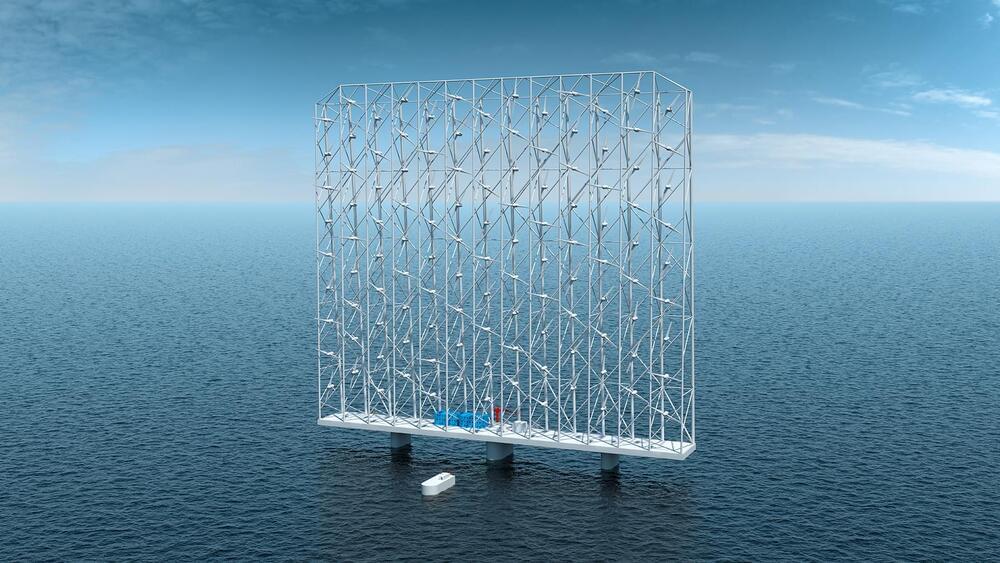
The system’s stacked formation effectively creates a wall of wind turbines.

New technologies have considerably improved scientists’ ability to locate the genetic variations that distinguish our DNA from that of other people. In some instances, these genetic differences give rise to diverse superhuman abilities. There is growing interest in identifying genes associated with special abilities, many of which seem to be inherited. Some consider people like Wim Hof a.k.a the iceman known for the Wim Hof method as a person with superhuman abilities.
As for the future, according to prominent scientists within 30 years, it will probably be possible to make essentially any kind of change to any kind of genome.
#superhuman #science #sciencetime.
Sources:
Supergenes — https://arep.med.harvard.edu/gmc/protect.html.
George Church — Genetic Superpowers: Changing Your Genome and Environment, Harvard Medical School.


𝙎𝙡𝙚𝙚𝙥 𝙢𝙖𝙮 𝙗𝙚 𝙤𝙣𝙚 𝙤𝙛 𝙩𝙝𝙚 𝙢𝙤𝙨𝙩 𝙥𝙤𝙩𝙚𝙣𝙩 𝙢𝙚𝙙𝙞𝙘𝙞𝙣𝙚𝙨 𝙛𝙤𝙧 𝙩𝙝𝙚 𝙗𝙧𝙖𝙞𝙣, 𝙨𝙘𝙞𝙚𝙣𝙩𝙞𝙨𝙩𝙨 𝙖𝙧𝙚 𝙙𝙞𝙨𝙘𝙤𝙫𝙚𝙧𝙞𝙣𝙜, 𝙖𝙨 𝙩𝙝𝙚𝙮 𝙚𝙭𝙥𝙡𝙤𝙧𝙚 𝙩𝙝𝙚 𝙞𝙣𝙣𝙚𝙧 𝙡𝙖𝙗𝙮𝙧𝙞𝙣𝙩𝙝𝙨 𝙤𝙛 𝙩𝙝𝙚 𝙩𝙝𝙧𝙚𝙚-𝙥𝙤𝙪𝙣𝙙 𝙤𝙧𝙜𝙖𝙣 𝙙𝙪𝙧𝙞𝙣𝙜 𝙙𝙚𝙚𝙥 𝙨𝙡𝙚𝙚𝙥 𝙖𝙣𝙙 𝙙𝙧𝙚𝙖𝙢 𝙘𝙮𝙘𝙡𝙚𝙨 𝙞𝙣 𝙗𝙤𝙩𝙝 𝙝𝙚𝙖𝙡𝙩𝙝 𝙖𝙣𝙙 𝙙𝙞𝙨𝙚𝙖𝙨𝙚.
The Neuro-Network.
𝐂𝐚𝐧 𝐝𝐞𝐞𝐩 𝐬𝐥𝐞𝐞𝐩 𝐡𝐞𝐥𝐩 𝐝𝐞𝐯𝐚𝐬𝐭𝐚𝐭𝐢𝐧𝐠 𝐛𝐫𝐚𝐢𝐧 𝐝𝐢𝐬𝐨𝐫𝐝𝐞𝐫𝐬? 𝐒𝐜𝐢𝐞𝐧𝐭𝐢𝐬𝐭𝐬 𝐬𝐭𝐮𝐝𝐲𝐢𝐧𝐠 𝐏𝐚𝐫𝐤𝐢𝐧𝐬𝐨𝐧’𝐬 𝐰𝐚𝐧𝐭 𝐭𝐨 𝐟𝐢𝐧𝐝 𝐨𝐮𝐭
𝙈𝙚𝙙𝙞𝙘𝙖𝙓𝙥𝙧𝙚𝙨𝙨:
Sleep may be one of the most potent medicines for the brain, scientists are discovering, as they explore the inner labyrinths of the three-pound organ during deep sleep and dream cycles in both health and disease.
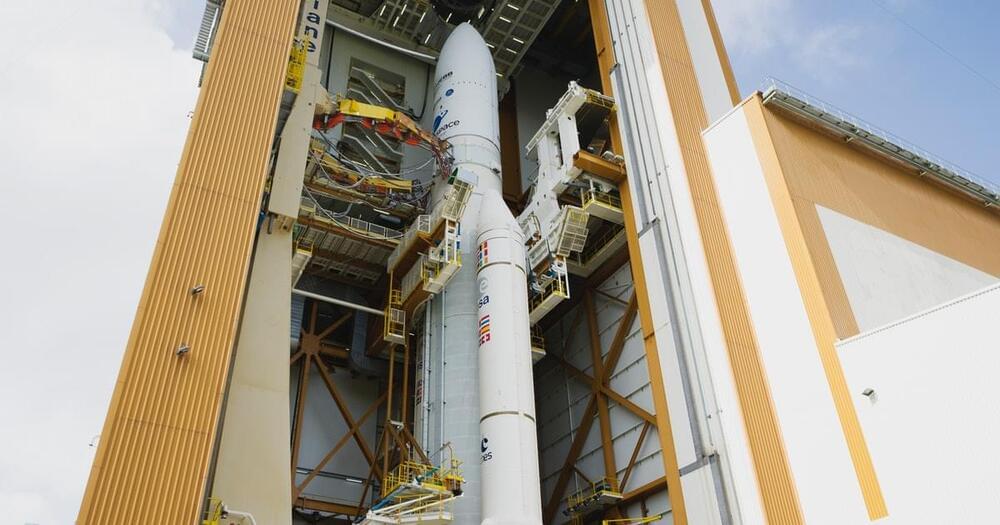

The December 25 launch of the James Webb Space Telescope was a career-capping triumph for the ESA Ariane 5 rocket. The Ariane 6 cometh soon.
While the December 25 launching of the James Webb Space Telescope was a triumph for the ESA Ariane 5 launch vehicle, it will cap its career. The Ariane 6 cometh.

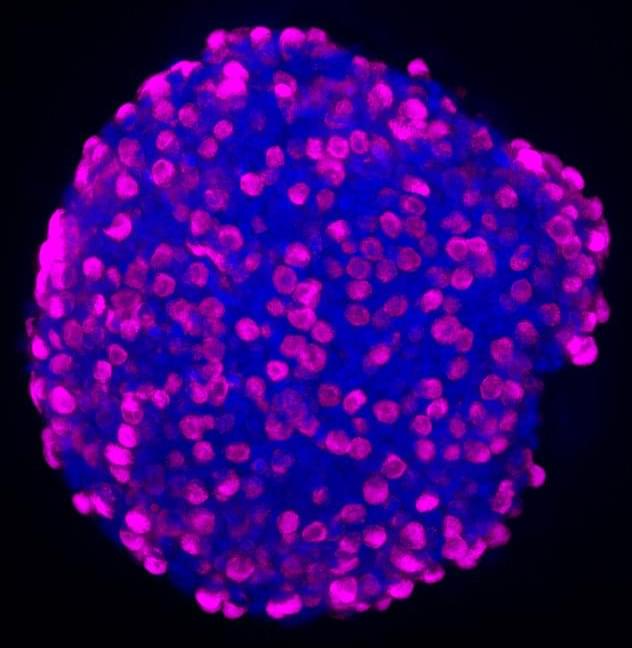
A newly developed technology platform has the potential to treat diseases like diabetes, IBS, and obesity by using enteroendocrine (EE) cells found in human intestinal cells, according to a recent study. Although enteroendocrine cells make up only about 1% of intestinal cells, they produce around fifteen different hormones that play a role in regulating digestion and metabolic function.
Creating Organoids
The new organoid platform, developed at Boston Children’s Hospital, is meant to pinpoint drugs that can increase the amount of EEs and encourage them to generate more needed hormones. “There’s been interest in exploiting human intestinal stem cells and EE cells to treat disease,” says David Breault, MD, Ph.D. in a statement. Breault is associate chief of the Division of Endocrinology at Boston Children’s. “But the field is still in a nascent stage. This will open new avenues of discovery.”
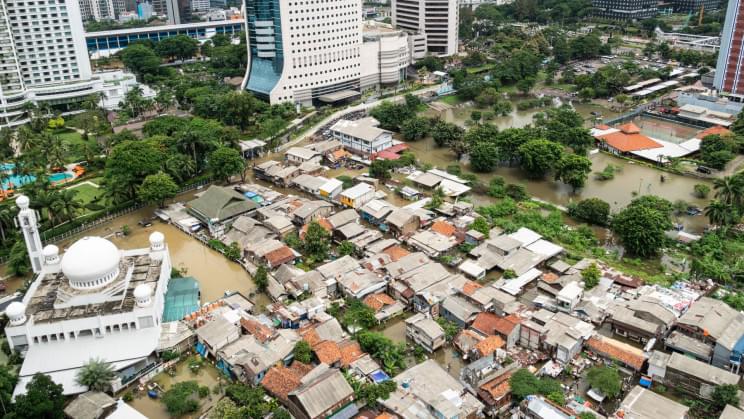

“The main goal is to build a smart new city, a new city that is competitive at the global level, to build a new locomotive for the transformation… toward an Indonesia based on innovation and technology based on a green economy.”
Environmental groups not on board However, not all are on board with Widodo’s new plans. Environmental groups worry that the new city may disturb the orangutans, leopards, and other wildlife that already live there. There is also the fact that the new development would cost a whopping $34 billion, a price much too high to pay during an already costly pandemic.
Full Story:
Pretty soon it won’t just be Indonesia’s Navy submarine that will have disappeared. Its capital city Jakarta is also sinking quickly.
Indonesia is looking to replace its capital city because it is very polluted, congested, susceptible to earthquakes, and quickly sinking, according to the Associated Press. The country now aims to build a more sustainable, cleaner, and resilient capital city.
A smart new city
