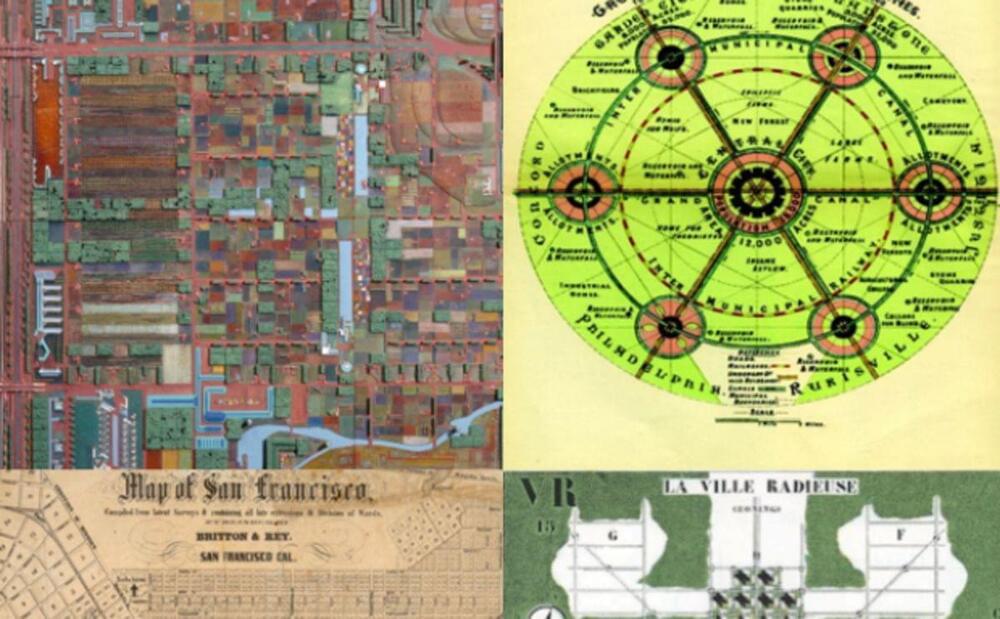
A new exhibit from the San Francisco Planning and Urban Research Association showcases the simple visualizations of complex ideas that have changed how we live.


What Gran Turismo Sophy learned on the racetrack could help shape the future of machines that can work alongside humans, or join us on the roads.
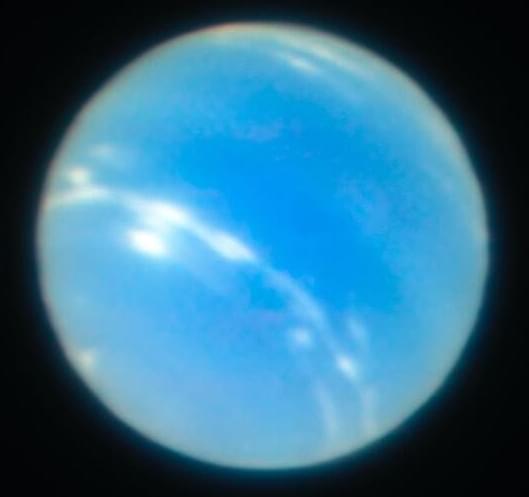

Ice giants like Neptune are a potential treasure trove of scientific discoveries.
There’s also Triton’s cryovolcanic activity, resulting from tidal flexing in its interior caused by Neptune’s gravitational pull. However, this activity increases when Triton is closest to the Sun (perihelion), resulting in greater eruptions from the interior. This will leave higher concentrations of nitrogen and other gases in the moon’s tenuous atmosphere, which could be studied to learn more about its interior composition and structure. As for the rings, the team noted several objectives there:
“Establish a complete list of planetary rings and their inner Shepherd satellites, study the characteristics, formation mechanism, material exchange, and gas transport of planetary rings of different orbital types, analyze the origin of different celestial bodies, and detect possible organic matter… The multiple planetary rings of Neptune are not uniformly distributed in longitude. Instead, it presents an arc-block-like discrete structure. Why these arc-block structures can exist, and whether they exist stably without spreading out, are all interesting dynamical problems.”
China’s space agency has made some rather impressive moves in recent years that illustrate how the nation has become a major power in space. These include the development of heavy launch rockets like the Long March 9, the deployment of space stations (the Tiangong program), and their success with the Chang’e and Tianwen programs that have sent robotic explorers to the Moon and Mars.
An XPrize competition funded by Tesla CEO Elon Musk just awarded teams of students $5 million to develop their ideas for carbon removal systems — and it still has another $95 million to give away.
The challenge: Between our cars, factories, and everything else, humans are pumping about 43 billion tons of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere every year.
To combat climate change, we not only need to cut that figure way down, we also need to capture and store a lot of the CO2 that’s already out there.
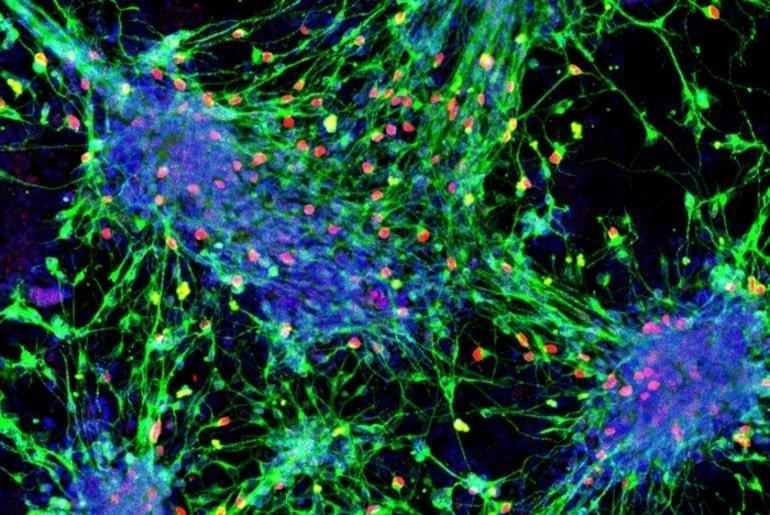
Summary: Researchers have created a new blueprint that outlines how embryonic stem cells from mice become sensory interneurons and identified a method for producing sensory interneurons in a lab setting. If the results can be replicated in human stem cells, researchers say the findings could contribute to the development of therapies to restore sensation to those suffering nerve damage and spinal cord injury.
Source: UCLA
Researchers at the Eli and Edythe Broad Center of Regenerative Medicine and Stem Cell Research at UCLA have developed a first-of-its-kind roadmap detailing how stem cells become sensory interneurons — the cells that enable sensations like touch, pain and itch.

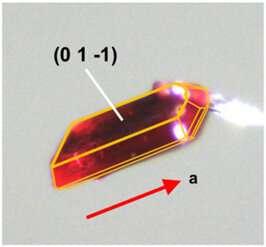
In a new paper in PNAS, “Triplet-Pair Spin Signatures From Macroscopically Aligned Heteroacenes in an Oriented Single Crystal,” National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) researchers Brandon Rugg, Brian Fluegel, Christopher Chang, and Justin Johnson tackle one of the fundamental problems in quantum information science: how to produce pure elements of quantum information—that is, those that start and remain in a well-defined “spin state”—at practical temperatures.
Quantum information science has the potential to revolutionize computation, sensing, and communications. But many of these applications are still beyond reach because of the challenges of producing units of quantum information, or qubits, without relying on extremely low temperatures to maintain their purity. Current approaches to identifying suitable quantum materials tend to rely on trial and error.
“The field of developing new molecules and materials [for quantum information science] sometimes progresses through ad hoc methods and serendipity. ‘This material just so happens to work better than the other one’—we saw a lot of that happening, and decided ultimately that it was not going to suffice for a project where the goal was to limit the set of possible options,” said Justin Johnson, a researcher in NREL’s Chemistry and Nanoscience Center. “We wanted to have the theory provide us with firm guidelines about what should happen.”

