Dr. Michio Kaku on what is likely and what is possible provides a stimulating vision of the future.
Get the latest international news and world events from around the world.
What’s Hidden Under the Type 6 Civilization?
Ridddle!
We are a smart and educated community of over 10 million subscribers worldwide. We can’t stand aside! $1 from each of you is $10 million to help Ukraine stand and fight back the evil. You can help stop the Russian invasion into an independent European country. Millions of civilians are now hiding in bomb shelters while their homes are being destroyed by Putin.
Act now!
Support Ukraine.
https://bank.gov.ua/en/news/all/natsionalniy-bank-vidkriv-sp…ebi-armiyi
This Insane Chinese Supercomputer Changes EVERYTHING
The smartest Scientists of both China and the United States are working hard on creating the fastest hardware for future Supercomputers in the exaflop and zettaflop performance range. Companies such as Intel, Nvidia and AMD are continuing Moore’s Law with the help of amazing new processes by TSMC. These supercomputers are secret projects by the government in hopes of beating each other in the tech industry and to prepare for Artificial Intelligence.
–
TIMESTAMPS:
00:00 A new Superpower in the making.
00:46 A Brain-Scale Supercomputer?
02:47 China Tech vs USA Tech.
05:30 Chinese Semiconductor Technology.
07:39 Last Words.
–
#china #computing #usa

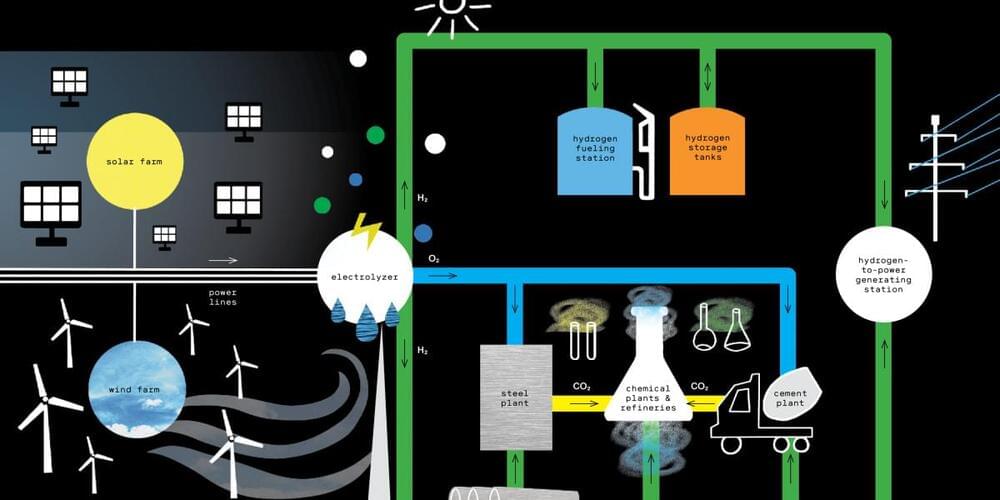
New Quantum Technology To Make Charging Electric Cars As Fast as Pumping Gas
Quantum charging will cut the charging time of electric vehicles from ten hours to three minutes.
Whether it’s photovoltaics or fusion, sooner or later, human civilization must turn to renewable energies. This is deemed inevitable considering the ever-growing energy demands of humanity and the finite nature of fossil fuels. As such, much research has been pursued in order to develop alternative sources of energy, most of which utilize electricity as the main energy carrier. The extensive R&D in renewables has been accompanied by gradual societal changes as the world adopted new products and devices running on renewables. The most striking change as of recently is the rapid adoption of electric vehicles. While they were hardly seen on the roads even 10 years ago, now millions of electric cars are being sold annually. The electric car market is one of the most rapidly growing sectors, and it helped propel Elon Musk to become the wealthiest man in the world.
Unlike traditional cars which derive energy from the combustion of hydrocarbon fuels, electric vehicles rely on batteries as the storage medium for their energy. For a long time, batteries had far lower energy density than those offered by hydrocarbons, which resulted in very low ranges of early electric vehicles. However, gradual improvement in battery technologies eventually allowed the drive ranges of electric cars to be within acceptable levels in comparison to gasoline-burning cars. It is no understatement that the improvement in battery storage technology was one of the main technical bottlenecks which had to be solved in order to kickstart the current electric vehicle revolution.

Space WiFi? A new startup wants to give NASA’s moonbase an internet connection
If we are to set up a permanent base on the Moon, we will need some solid connection.
A space startup company is trying to make that happen. Aquarian Space recently announced receiving $650,000 in seed funding to develop a possible broadband internet connection that would link the Earth to the Moon, and maybe even Mars.
The company aims to deploy its first communications system to the Moon by 2024 in anticipation of increased demand from planned space missions to the Moon and beyond, both public and private ventures.
“In 2021 there were 13 landers, orbiters, and rovers on and around the moon,” Kelly Larson, CEO of Aquarian Space, said in a statement released Thursday. “By 2030, we will have around 200, creating a multibillion-dollar lunar economy. But this can’t happen without solid, reliable Earth-to-moon communications.”

Malware That Can Survive OS Reinstalls Strikes Again, Likely for Cyberespionage
A new malware strain that can survive operating system reinstalls was spotted last year secretly hiding on a computer, according to the antivirus provider Kaspersky.
The company discovered the Windows-based malware last spring running on a single computer. How the malicious code infected the system remains unclear. But the malware was designed to operate on the computer’s UEFI firmware, which helps boot up the system.
The malware, dubbed MoonBounce, is especially scary because it installs itself on the motherboard’s SPI flash memory, instead of the computer’s storage drive. Hence, the malware can persist even if you reinstall the computer’s OS or swap out the storage.