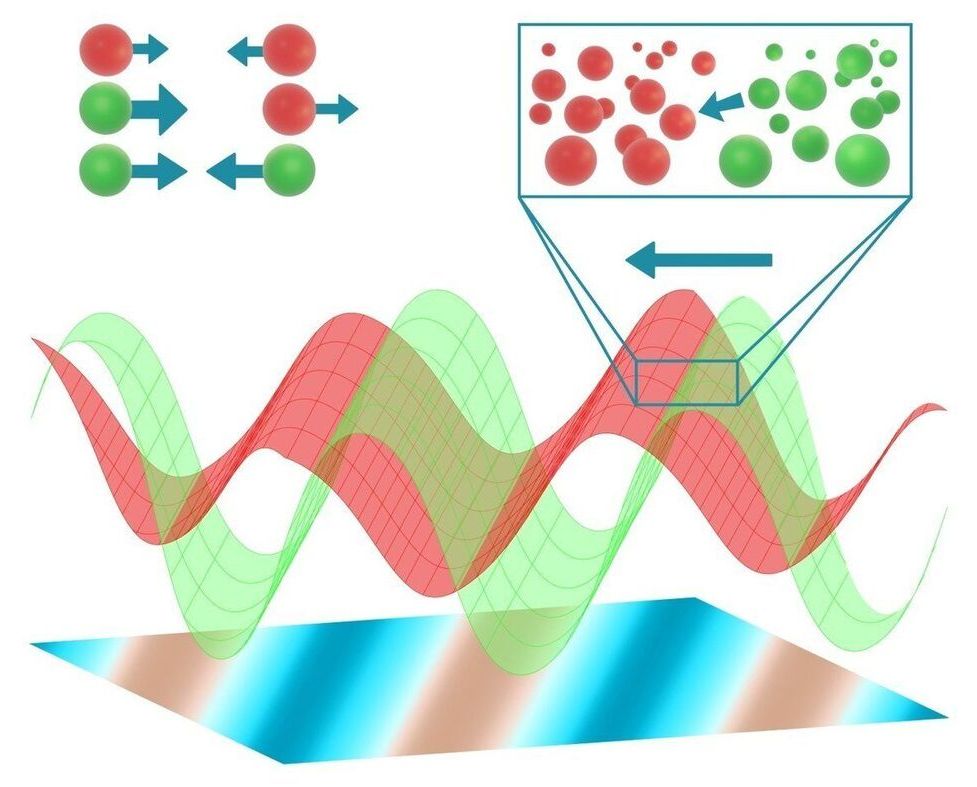
At first glance, a pack of wolves has little to do with a vinaigrette. However, a team led by Ramin Golestanian, Director at the Max Planck Institute for Dynamics and Self-Organization, has developed a model that establishes a link between the movement of predators and prey and the segregation of vinegar and oil. They expanded a theoretical framework that until now was only valid for inanimate matter. In addition to predators and prey, other living systems such as enzymes or self-organizing cells can now be described.
Order is not always apparent at first glance. If you ran with a pack of wolves hunting deer, the movements would appear disordered. However, if the hunt is observed from a bird’s eye view and over a longer period of time, patterns become apparent in the movement of the animals. In physics, such behavior is considered orderly. But how does this order emerge? The Department of Living Matter Physics of Ramin Golestanian is dedicated to this question and investigates the physical rules that govern motion in living or active systems. Golestanian’s aim is to reveal universal characteristics of active, living matter. This includes not only larger organisms such as predators and prey but also bacteria, enzymes and motor proteins as well as artificial systems such as micro-robots. When we describe a group of such active systems over great distances and long periods of time, the specific details of the systems lose importance.