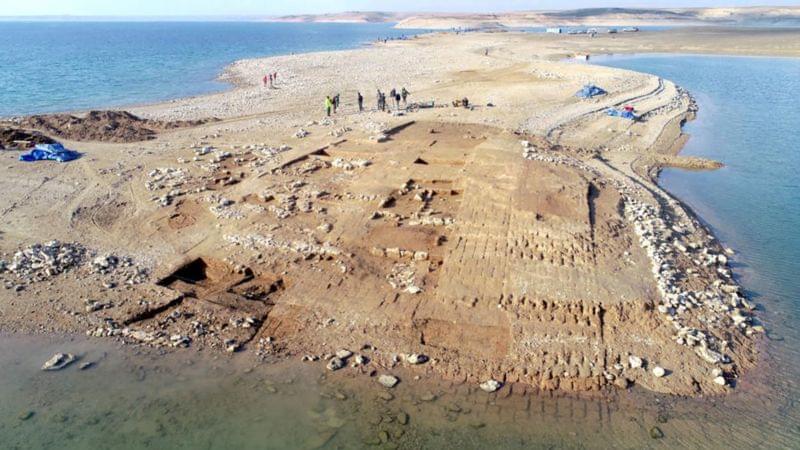
Little is known about the ancient Mittani people who built the city, largely due to the fact that researchers have not identified the empire’s capital or discovered their archives, Puljiz said. However, certain artifacts unearthed during the latest excavation could help provide insight.
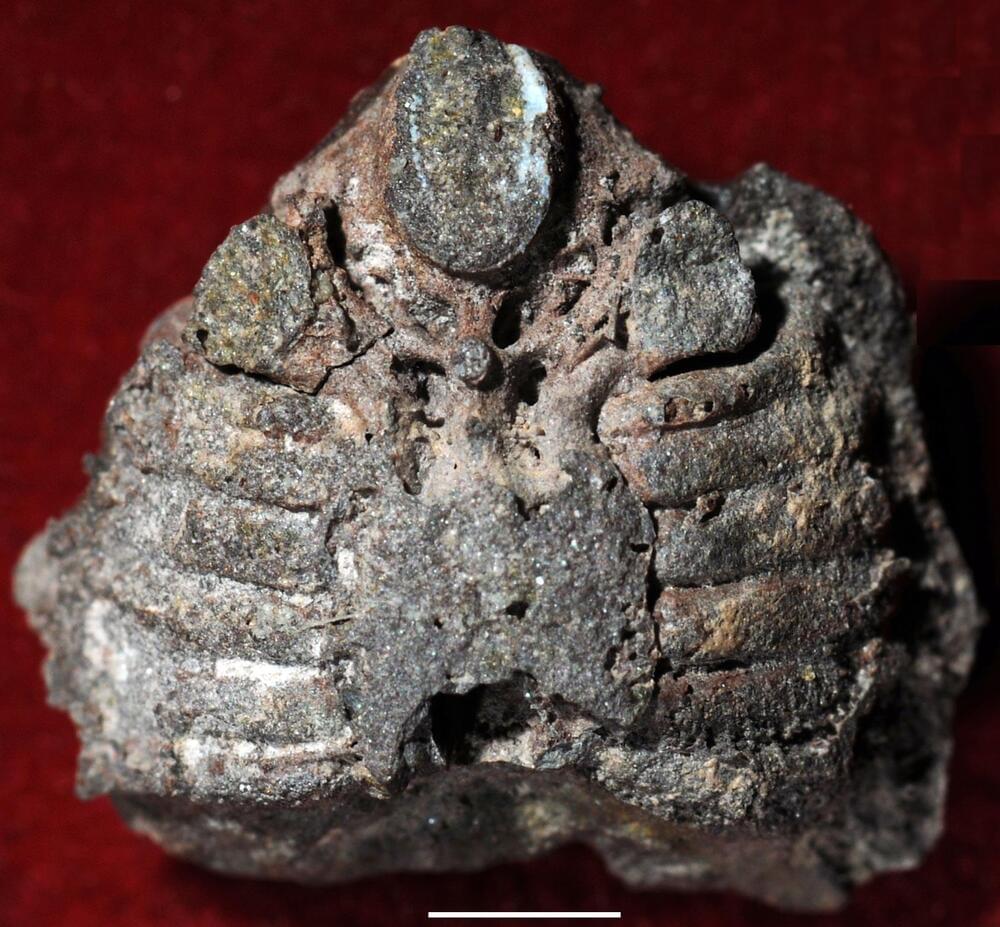
Archaeologists found five ceramic vessels holding over 100 clay cuneiform tablets, dating back to closely after the earthquake event. They are believed to be from the Middle Assyrian period, which lasted from 1,350 to 1,100 BC, and could shed light on the city’s demise and the rise of Assyrian rule in the area, according to a news release.
“It is close to a miracle that cuneiform tablets made of unfired clay survived so many decades under water,” said Peter Pfälzner, professor of near eastern archaeology at University of Tübingen and one of the excavation directors, in a statement.