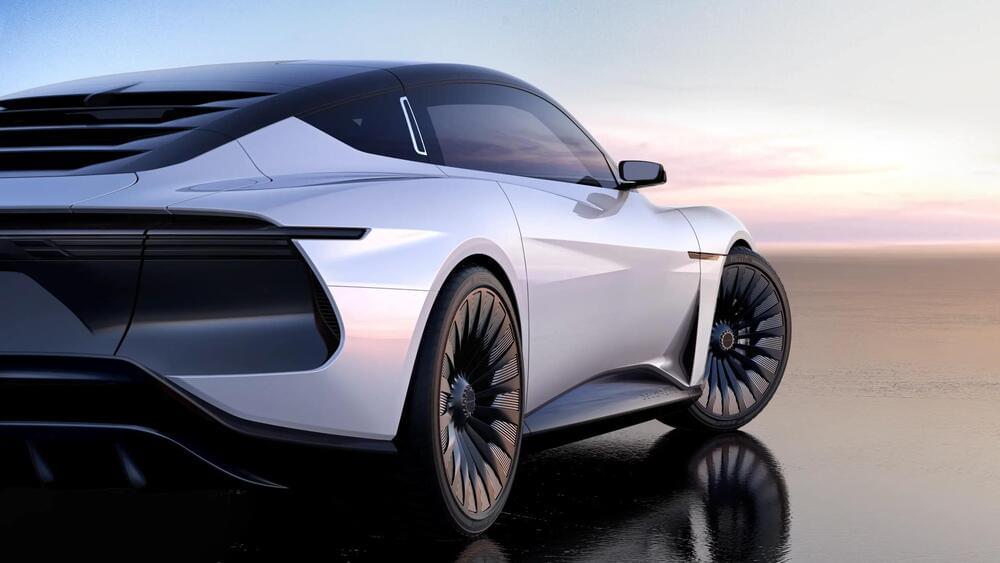
DeLorean released images and information on its upcoming 2024 electric car.
DeLorean is unapologetically human. A New Energy mobility brand.
We have a clear vision of our future, knowing it does not represent today. The DMC-12 was never meant to be a static interpretation of the brand, the brand would constantly evolve. Our icons are reimagined. DMC is and always was in constant evolution. An Icon is validated over time but to constantly reimagine mobility allows new icons to come into existence.
DeLorean is a legacy mobility company focused on redefining human connections through creative technologies.