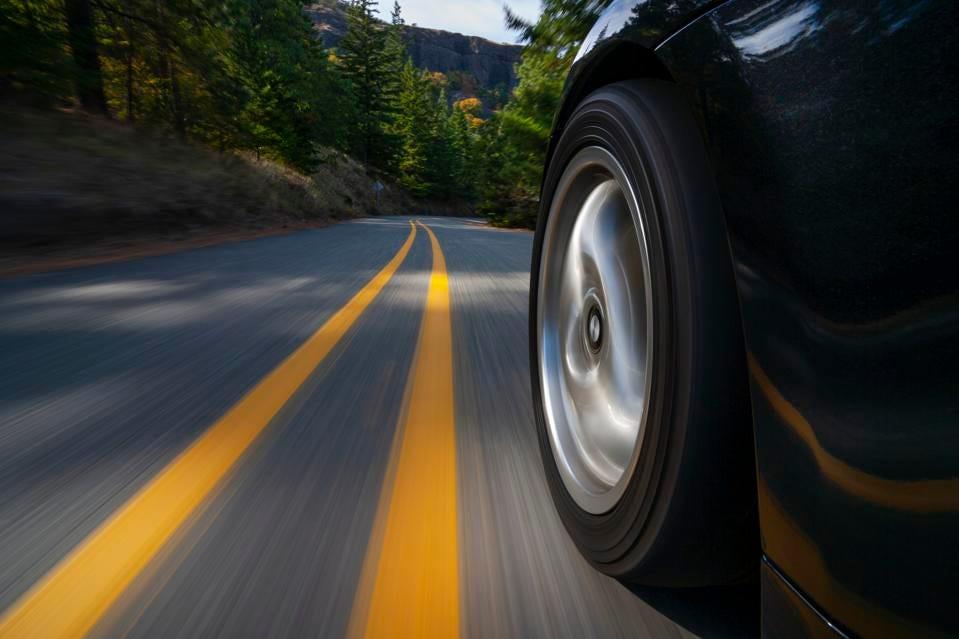
Think about the last time that you found yourself driving a particularly treacherous blind curve.
Pretty darned scary, I’d bet.
Indeed, I realize that even the mere act of thinking about such an alarming encounter can be traumatic, so no need to reflectively linger on that reenactment in your mind. Go ahead and change your thought patterns to something less stressful such as mulling over the latest online cat videos or perhaps that delicious scoop of ice cream you recently consumed.
Meanwhile, let’s have a heart-to-heart serious talk about blind curves.
When first learning to drive, few newbies are specifically instructed about blind curves. Sure, there might be discussions about what to do when reaching an especially sharp curve, but the whole conundrum of dealing with a sharp and blind curve is not necessarily resolutely covered.
Full Story: