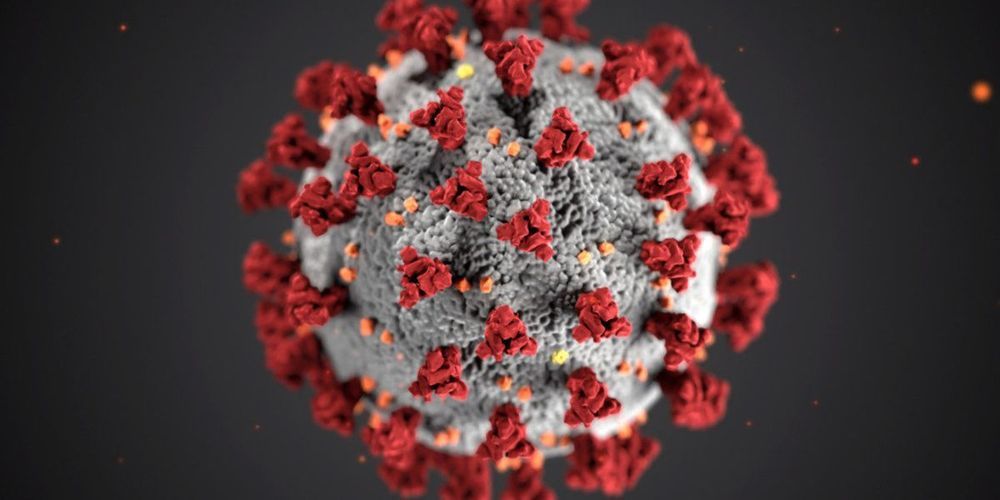
Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) is an emerging global pandemic that is threatening the viability of healthcare systems worldwide. The virus responsible for the disease is also known as severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 and abbreviated as SARS-CoV-2. The eruption started in China on December 29, 2019 and by March 2020 it was reported that it had spread to several countries across the world.

In the final days of 2019, Chinese doctors identified a number of similar cases of pneumonia in the city of Wuhan in China. Wuhan is the capital city of Hubei Province in China accommodating 11 million inhabitants. Soon, it was discovered that the disease was caused by a new strain of virus which was named SARS-CoV-2.