On large, isolated construction sites, reliable remote operations are a game changer. See how BAM Nuttall remotely deployed Spot for 3D laser scanning using a p… See more.
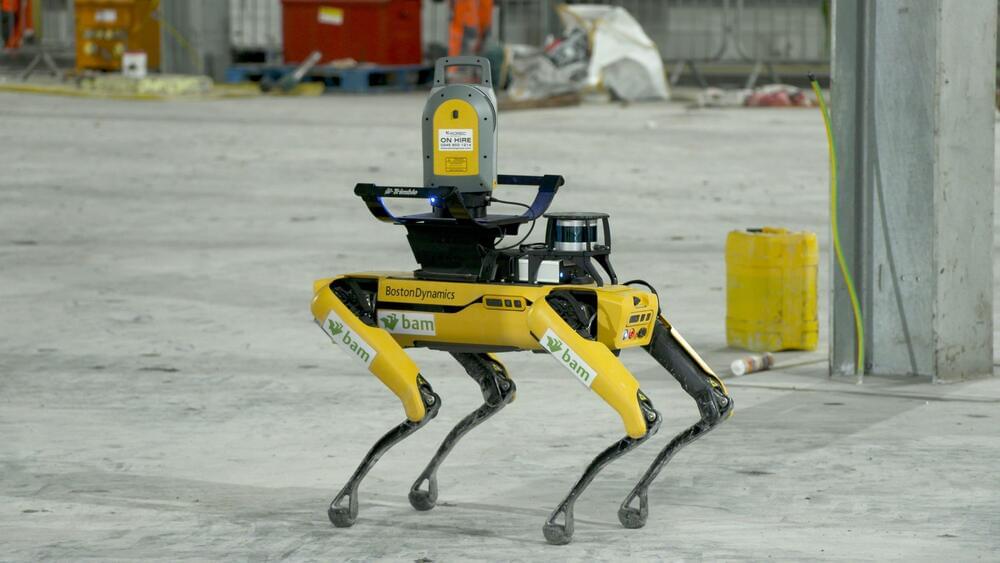
On a large and remote construction site in Shetland, where the team is battling the elements, covering large distances every day, the Trimble and Boston Dynamics integrated robot solution has become man’s newest four-legged friend.
BAM Nuttall has successfully trialled the integrated Trimble X7 laser scanner with Boston Dynamics’ Spot® robot in a remote construction setting — utilising a private stand-alone 5G network for remote control — in the first use case of its kind.
Enlisting Spot as the newest member of the site team, the four-legged robot has used specially adapted 3D laser scanning equipment to collect data and create site records. Spot and the Trimble X7 payload were controlled remotely using a private 5G communications network covering the 55,176 m2 site, marking the robot’s first 5G deployment in the U.K.