Lung cancer cases are increasing in people who have never smoked, especially in women, a new study by the World Health Organization’s cancer agency ha


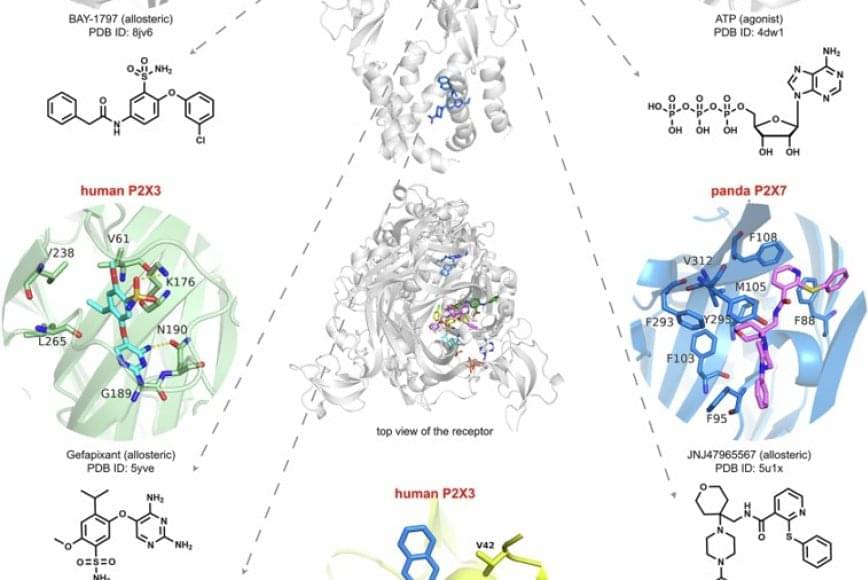
Sarcomas comprise a heterogeneous group of malignant neoplasms that include genomically simple and genomically complex subtypes. This consensus provides guidelines for efficient, rational use of next-generation sequencing in their clinical management.
This consensus review establishes guidelines for the rational and efficient use of next-generation sequencing−based technology in the clinical management of sarcoma.

New in JNeurosci from Wei, Tao, Bi et al: Smokers who have quit their nicotine use have altered brain activity linked to heightened pain sensitivity and a need for more postoperative pain relief.
▶️
Perioperative abstinent smokers experience heightened pain sensitivity and increased postoperative analgesic requirements, likely due to nicotine withdrawal-induced hyperalgesia. However, the underlying neural mechanisms in humans remain unclear. To address this issue, this study enrolled 60 male patients (30 abstinent smokers and 30 nonsmokers) undergoing partial hepatectomy, collecting clinical data, smoking history, pain-related measures, and resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging (rs-fMRI). Compared to nonsmokers, abstinent smokers showed lower pain threshold and higher postoperative analgesic requirements. Neuroimaging revealed altered brain function in abstinent smokers, including reduced fractional amplitude of low-frequency fluctuations (fALFF, 0.01 – 0.1 Hz) in the ventromedial prefrontal cortex (vmPFC), increased regional homogeneity (ReHo) in the left middle occipital gyrus, and decreased functional connectivity (FC) between the vmPFC to both the bilateral middle temporal gyrus and precuneus. Preoperative pain threshold was positively correlated with abstinence duration and specific regional brain activities and connectivity. Further, the observed association between abstinent time and pain threshold was mediated by the calcarine and posterior cingulate cortex activity. The dysfunction in vmPFC and left anterior cingulate cortex was totally mediated by the association between withdrawal symptoms and postoperative analgesic requirements. These findings suggest that nicotine withdrawal might alter brain functional activity and contribute to hyperalgesia for the abstinent smokers. This study provided novel insights into the supraspinal neurobiological mechanisms underlying nicotine withdrawal-induced hyperalgesia and potential therapeutic targets for postoperative pain in abstinent smokers.
Significance statement Abstinent smokers experienced heightened pain and require more analgesics after surgery, yet the underlying neural mechanisms remain poorly understood. This prospective cohort study identified altered regional brain activity associated with reduced pain thresholds and increased postoperative analgesic requirements in abstinent smokers. We found specific brain regions that were functionally altered and correlated with pain-related outcomes, which mediated the relationship between abstinence and pain-related behaviors. These findings provided novel insights into the supraspinal mechanisms of nicotine withdrawal-induced hyperalgesia and point to potential therapeutic targets for improving postoperative pain management in abstinent smokers.
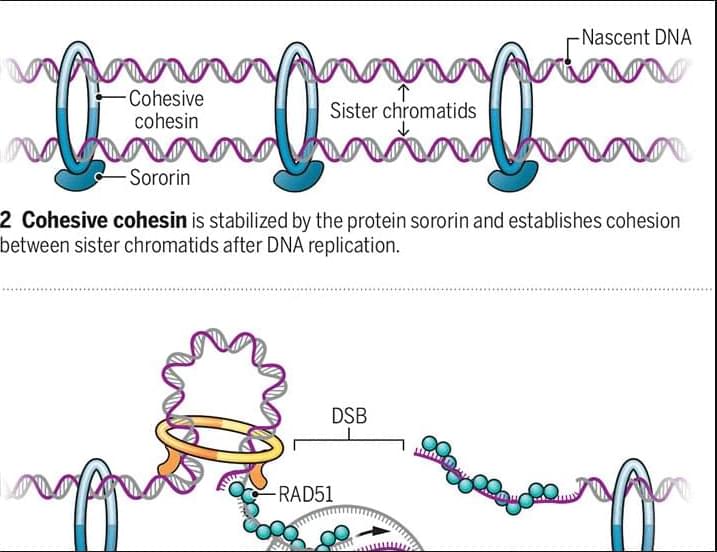
Extrusive and cohesive cohesin cooperate to repair double-strand breaks in DNA.
Learn more in a new Science Perspective.
Jiazhi Hu Authors Info & Affiliations
Science.
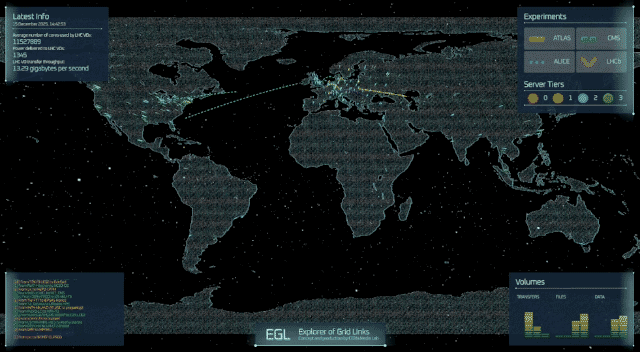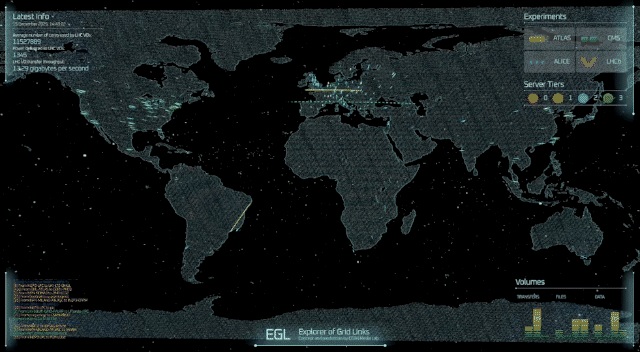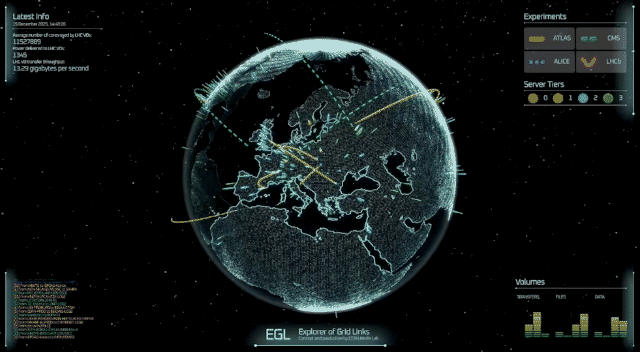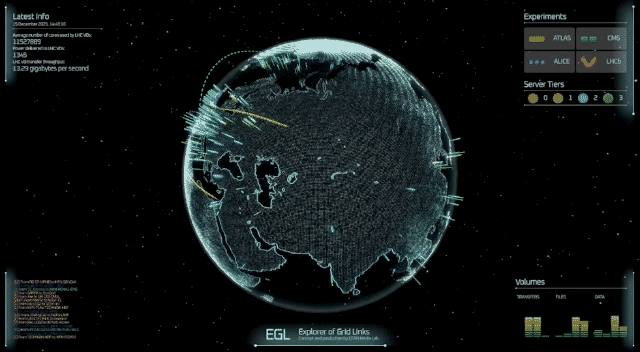
Imagine a planetary computer capable of storing and processing hundreds of petabytes of data for the research needs of a worldwide community of scientists. This is the Worldwide LHC Computing Grid (WLCG), which is celebrating its 20th anniversary.
Originally conceived to handle the unprecedented data volumes of the Large Hadron Collider (LHC), the WLCG has evolved into a global network connecting hundreds of computing centres across more than 40 countries. It enables thousands of scientists worldwide to store, process and analyse massive amounts of data in quasi-real time, supporting discoveries in particle physics.
On 8 December, a special event at the CERN Science Gateway brought together the international community that has turned this ambitious project into one of the largest distributed computing collaborations in the world. Key figures from the project highlighted its history, challenges and future prospects. Les Robertson, whose efforts and leadership were instrumental during the early days of the Grid, reflected on how the idea was born and the challenges of building something that had never been done before. It was an ambitious idea for its time, one that required both technological innovation and unprecedented cooperation across countries. Yet this early confidence proved justified: the Grid rapidly moved from concept to reality, paving the way for a new model of large-scale scientific computing.

When two black holes merge or two neutron stars collide, gravitational waves can be generated. They spread at the speed of light and cause tiny distortions in space-time. Albert Einstein predicted their existence, and the first direct experimental observation dates from 2015.
Now, Prof. Ralf Schützhold, theoretical physicist at the Helmholtz-Zentrum Dresden-Rossendorf (HZDR), is going one step further. He has conceived an experiment through which gravitational waves can not only be observed but even manipulated. Published in the journal Physical Review Letters, the idea could also deliver new insights into the hitherto only conjectured quantum nature of gravity.
“Gravity affects everything, including light,” says Schützhold. And this interaction also occurs when gravitational waves and light waves meet.
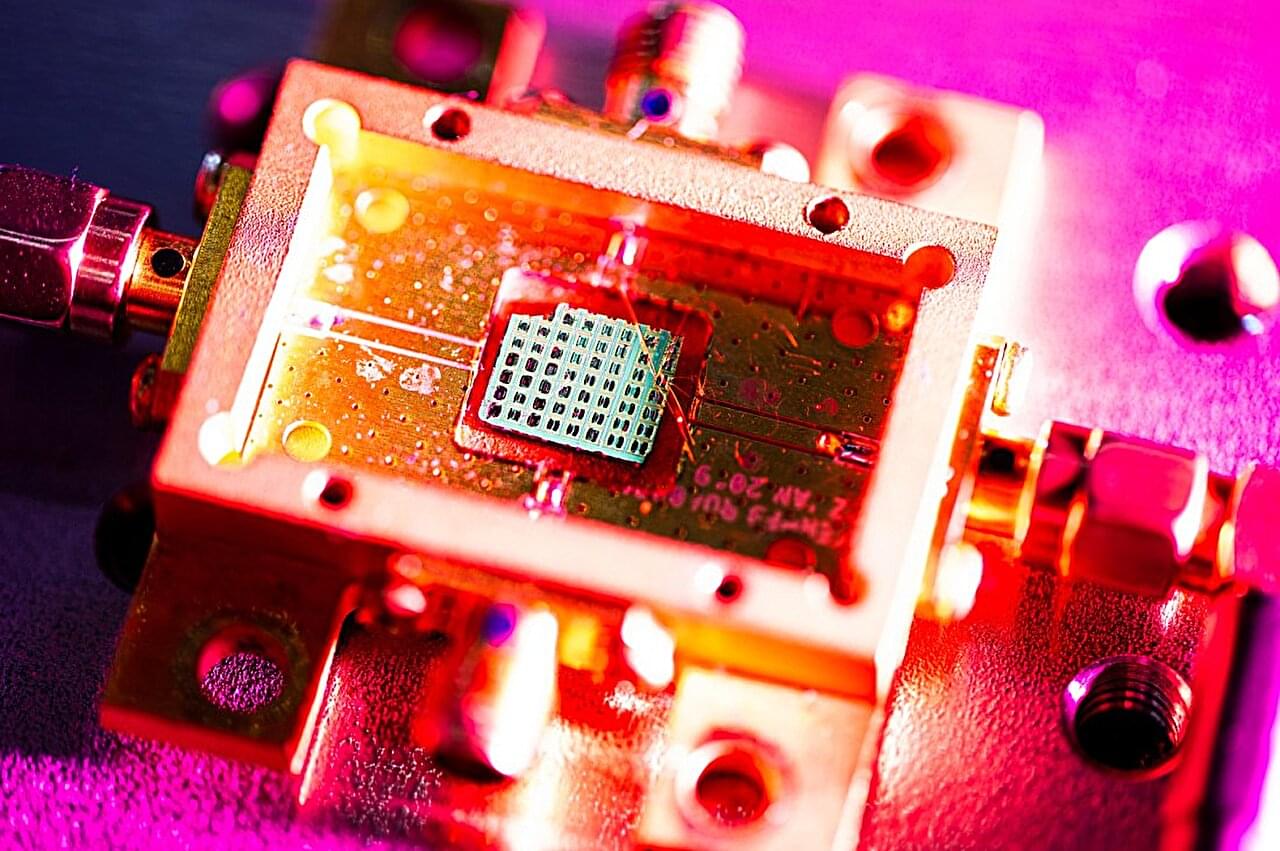
At the heart of every camera is a sensor, whether that sensor is a collection of light-detecting pixels or a strip of 35-millimeter film. But what happens when you want to take a picture of something so small that the sensor itself has to shrink down to sizes that cause the sensor’s performance to crater?
Now, Northeastern University researchers have made a breakthrough discovery in sensing technologies that allows them to detect objects as small as individual proteins or single cancer cells, without the additional need to scale down the sensor. Their breakthrough uses guided acoustic waves and specialized states of matter to achieve great precision within very small parameters.
The device, which is about the size of a belt buckle, opens up possibilities for sensing at both the nano and quantum scales, with repercussions for everything from quantum computing to precision medicine.