Get the latest international news and world events from around the world.


California declares a state of emergency over monkeypox outbreak, following New York and Illinois
😳!
Newsom said the emergency declaration would help support the state’s vaccination efforts. Demand for the vaccines has outstripped supply as infections rise. Staff at sexual health clinics and other sites have struggled to keep up with the influx of people seeking the shots.
California is mobilizing personnel from its Emergency Medical Services to help administer the vaccines. Newsom said the state is working across all levels of government to slow the spread through testing, contract tracing and community outreach.
California’s declaration comes after Illinois declared a public health emergency earlier Monday. New York declared a state disaster emergency in response to the outbreak late Friday.


The End of Schizophrenia
Basically what this article says that schizophrenia is hard to pin down on the actual source of the symptoms so as of now the dsm 5 has it as a illness type but it is no longer on the dsm 5 essentially. This can relieve the stigma relating to it because it’s actually source of the disease is still not truly know. There are still medications for it but the actual source seems to be kinda unknown as it seems like other diseases aswell.
As human beings and scientists, we can think about phenomena in terms of categories and continuities. The distinction between light “particles” and “waves,” discovered by 20th-century quantum mechanics, is a case in point. Just as the particle-wave duality necessitated revisions in the understanding of the basic concepts and fundamental methods of theoretical physics, the revolution in psychiatric classification seems to bring with it the end of the fixed and fateful category of schizophrenia.
Still, most clinicians agree that some individuals do experience delusions, hallucinations, and disorganized speech that make them sound irrational. They attest that they have seen individuals who clearly exhibit disorganized or catatonic behavior, flat affect, or the failure to maintain basic self-care. Yet a growing number of psychiatrists maintain that, as a presumed disease entity, as an identifiable state, with clear subtypes, schizophrenia simply does not “exist.” Some consider schizophrenia no more than an “end stage” of other untreated mental disorders (in the same way that heart failure is the terminal stage of various heart diseases); others propose to abolish the diagnosis altogether.

Neurons Sync Their Beats Like Clocks on the Wall
Summary: A group of hippocampal neurons show rhythmic activity at different frequencies in the desynchronized state, but can align their rhythmic frequency to produce a synchronized brain rhythm upon activation.
Source: Institute for Experimental Medicine.
In the 17th century, the Dutch scientist Christiaan Huygens hung two of his recently invented pendulum clocks on a wooden beam and observed that as time passed, the clocks aligned their beats. He reported this finding, which he called an “odd sympathy,” in 1665. Three and a half centuries later, neurons in the brain were found to sync their activities in a similar way.
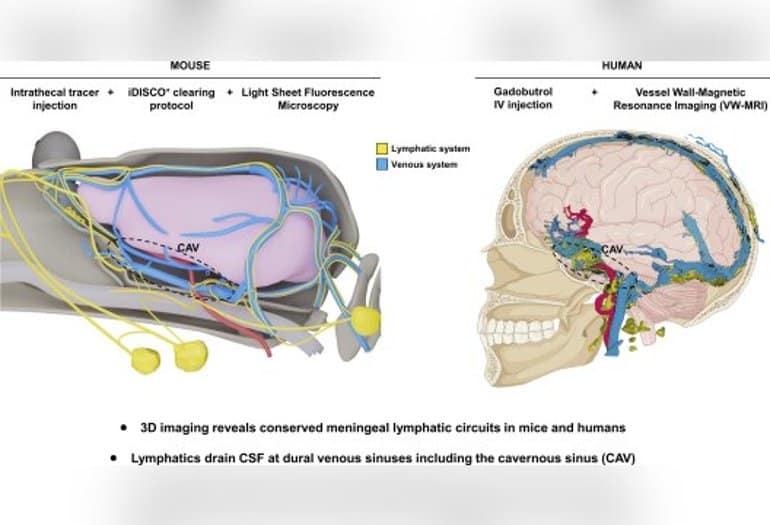
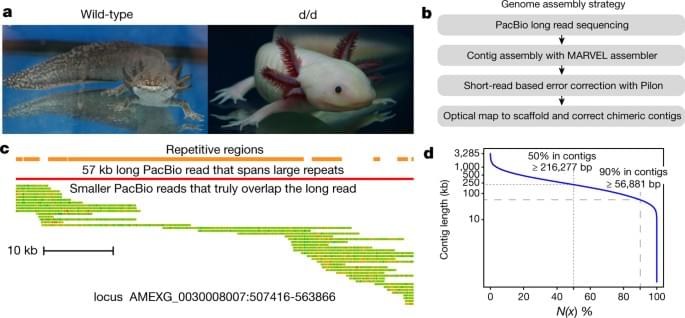
The Brain’s Drainage System in 3D
Summary: The CSF drainage pathways are similar between mice and humans, researchers discovered.
Source: Yale.
Meningeal lymphatic vessels are potential targets to treat brain diseases. Laboratories at Yale and the Paris Brain Institute (Pitié-Salpêtrière Hospital, Paris) have imaged brain drainage by meningeal lymphatics in mice and in humans.
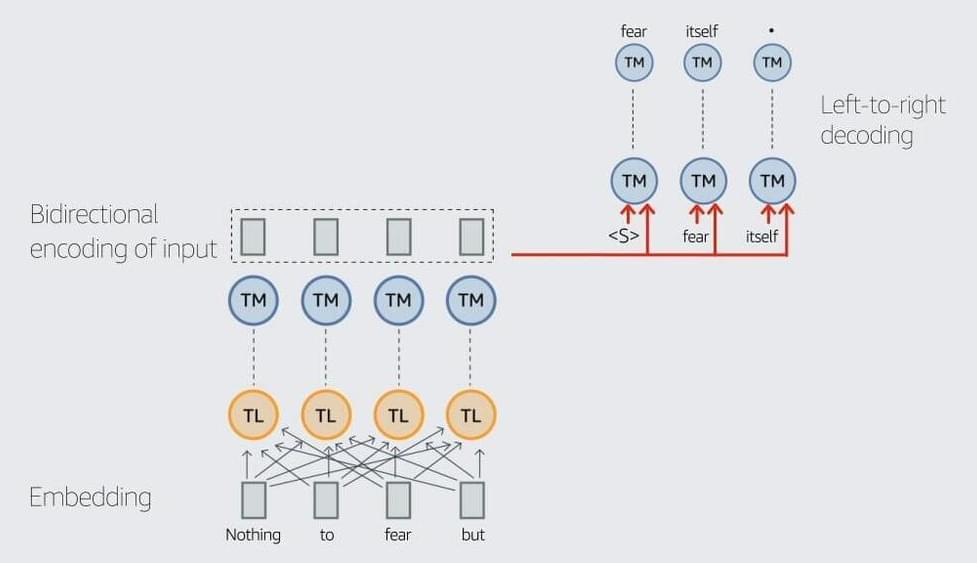
20B-parameter Alexa model sets new marks in few-shot learning
To train AlexaTM 20B, we break with convention, training on a mix of denoising and causal-language-modeling (CLM) tasks. On the denoising task, the model is required to find dropped spans and generate the complete version of the input. This is similar to how other seq2seq models like T5 and BART are trained. On the CLM task, the model is required to meaningfully continue the input text. This is similar to how decoder-only models like GPT-3 and PaLM are trained.
Training on a mix of these two pretraining tasks enables AlexaTM 20B to generalize based on the given input and generate new text (the CLM task), while also performing well on tasks that seq2seq models are particularly good at, such as summarization and machine translation (the denoising task).
For example, we demonstrated that, given a single article-summarization pair, AlexaTM 20B can generate higher-quality summaries in English, German, and Spanish than the much larger PaLM 540B can (see example, below).

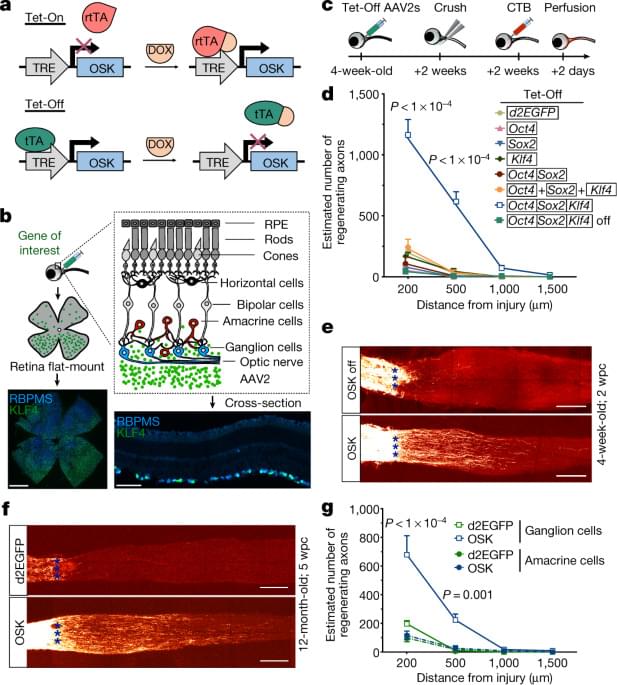
Reprogramming to recover youthful epigenetic information and restore vision
Circa 2020 Reversing the biological clock to essentially reverse aging.
Expression of three Yamanaka transcription factors in mouse retinal ganglion cells restores youthful DNA methylation patterns, promotes axon regeneration after injury, and reverses vision loss in a mouse model of glaucoma and in aged mice, suggesting that mammalian tissues retain a record of youthfu…