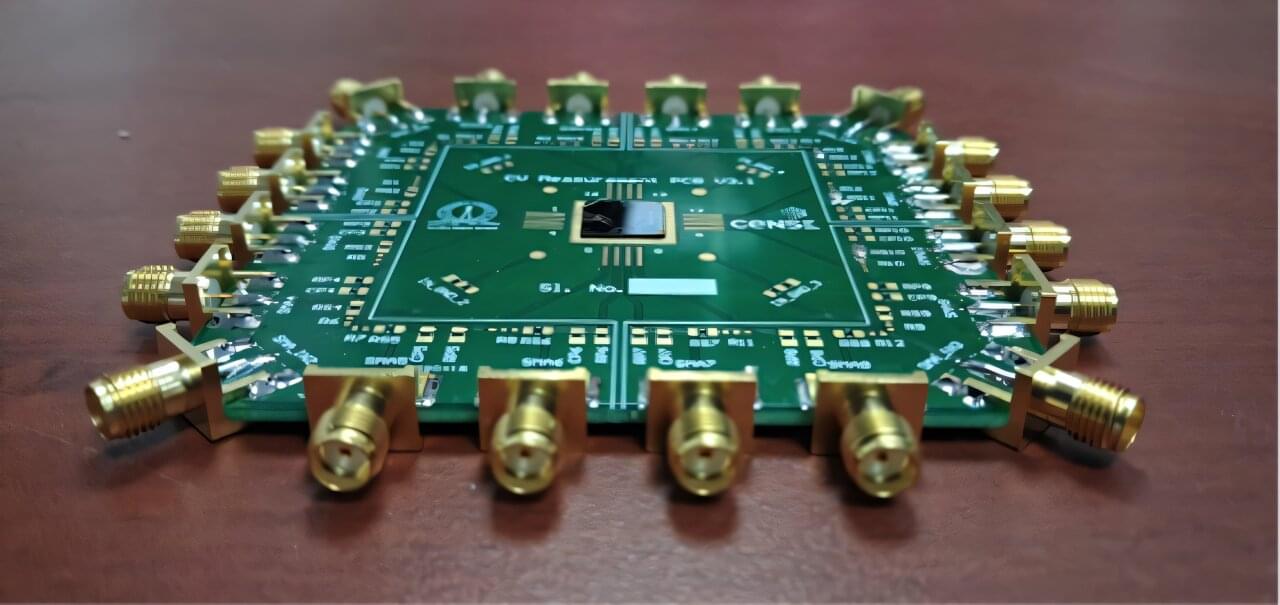
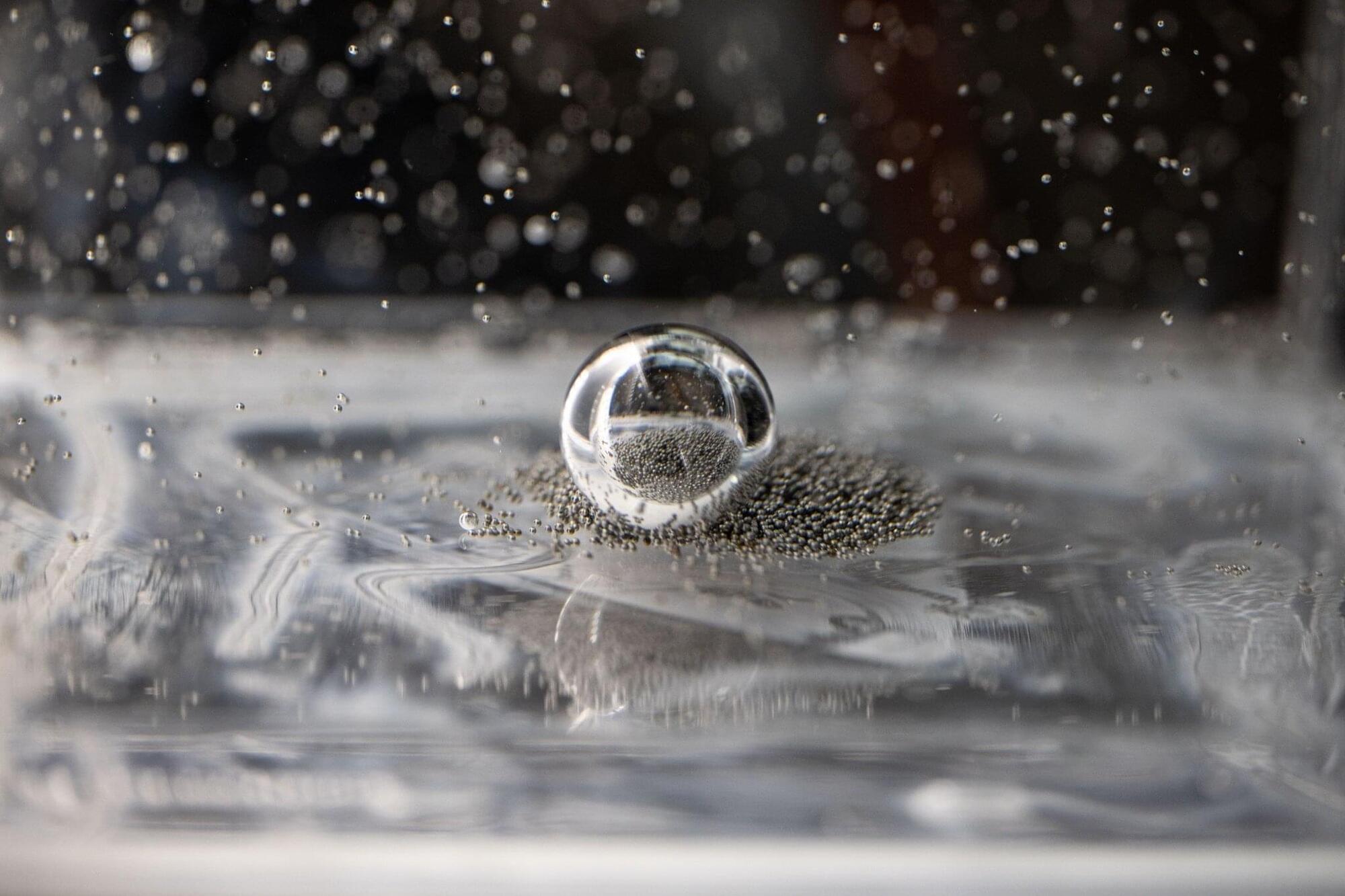
For more than 50 years, scientists have sought alternatives to silicon for building molecular electronics. The vision was elegant; the reality proved far more complex. Within a device, molecules behave not as orderly textbook entities but as densely interacting systems where electrons flow, ions redistribute, interfaces evolve, and even subtle structural variations can induce strongly nonlinear responses. The promise was compelling, yet predictive control remained elusive.
Meanwhile, neuromorphic computing—hardware inspired by the brain—has followed a parallel ambition: to discover a material that can store information, compute, and adapt within the same physical substrate and in real time. Yet today’s dominant platforms, largely based on oxide materials and filamentary switching mechanisms, continue to behave as engineered machines that emulate learning, rather than as matter that intrinsically embodies it.
A new study from the Indian Institute of Science (IISc) published in Advanced Materials suggests that these two long-standing challenges may finally converge.