Caption :
MIT researchers developed a technique that reduces the tendency for contrastive learning models to use shortcuts, by forcing the model to focus on features in the data that it hadn’t considered before.



The concept and technology behind Neuralink are so far ahead of what we’ve grown accustomed to that it might as well be magic. Make no mistake Neuralink is happening and it’ll be here sooner than you think…
I remember the first time I heard about Neuralink. I thought it was a joke or something far off in the future. Then I heard Elon Musk was behind it and immediately knew that this bonkers technology would be with us a lot sooner than any of us imagined.
The concept of Neuralink is simple: you have a chip implanted in your brain and with this chip, you can control things – computer games, applications, your phone, beam thoughts to other Neuralink users. Elon has even demoed the tech working inside a monkey’s head.
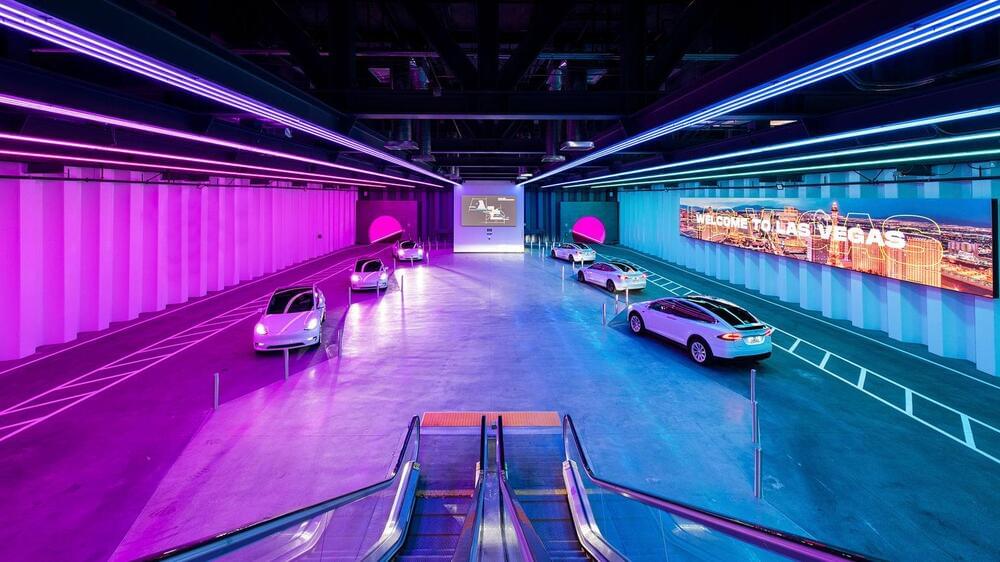


“This is not transportation for the wealthy,” Davis said. “It’s very affordable, very accessible and very, very comfortable.”
Davis told the commission that the system would be built in phases, with initial plans for five to 10 stations to open within the first six months once construction begins. About 15 to 20 stations would be added each year until full buildout, he said.
Whether the underground system makes a dent on the often-gridlocked Strip remains to be seen, but Hill is optimistic that Vegas Loop riders will be able to see more of Vegas once they emerge from the tunnels because they will be able to get around quicker. The innovation also creates a new point of interest in a town well known for its curiosities.

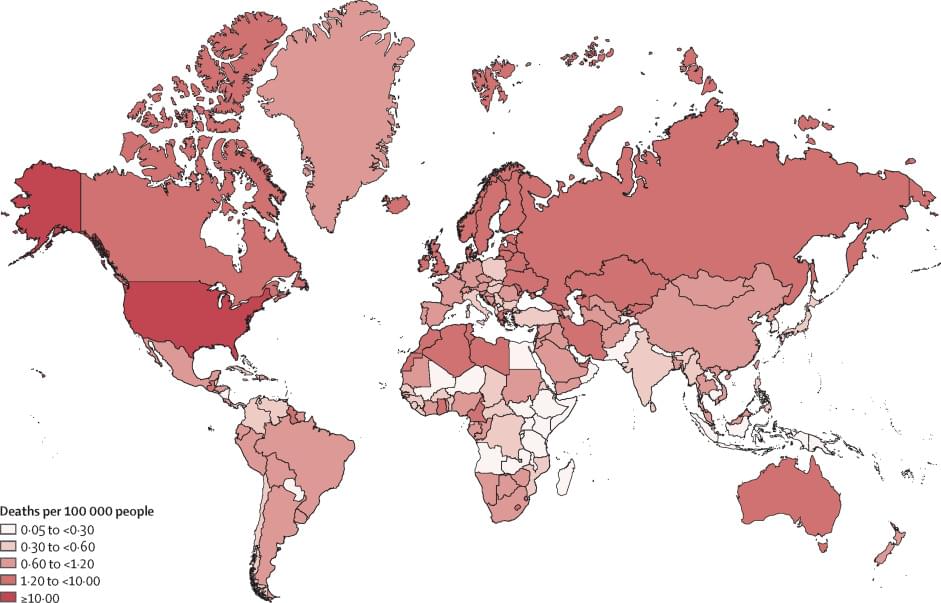
A need exists to accurately estimate overdose risk and improve understanding of how to deliver treatments and interventions in people with opioid use…
The Microsoft 365 Defender security research team discovered a new vulnerability in macOS that allows an attacker to bypass the System integrity protection or SIP. This is a critical security feature in macOS which uses kernel permissions to limit the ability to write critical system files. Microsoft explains that they also found a similar technique […].

The Microsoft 365 Defender security research team discovered a new vulnerability in macOS that allows an attacker to bypass the System integrity protection or SIP. This is a critical security feature in macOS which uses kernel permissions to limit the ability to write critical system files.
Microsoft explains that they also found a similar technique that could allow an attacker to gain elevated root privileges on an affected device, basically allowing to install a rootkit on macOS.

Evolutionary genomics approach identifies genes that enable plants to live in the Atacama Desert, offering clues for engineering more resilient crops to face climate change.
An international team of researchers has identified genes associated with plant survival in one of the harshest environments on Earth: the Atacama Desert in Chile. Their findings, published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS), may help scientists breed resilient crops that can thrive in increasingly drier climates.
“In an era of accelerated climate change, it is critical to uncover the genetic basis to improve crop production and resilience under dry and nutrient-poor conditions,” said Gloria Coruzzi, Carroll & Milton Petrie Professor in the New York University (NYU) Department of Biology and Center for Genomics and Systems Biology, who co-led the study with Rodrigo Gutiérrez.