Microsoft is already aware of the problem.



At what point do “you” end and the outside world begins?
It might feel like a weird question with an obvious answer, but your brain has to work surprisingly hard to judge that boundary. Now, scientists have linked a specific set of brain waves in a certain part of the brain to a sense of body ownership.
In a series of new experiments, researchers from Sweden and France put 106 participants through what’s called the rubber hand illusion, monitoring and stimulating their brain activity to see what effect it had.
Now online! (Cell 186786–802.e1–e15; February 16, 2023)
Now online! (Cell 186, 786–802.e1–e15; February 16, 2023)
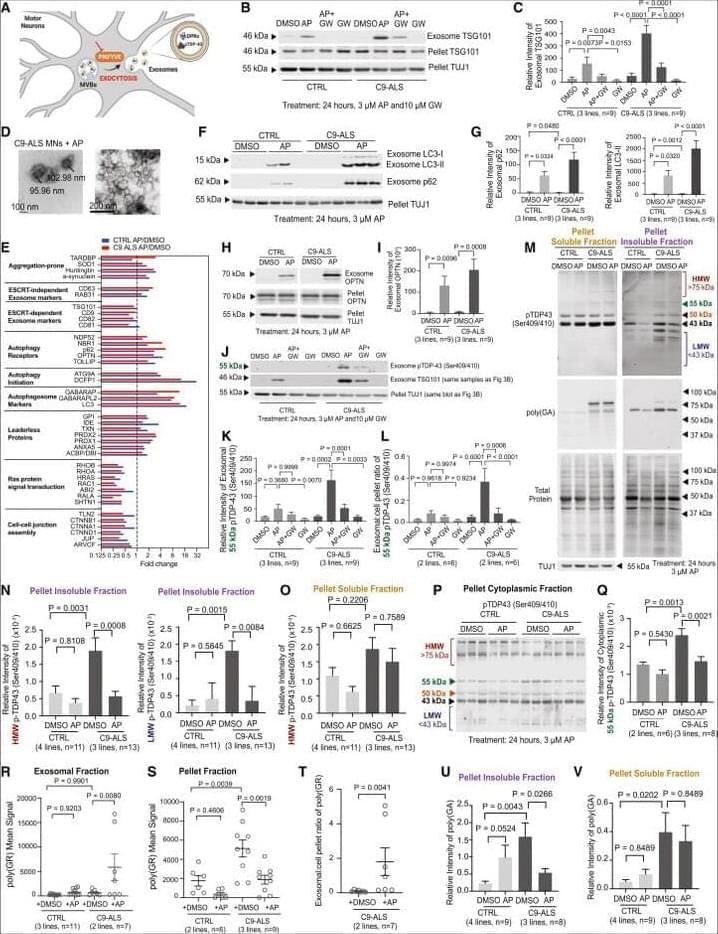
In our original published article, we performed western blots and imaging of induced motor neurons (iMNs) to elucidate the mechanism through which PIKFYVE inhibition causes secretion and clearance of aggregation-prone proteins such as phosphorylated TDP-43 (pTDP-43). Since publication, we have become aware of 3 errors in figure legends or images that we are now correcting.

Structure basis for the activation of KCNQ2 by endogenous and exogenous ligands.
Zhao et al. report cryo-EM structures of human KCNQ2 in complex with QO-58 and QO-83 in multiple conformations, with or without PIP2. Together with electrophysiological and computational analyses, these structures provide insight into the channel’s activation mechanism and support the rational design of targeted anti-epileptic therapies.
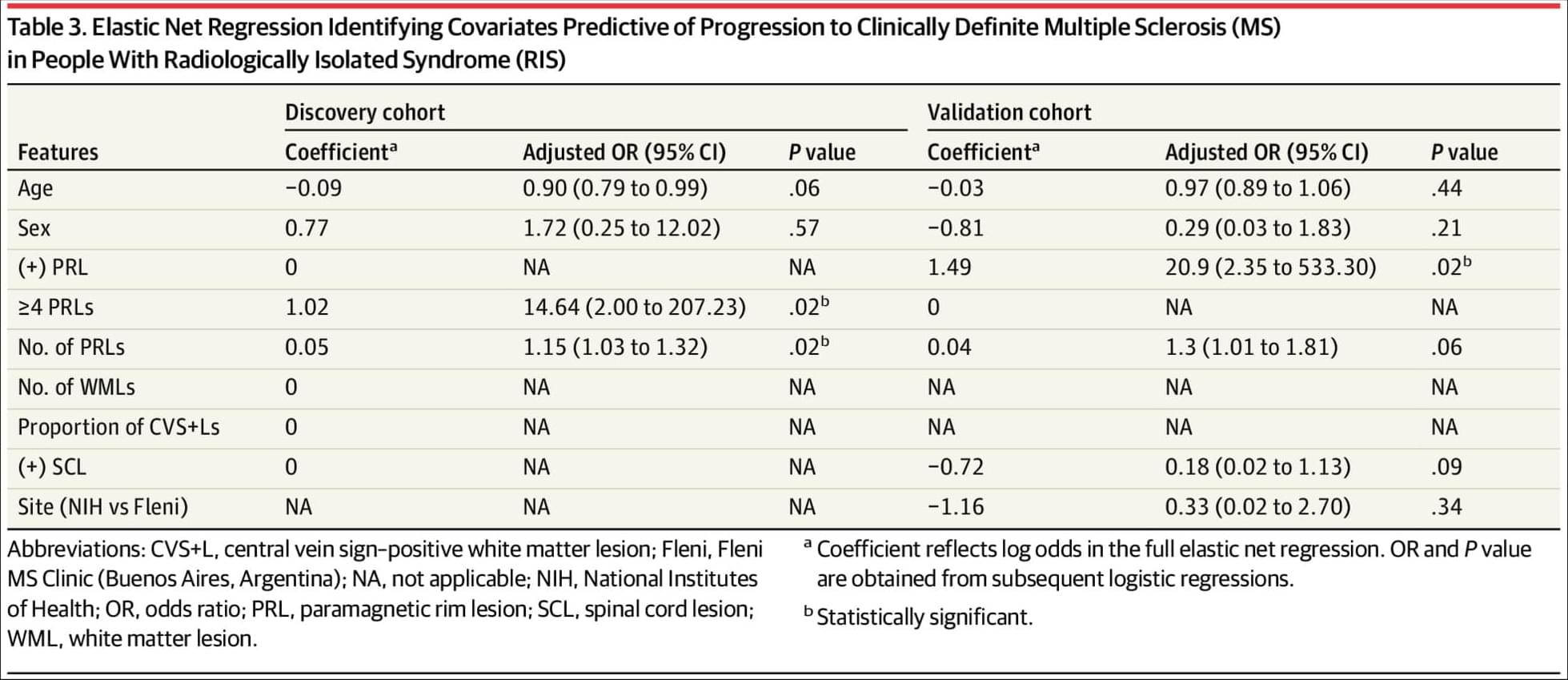
In #RadiologicallyIsolatedSyndrome, greater paramagnetic rim lesion burden on MRI was associated with increased risk and earlier development of clinical MultipleSclerosis.
Question Are paramagnetic rim lesions (PRLs) and central vein sign–positive white matter lesions (CVS+L) associated with developing clinical symptoms of multiple sclerosis (MS) in people with radiologically isolated syndrome (RIS)?
Findings In this cohort of 36 people with RIS, a higher PRL count was associated with a shorter time to developing clinical symptoms of MS and was an independent predictor of symptom onset; these findings were validated in an independent cohort of 43 people with RIS.
Meaning Results show that PRLs may have prognostic utility for risk stratification and help guide treatment decisions in people with RIS, the earliest detectable stage of MS.

Complement inhibition showed promising clinical improvement in this single case of dysferlinopathy.
Dysferlinopathy is a rare autosomal recessively inherited myopathy, presenting as several phenotypes, including a proximal weakness dominant limb-girdle muscular dystrophy R2 phenotype and a distal weakness dominant Miyoshi distal myopathy phenotype.1,2 Muscle weakness usually emerges in young adulthood, followed by a progressive motor decline over the first decade, which tends to be more rapid in individuals with earlier onset.3 Dysferlinopathy is caused by pathogenic variants of the DYSF gene that impair function of dysferlin, a protein that cooperates with others to repair membranes and restore skeletal muscle integrity after injury.4
To date, no effective treatment for dysferlinopathy has been clinically validated. Promising approaches, including exon skipping and gene editing targeting the DYSF gene, as well as myoblast transplantation, are still under investigation in preclinical models.5 Although dysferlinopathy often presents with inflammatory features on muscle pathology and is prone to misdiagnosis as myositis, it is characterized by the absence of focal MHC-I expression and complement C5b-9 deposition on nonnecrotic sarcolemma, which help distinguish it from other muscular dystrophies and inflammatory myopathies.6,7 Specially, complement C3 gene knockout in dysferlin-deficient mice has been demonstrated being able to reverse muscle pathology and improve motor function in the previous animal research.

Even with delayed intervention, this neuroprotective agent delivers lasting protection to the hypertensive brain from ischemic injury.
BackgroundIn spite of the advances in understanding the pathophysiology of stroke, successful treatment remains a major challenge. The lack of consideration of preclinical studies with associated comorbidities is a primary factor for the translational failure, as ~94% of patients with stroke have ≥1 preexisting comorbidities. Because hypertension is the most common comorbid condition in patients with stroke and predisposition to hypertension is known to worsen stroke outcome, we evaluated the efficacy of a novel neuroprotective peptide derived from the brain‐enriched and neuron‐specific tyrosine phosphatase striatal enriched phosphatase (STEP) in attenuating ischemic brain damage under hypertensive conditions.

Internal carotid artery (ICA) bifurcation (ICAB) aneurysms carry high rupture risk, treatment challenges, and recurrence due to complex morphology and origination patterns. Given their relatively low incidence, research on ICAB morphology is limited. This study analyzed ICAB morphology in aneurysmal, contralateral, and healthy bifurcations, highlighting bilateral differences, anterior cerebral artery (ACA) dominance, and deviations from the vascular optimality principle (VOP).
A total of 194 angiographic volumes (40 aneurysmal, 28 contralateral, 126 healthy) were evaluated. ICAB morphology included parent/daughter vessel diameters and angle between the ICA and middle cerebral artery (MCA; ФMCA), angle between the ICA and ACA (ФACA), total ICAB angle (ФICAB; ФMCA + ФACA). Aneurysm characteristics (size, neck, origination) and VOP parameters (radius ratio [RR] and junction exponent [n]) were evaluated. Bilateral analysis accounted for ACA dominance.
Compared with controls, aneurysmal ICABs exhibited wider ΦMCA (57.22° ± 12.22° vs 43.74° ± 9.41°, p < 0.001; area under the curve [AUC] = 0.83) and ΦICAB (160.27° ± 16.16° vs 143.66° ± 10.74°, p < 0.001; AUC = 0.79), but not ΦACA, in univariate, multivariate (AUC = 0.85), and bilateral analyses. Angle thresholds of 51.7° for ΦMCA and 152.4° for ΦICAB were identified. Aneurysms originated predominantly off the apex (65%) and ACA (30%). Most occurred on ICABs with dominant (31%) and codominant (58%) A1 segments. Aneurysm neck, but not size, correlated with ΦMCA and ΦICAB, but not ΦACA. In controls, ΦMCA was larger and ΦACA smaller on the dominant A1 side, with no ΦICAB difference. There was no statistically significant difference in RR and n values regardless of aneurysm presence and dominance status.
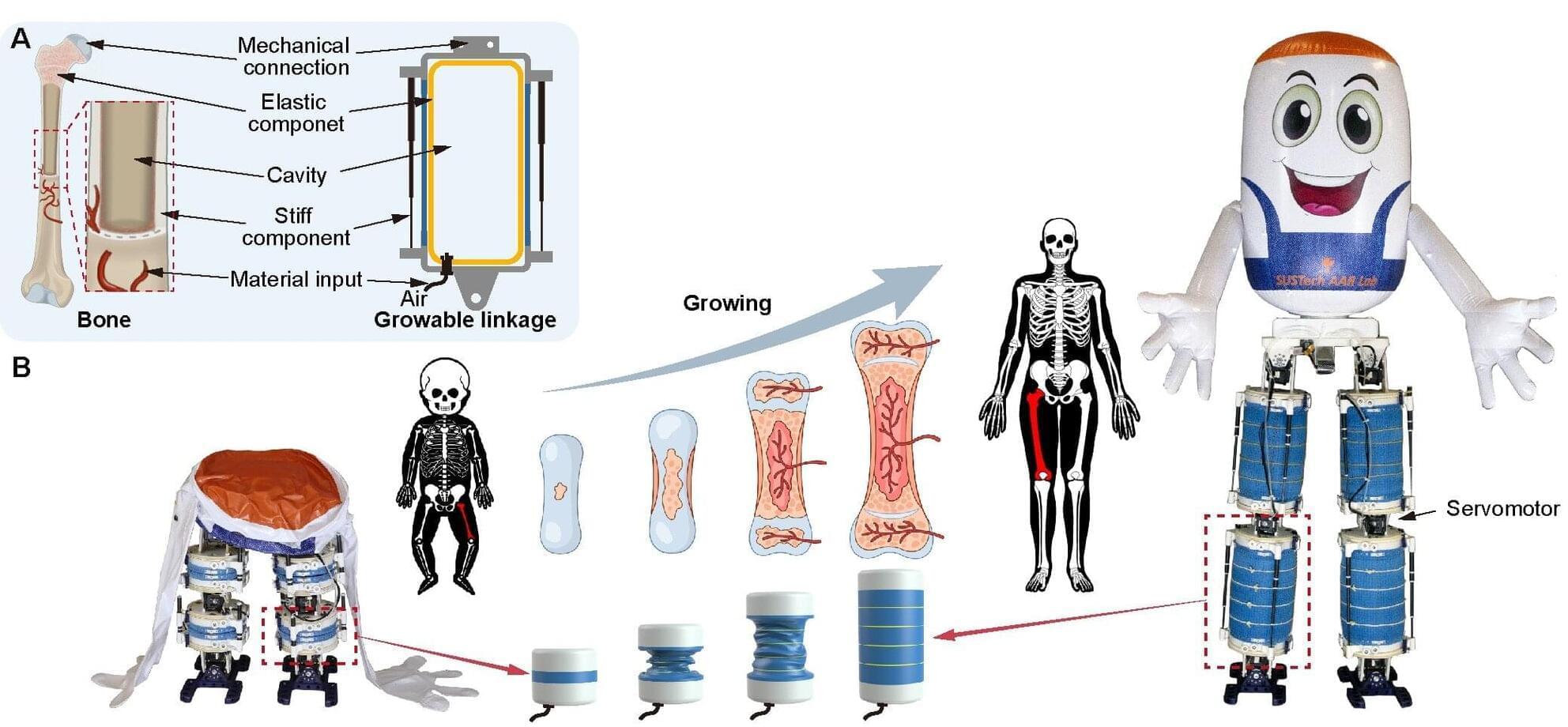
Humanoid robots look impressive and have enormous potential to change our daily lives, but they still have a reputation for being clunky. They’re also heavy and stiff, and if they fall, they can easily break and injure people around them.
But that could be about to change. Researchers at the Southern University of Science and Technology (SUST) in Shenzhen have unveiled a soft humanoid robot that can change its size, squeeze through spaces, and even walk on water. The key to this outstanding flexibility is a system the team developed called GrowHR. The research, published in Science Advances, describes how the robot was inspired by the way human bones develop.